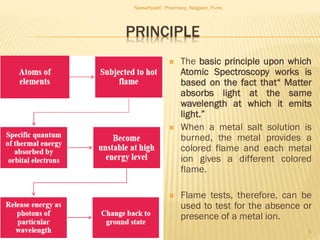
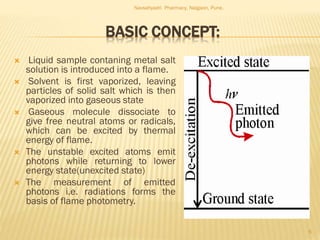
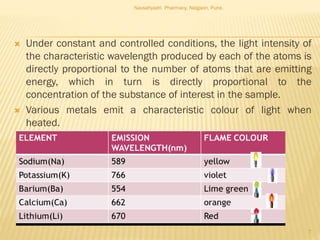
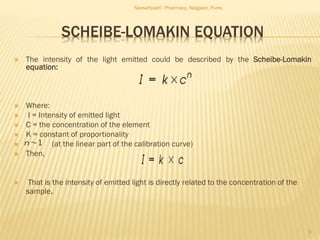
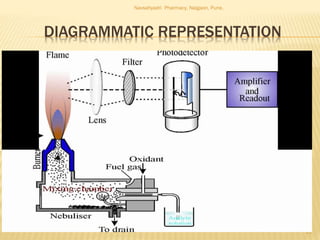
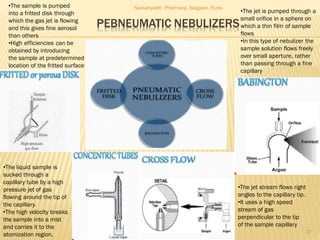
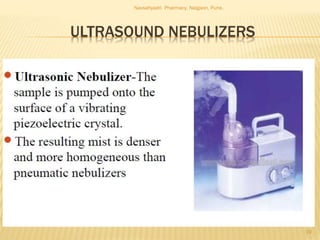
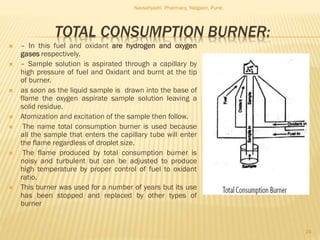
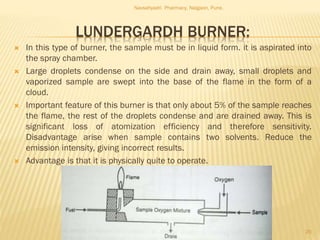
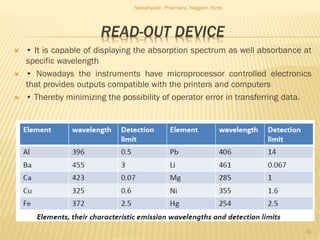
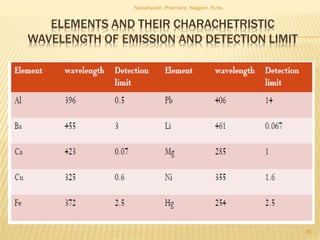
Flame photometry is a technique used to analyze metals in solutions. It works by measuring the intensity of light emitted from a flame when a metal salt solution is introduced. Each metal emits a characteristic wavelength of light that can be used to identify the metal qualitatively, and the intensity is proportional to the concentration quantitatively. The sample is nebulized and introduced into a flame, where it is vaporized, dissociated into atoms, and the atoms are excited by the flame's thermal energy to emit photons. Interferences can occur from overlapping emission lines, ionization, or chemical reactions. The instrumentation includes components for sample delivery, a burner to produce the flame, mirrors to direct the light, and a detector to measure