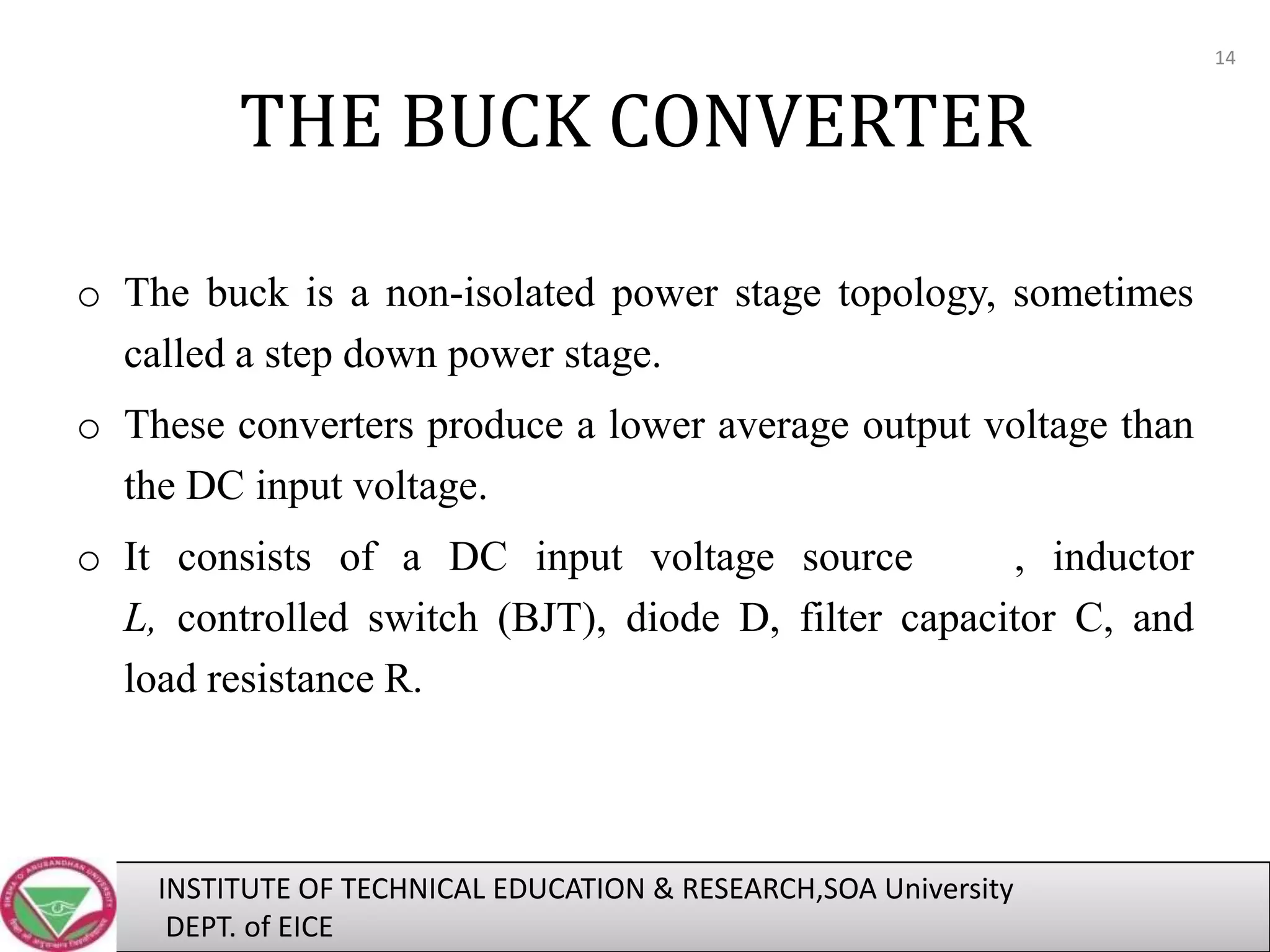
The document discusses a technical seminar on a buck converter fed by a PV array. It introduces PV systems and their applications. It describes the components of a PV system including PV modules, charge controllers, and buck converters. It explains that a buck converter connected between the PV array and battery uses maximum power point tracking to efficiently charge the battery by operating the PV array at its maximum power point. The document concludes that a buck converter increases the system efficiency when used with an MPPT technique in a PV system.



![4
PV SYSTEM
PV MODULE
Imodule
ILOAD
+
+
Vmodule
-
CONVERTER
V load
LOAD
-
Fig.1. Block diagram of the PV system [1]
INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION & RESEARCH,SOA University
DEPT. of EICE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalseminar2-140128003113-phpapp01/75/BUCK-converter-fed-by-PV-array-4-2048.jpg)
![5
Fig.2.Simplified equivalent circuit diagram of pv cell[3]
INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION & RESEARCH,SOA University
DEPT. of EICE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalseminar2-140128003113-phpapp01/75/BUCK-converter-fed-by-PV-array-5-2048.jpg)

![8
EUROPE
3%
7%
ASIA,JAPAN
15%
30%
NORTH AMERICA
INDIA,CHINA
20%
25%
SOUTH AMERICA
REST
Fig.3.Status of the PV technology worldwide.[6]
INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION & RESEARCH,SOA University
DEPT. of EICE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalseminar2-140128003113-phpapp01/75/BUCK-converter-fed-by-PV-array-8-2048.jpg)
![10
SHUNT TYPE CHARGE CONTROLLER
S2
Blocking diode
battery
+
_
Pv array
Charge
controller
S1
Fig.4 circuit diagram for shunt charge controller[2]
load](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalseminar2-140128003113-phpapp01/75/BUCK-converter-fed-by-PV-array-10-2048.jpg)
![11
SERIES TYPE CHARGE CONTROLLER
S1
S2
battery
+
_
Pv array
Charge
controller
Fig.5 circuit diagram for series charge controller[2]
load](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalseminar2-140128003113-phpapp01/75/BUCK-converter-fed-by-PV-array-11-2048.jpg)
![DC TO DC CONVERTER TYPE
CHARGE CONTROLLER
Pv array
Dc to dc converter
battery
Fig.6 circuit diagram for dc to dc charge controller[2]
12
load](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalseminar2-140128003113-phpapp01/75/BUCK-converter-fed-by-PV-array-12-2048.jpg)
![15
Fig.7 circuit diagram for buck converter[5]
INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION & RESEARCH,SOA University
DEPT. of EICE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalseminar2-140128003113-phpapp01/75/BUCK-converter-fed-by-PV-array-15-2048.jpg)
![16
Fig.8 waveform diagram for buck converter[5]
INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION & RESEARCH,SOA University
DEPT. of EICE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalseminar2-140128003113-phpapp01/75/BUCK-converter-fed-by-PV-array-16-2048.jpg)
![18
Fig.7. Current/power Vs Voltage plot with MPPT [2]
INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION & RESEARCH,SOA University
DEPT. of EICE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalseminar2-140128003113-phpapp01/75/BUCK-converter-fed-by-PV-array-18-2048.jpg)


![REFERENCE
[1] S. Rahmam, M. A. Khallat, and B. H. Chowdhury, “A discussion on
thediversity in the applications of photovoltaic system,” IEEE Trans.,Energy
Conversion, vol. 3, pp. 738–746, Dec. 1988.
[2]Chetan Singh Solanki,”Solar Photovoltaics,fundamentals,technologies and
applications”, second edition, PHI LEARNING Private Limited,2012.
[3]B.Chitti Babu, R.Vigneshwaran, Sudarshan Karthik, Nayan Ku. Dalei,Rabi
Narayan Das, “A Novel Technique for Maximum Power Point Tracking of PV
Energy Conversion System”, Proc. of International Conf. on Computer
Applications in Electrical Engineering, IIT Roorkee. pp.276-279,CERA 2010.
[4] S.Sukhatme,J.nayak “SOLAR ENERGY : PRINCIPLES OF THERMAL
COLLECTION AND STORAGE”, Third edition,Tata McGraw-Hill, 2008.
[5]Dr. P.S Bimbhra: “Power electronics”, KHANNA PUBLISHERS, New
Delhi,2010.
[6] G. Foley: “Photovoltaic Applications in Rural Areas of the Developing
World”. World Bank, 2012.
INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION & RESEARCH,SOA University
DEPT. of EICE
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalseminar2-140128003113-phpapp01/75/BUCK-converter-fed-by-PV-array-21-2048.jpg)