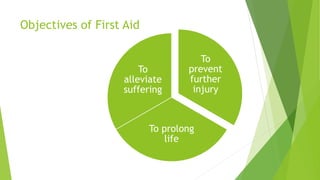
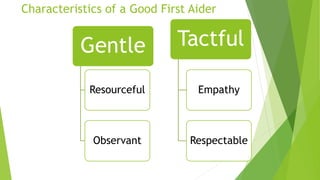
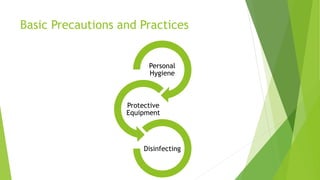
The document provides information on first aid, including roles and responsibilities of first aiders, objectives of first aid, characteristics of good first aiders, basic precautions and practices, emergency action principles, vital signs, common injuries and their treatments, and bandaging techniques. A first aider is responsible for ensuring safety, providing immediate care, summoning medical help, and documenting care provided to bridge the gap between injury and medical treatment. The goals of first aid are to prevent further injury, prolong life, and alleviate suffering.