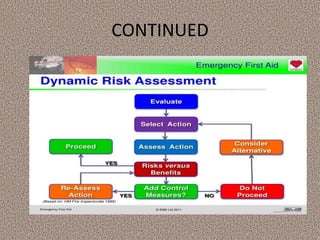
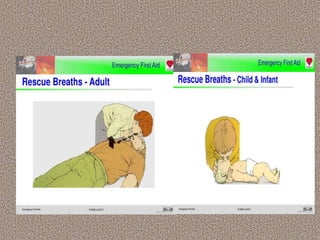
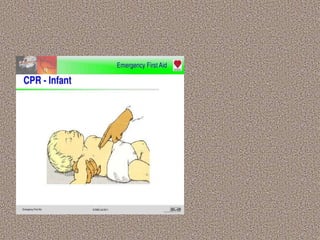
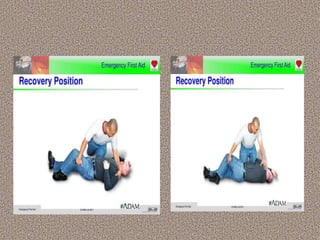
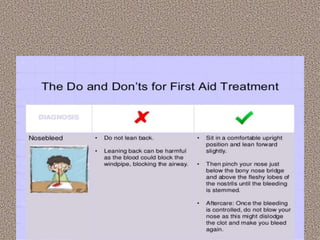
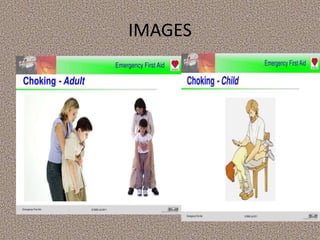
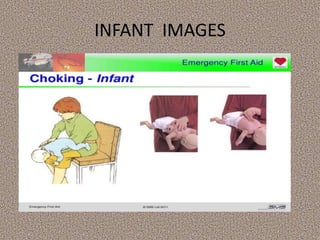
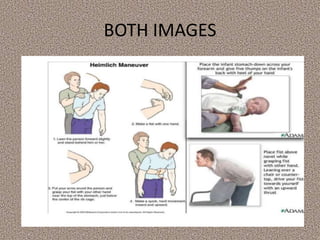
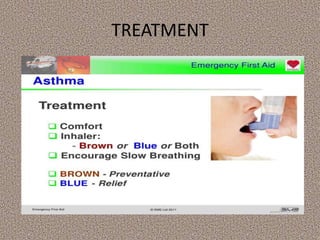
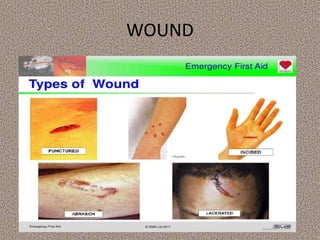
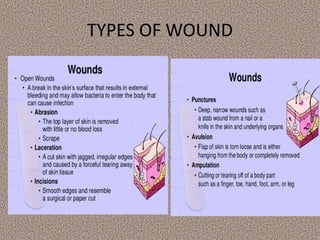
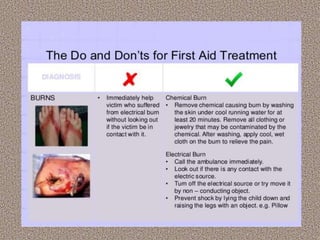
This document provides information on first aid, including its aims, principles, priorities, and how to treat common medical emergencies. The goals of first aid are to preserve life, prevent worsening of conditions, promote recovery, and ensure safe transport to further care. It discusses assessing situations calmly, protecting oneself and casualties, treating life-threatening conditions first, and calling for help. Key first aid skills taught include focusing on a person's airway, breathing, and circulation. Common treatments covered include handling bleeding, shock, burns, wounds, fractures, and respiratory or cardiac emergencies. The roles and responsibilities of first aiders are also outlined.