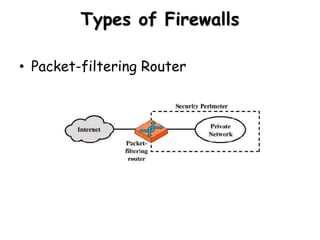
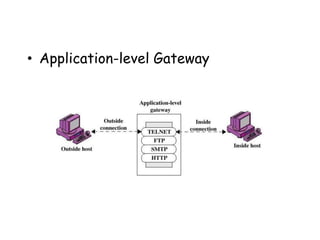
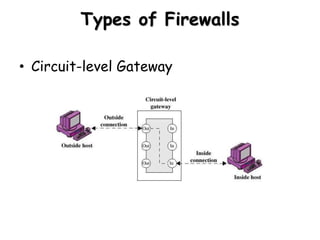
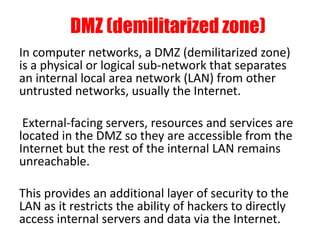
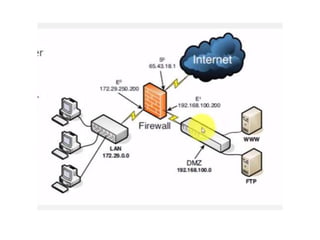
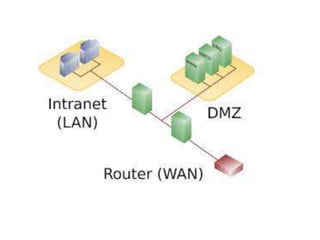
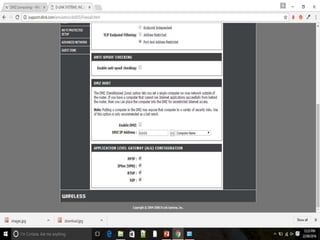
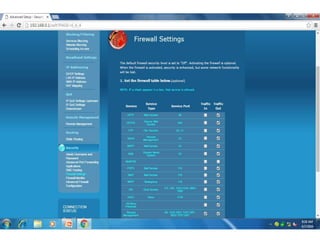
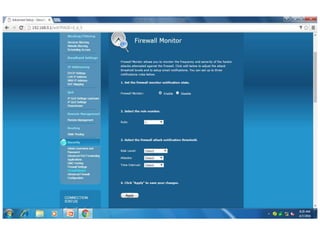
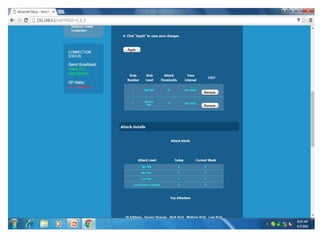
The document discusses different types of firewalls, their purposes, and characteristics. It describes how firewalls establish controlled links between networks to protect internal systems from external threats while allowing authorized access. Packet filters, application-level proxies, and circuit-level gateways are firewalls that operate at different layers of the OSI model and have varying levels of security and performance impacts. The document also explains what a DMZ is and the purpose it serves in network security architectures.