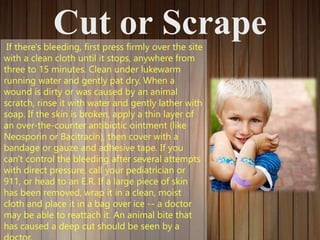
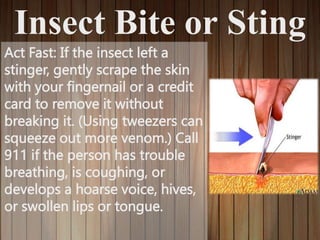
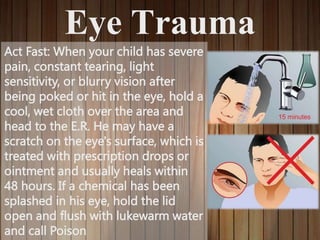
This document provides information on first aid, including what it is, why it's important, and common first aid topics. It explains that first aid involves basic assistance given to an injured or ill victim until professional help arrives. First aid is important because it allows people to help during emergencies and benefits individuals by making them prepared for medical situations. Common first aid topics covered include cuts/scrapes, burns, nosebleeds, insect bites, eye injuries, and why a first aid kit is necessary. The document recommends basic supplies and medications to include in a well-stocked first aid kit.