Embed presentation
Downloaded 34 times






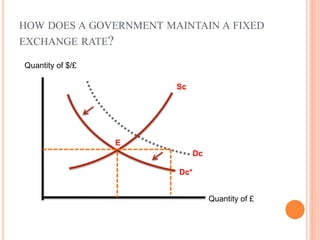

Under a fixed exchange rate system, governments try to maintain a constant value for their currencies against other currencies. A country's central bank commits to buying and selling its currency at a fixed price in order to maintain this exchange rate. Fixed exchange rates provide stability for international trade and control of inflation. Governments intervene in currency markets by buying and selling their own currency to influence supply and demand and maintain the fixed exchange rate when market forces would otherwise cause the rate to change.







