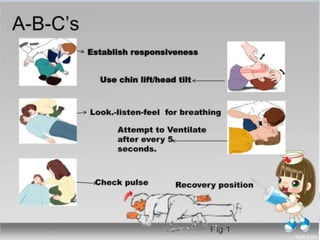
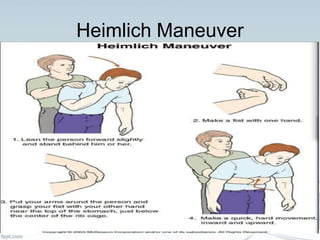
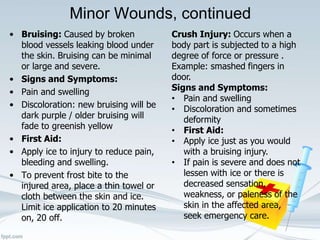
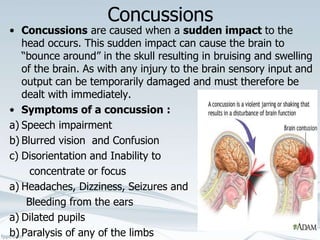
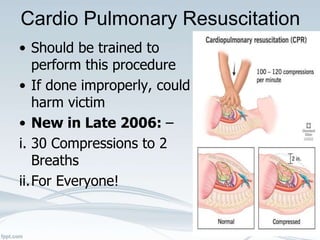
This document provides comprehensive guidelines on first aid, defining it as emergency care given before professional medical treatment. It includes essential information on handling various medical emergencies, the contents of a first aid kit, and specific treatments for conditions like choking, burns, bites, and fractures. The document emphasizes the importance of personal safety for the first aider and the need for immediate professional assistance when necessary.