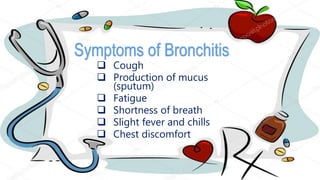
This document discusses communicable diseases and provides details about Dengue Fever and Bronchitis. It defines communicable diseases as those spread between people through contact with bodily fluids, airborne viruses, or insect bites. Dengue Fever is a mosquito-borne disease caused by dengue viruses and spread by the Aedes aegypti and albopictus mosquitoes. Symptoms include high fever, headaches, joint and muscle pain, and rash. Treatment involves rest, fluids and medication. Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes causing cough, mucus, and shortness of breath. It can be acute from viruses or chronic from smoking. Prevention methods are also outlined.