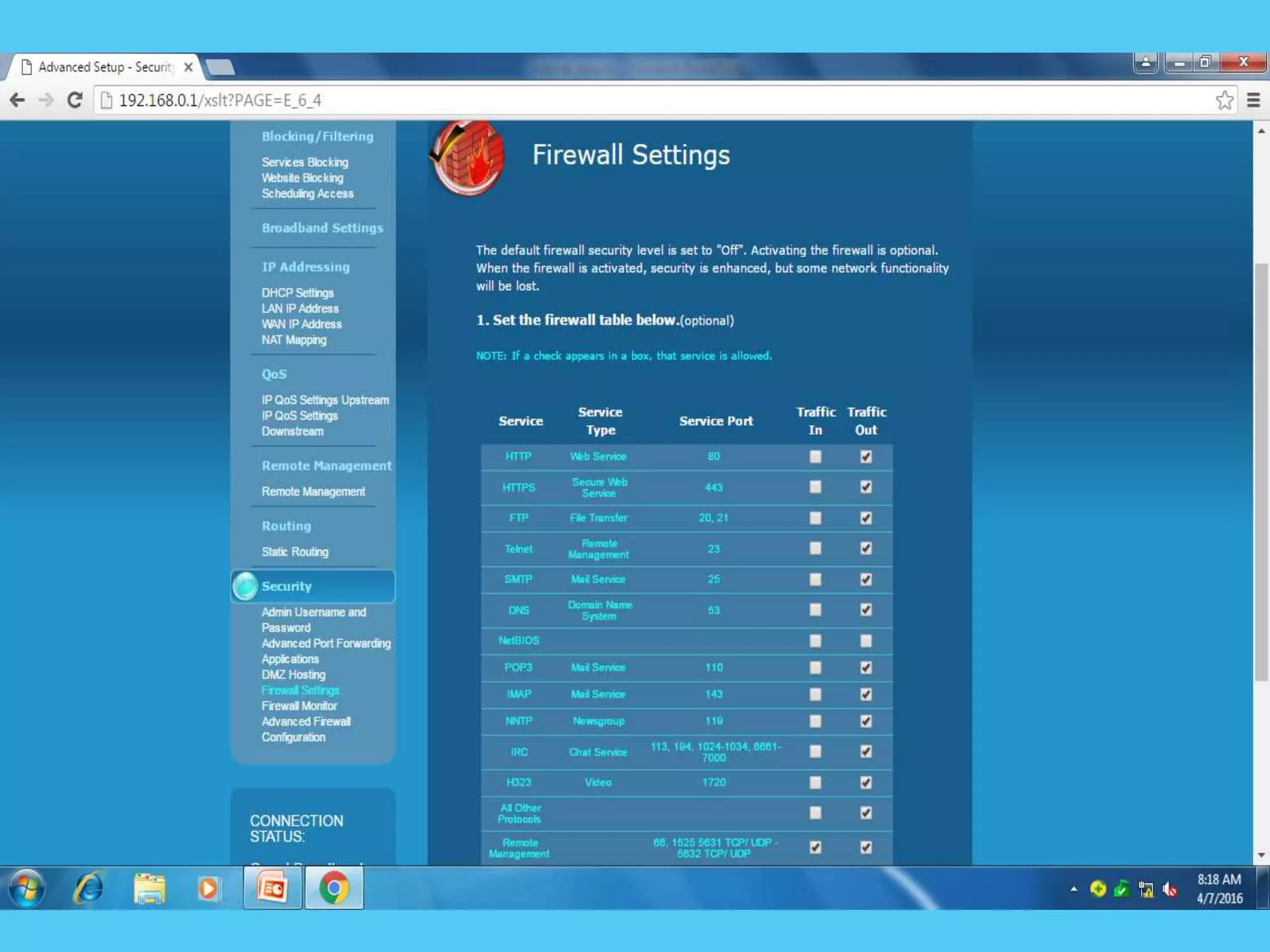
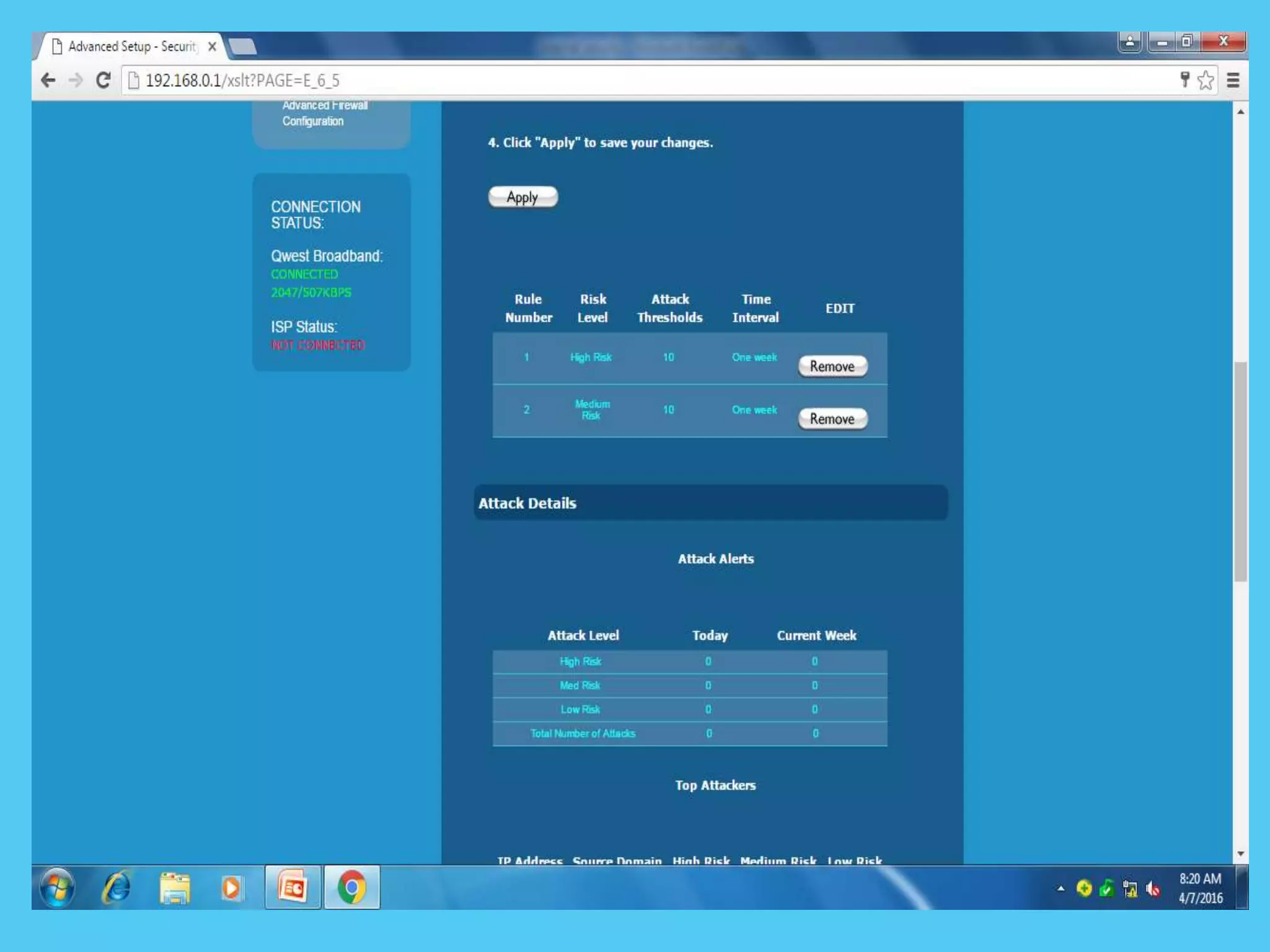
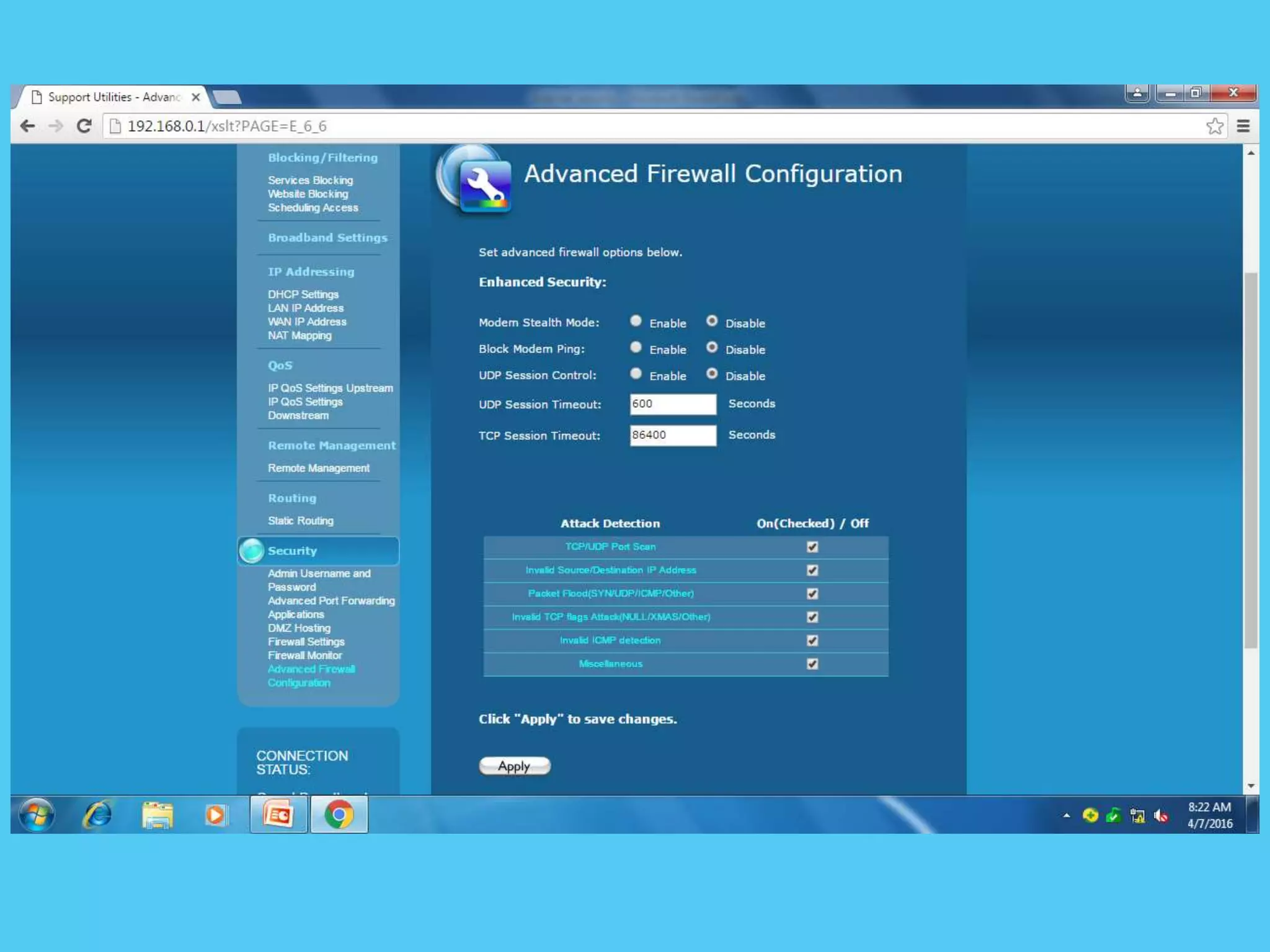
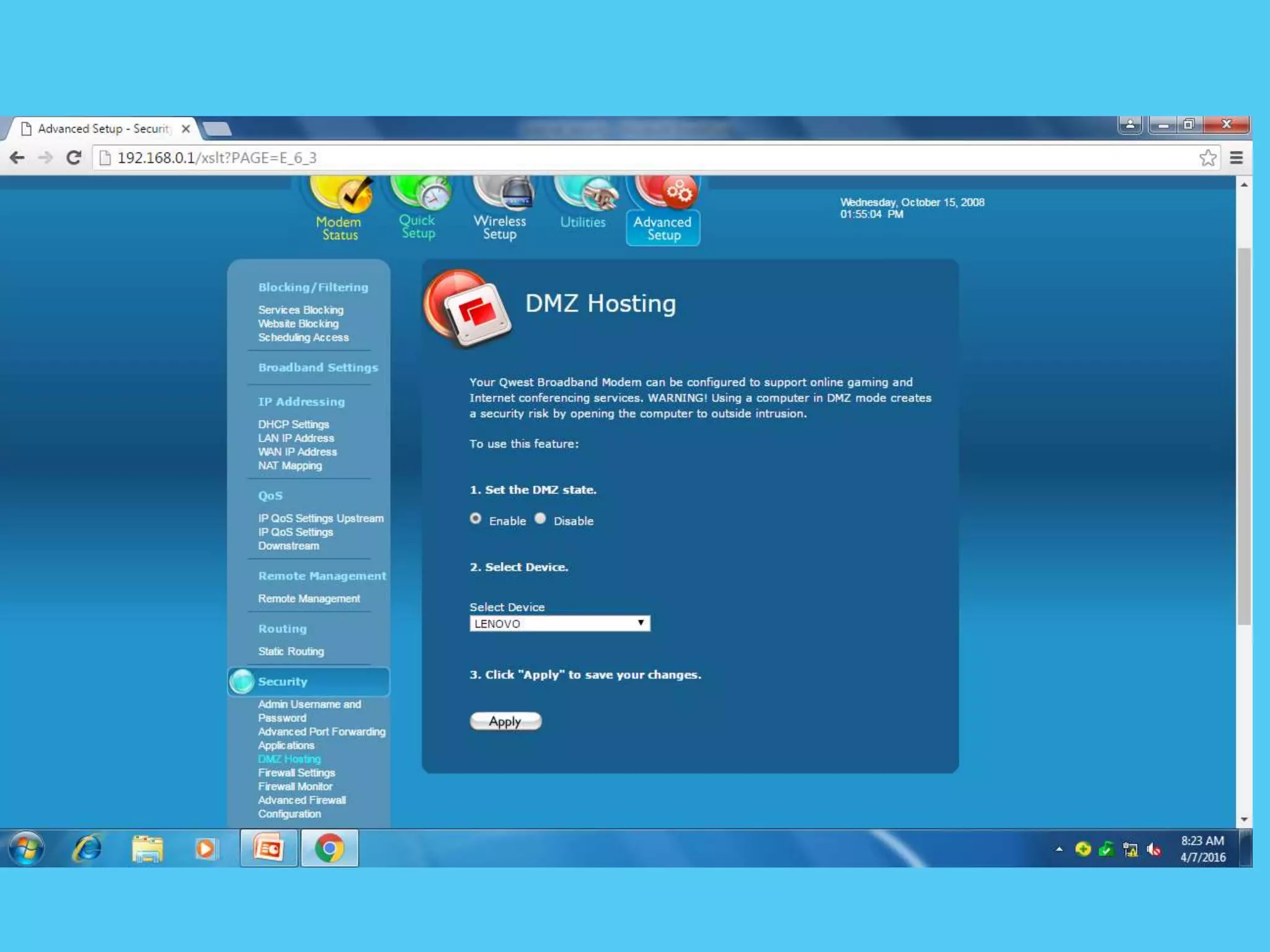
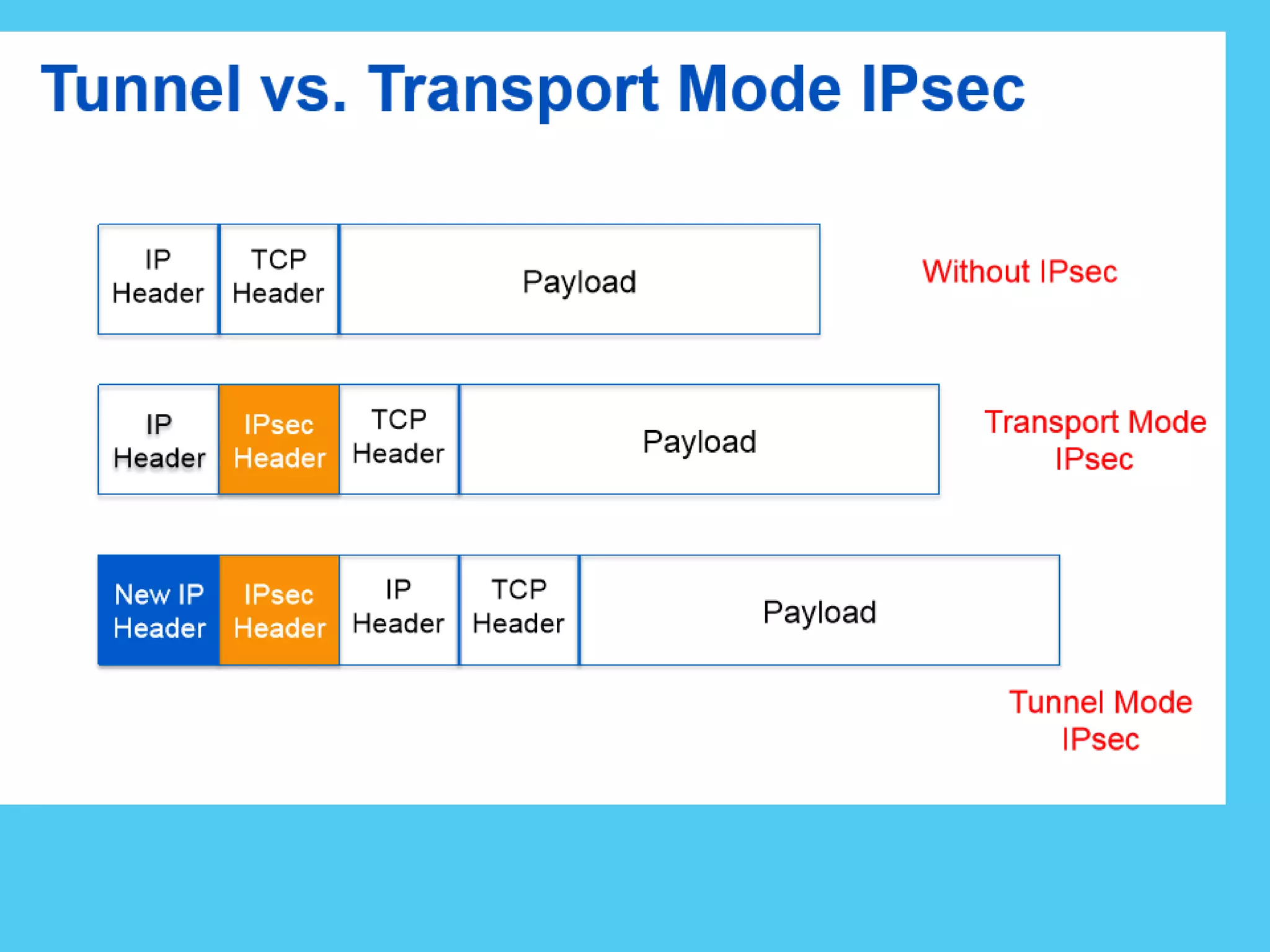
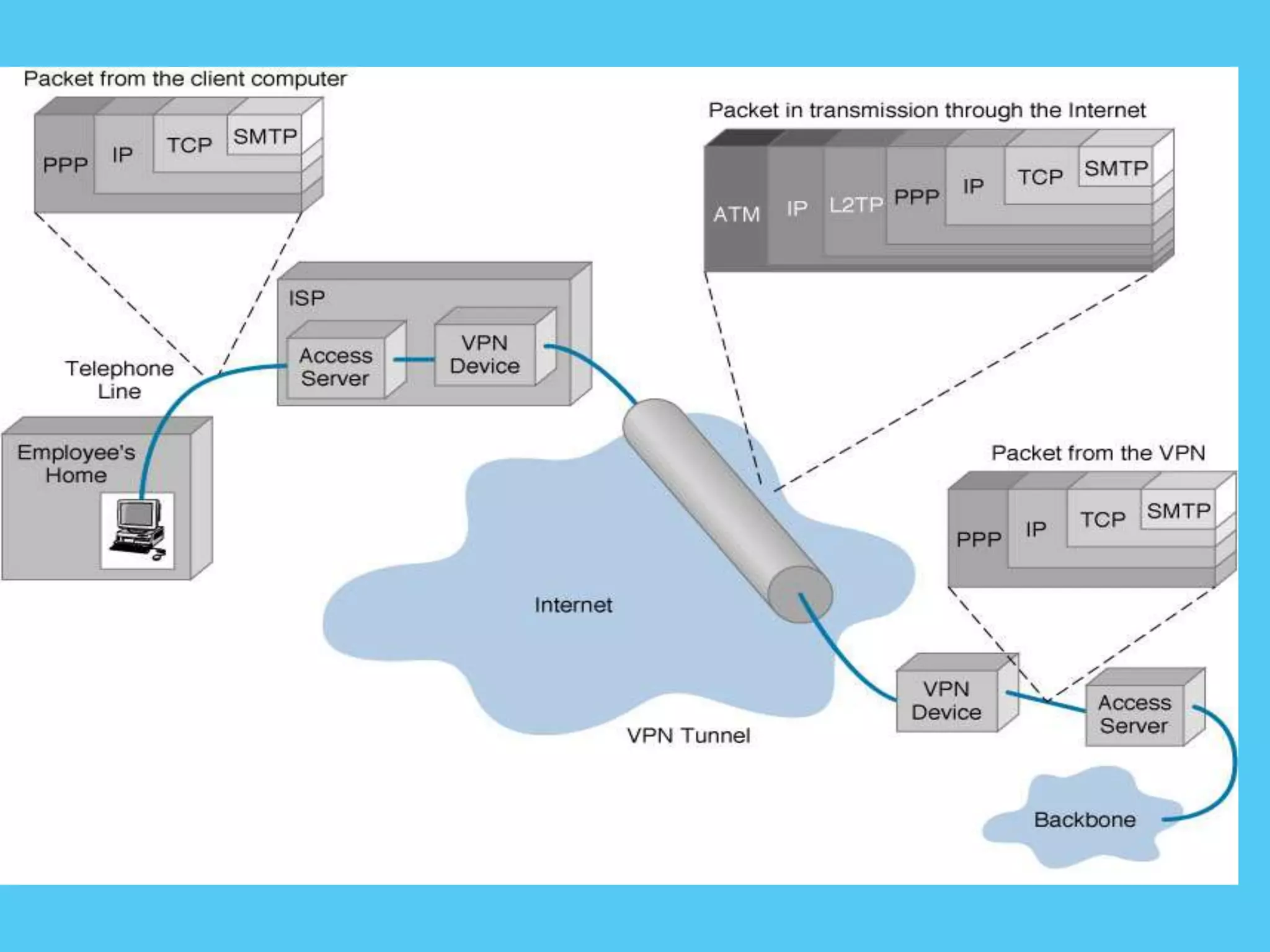
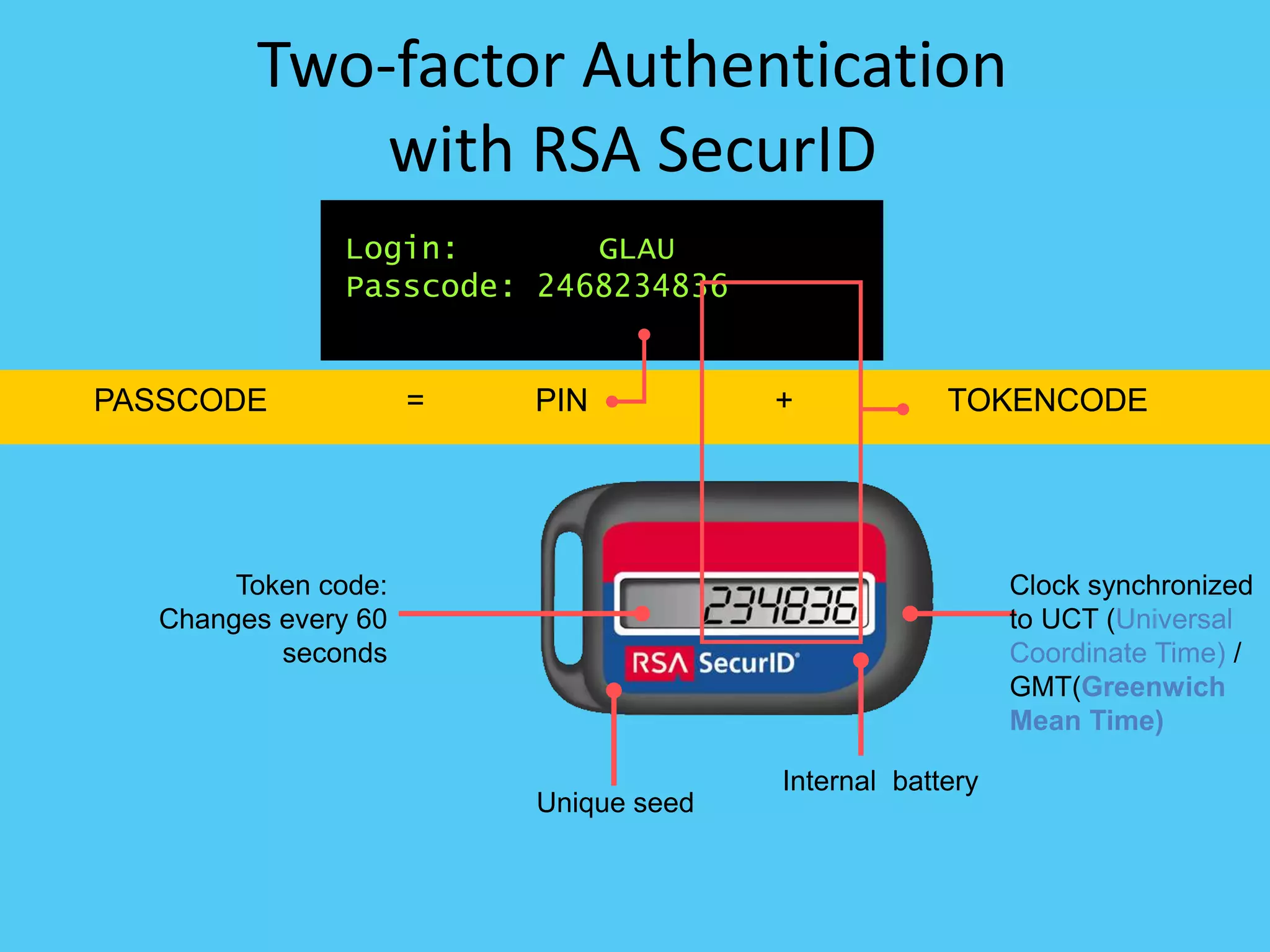
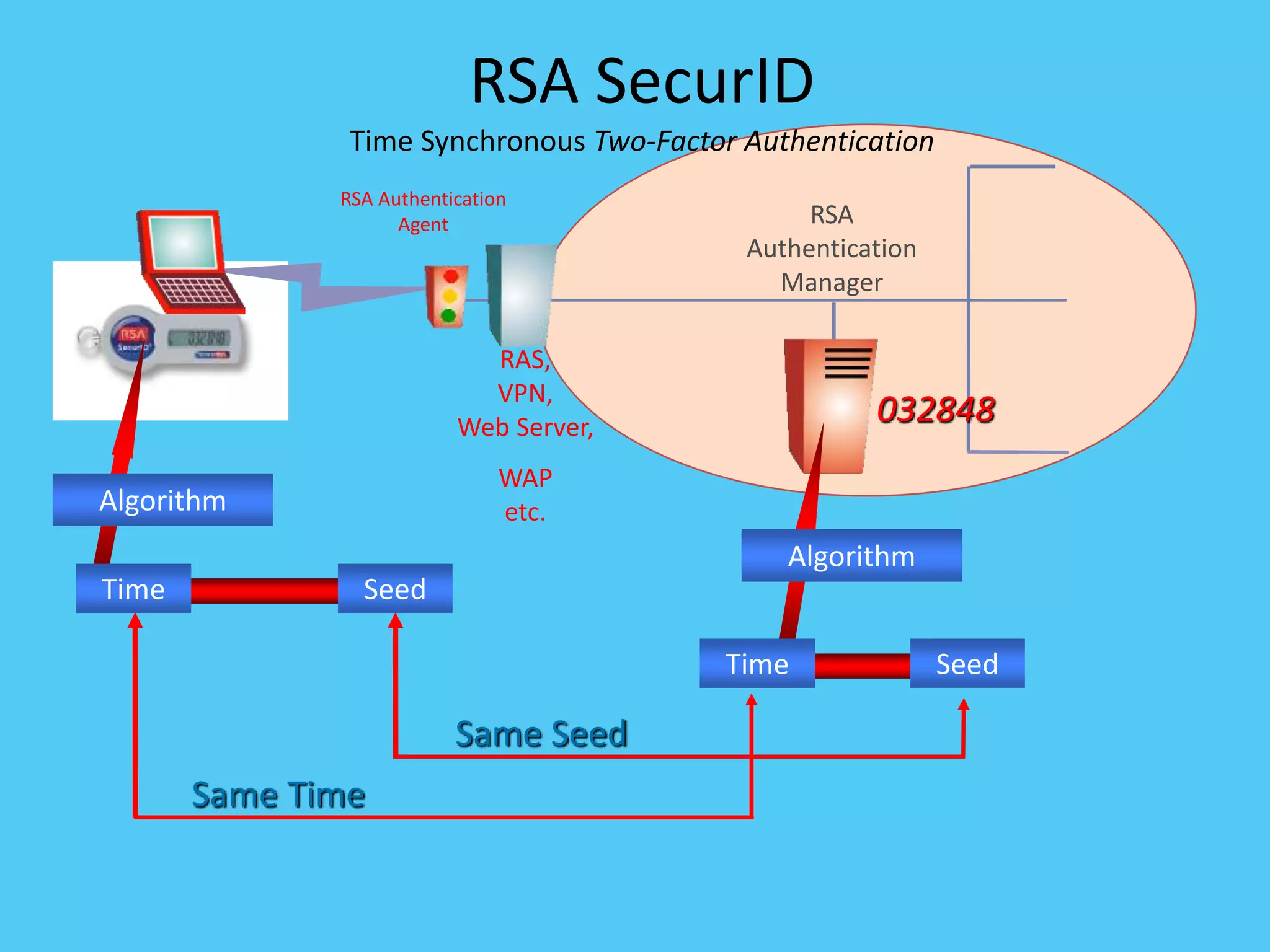
This document discusses various topics related to internet security including protocols like IPSec and SSL. It provides details on IPSec, how it provides security at the network layer and creates authenticated and confidential IP packets. It also describes SSL, how it provides security at the transport layer and addresses privacy, integrity and authentication issues. The document discusses internet security threats like malware, phishing etc. It covers SSL in more detail including how it establishes encrypted links between servers and clients and allows secure transmission of sensitive data. It also discusses proxy servers and how they can be used to implement access control and bypass restrictions.