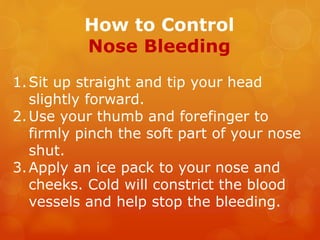
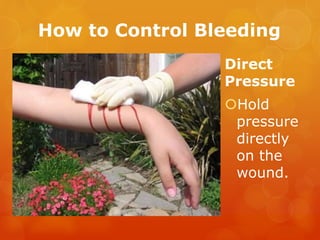
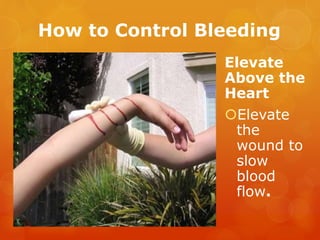
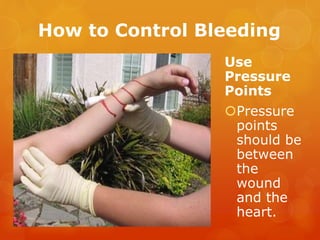
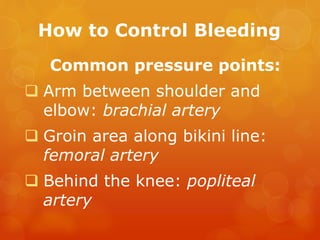
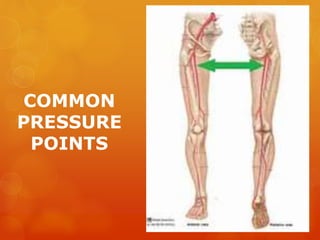
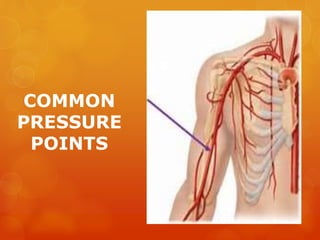
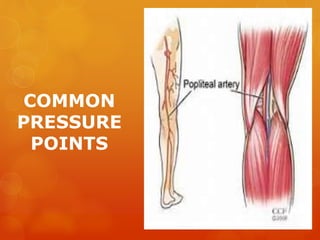
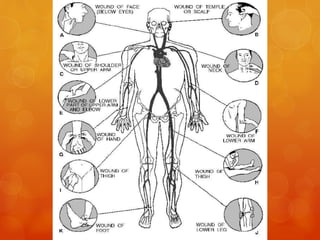
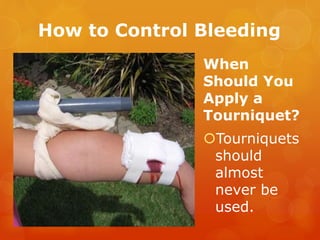
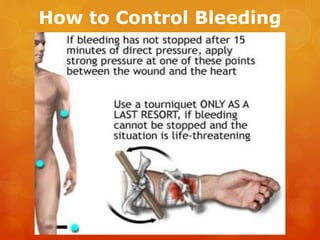
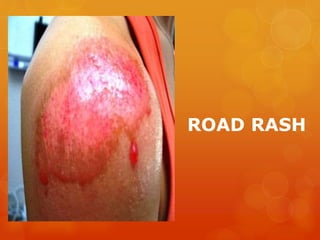
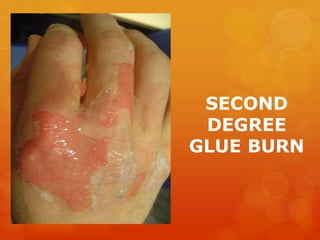
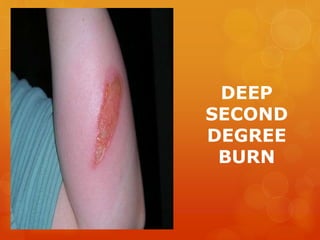
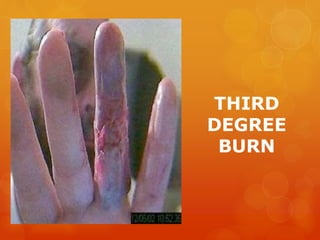
The document provides information on essential supplies and equipment for a first aid kit, including instructions for use. It discusses first aid manuals, tweezers, antibiotic ointment, bandages, gauze pads, medical tape, elastic bandages, cold packs, and how to control nosebleeds, bleeding, burns, and perform CPR. Proper first aid requires supplies to clean, dress, and treat wounds as well as knowledge of basic procedures. A well-stocked first aid kit is crucial for dealing with common injuries and medical situations until emergency help arrives.