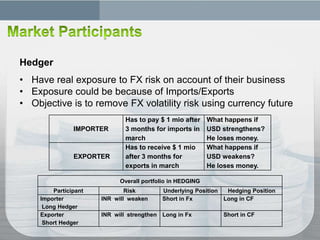
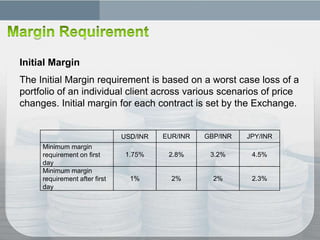
The document discusses financial derivatives such as forwards, futures, options, and swaps used to hedge currency risk, noting that currency futures traded on an exchange provide benefits like price transparency, elimination of counterparty credit risk, and access for retail traders compared to over-the-counter currency forwards. Hedgers use derivatives to offset currency risk from imports/exports while speculators take views on market direction hoping to profit, and arbitrageurs look for mispricing opportunities; exchanges require initial and maintenance margin as well as mark positions to market daily to reduce default risk.