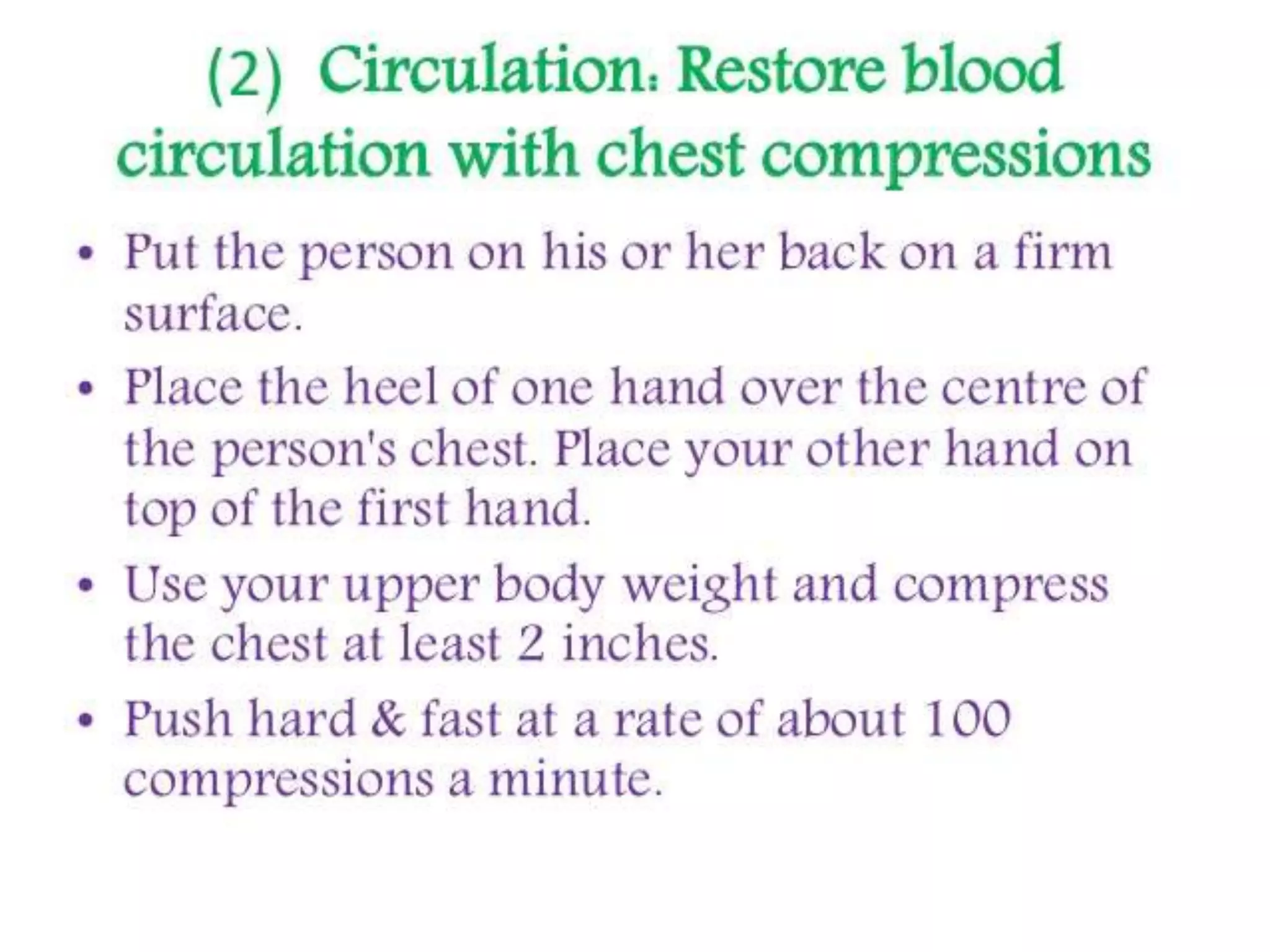
First aid is the immediate care provided to an injured or ill person until more advanced medical treatment can be accessed, with the goals of preventing further harm, promoting recovery, and sustaining life. Proper first aid includes assessing the situation for dangers, checking the person's response, airway, breathing, and circulation, controlling any bleeding, treating for shock, and seeking medical help if needed. The key principles of first aid are prioritizing life-threatening issues, ensuring one's own safety, avoiding further harm, and handling each situation calmly while rendering temporary aid.