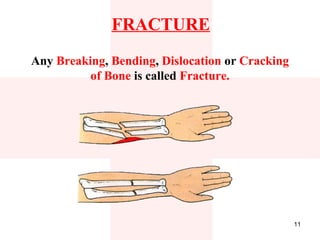
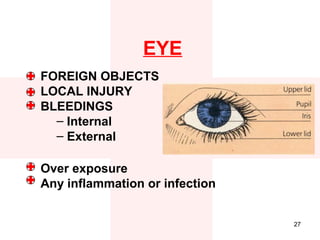
First aid is the immediate assistance given to any person suffering from either a sudden illness or an injury with the goal of preventing any further worsening of their condition until they can receive full medical care. It involves assessing the situation, providing appropriate care like stopping blood loss, treating for shock, immobilizing fractures, and making the individual comfortable while arranging for their transfer to the emergency room if needed. Key priorities include checking for breathing issues, blood loss, and treating shock before addressing less severe injuries or ailments. Proper first aid requires remaining calm, thinking clearly, and knowing how to handle common medical emergencies through basic techniques.