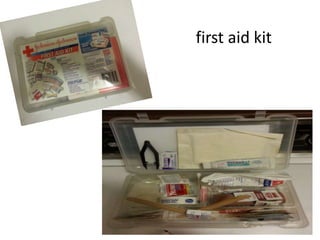
The document provides information on the contents of a standard first aid kit and how to use it in common medical emergencies. It lists supplies such as dressings, bandages, antiseptic wipes, medications, and instructions. It describes how to treat wounds by cleaning and covering them. It advises applying pressure and elevating injuries for severe bleeding. It recommends cooling burns with running water for 20 minutes. It also provides steps for handling traumatic amputations such as applying pressure and storing severed parts in bags with air and ice water.