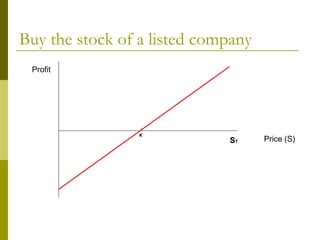
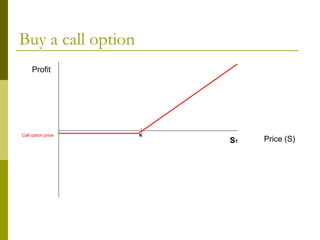
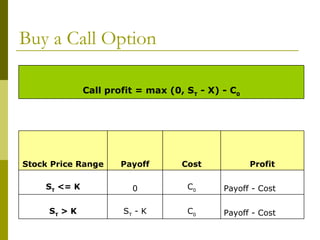
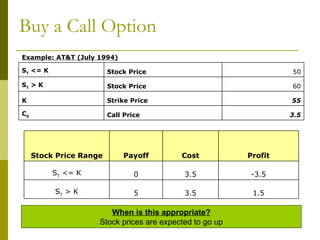
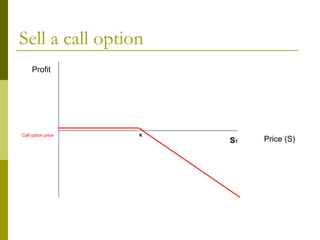
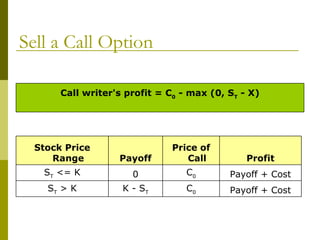
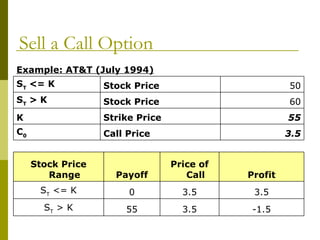
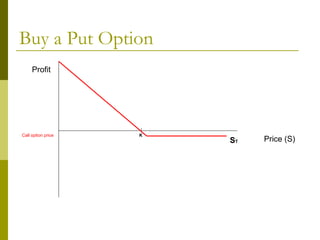
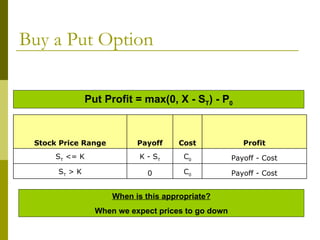
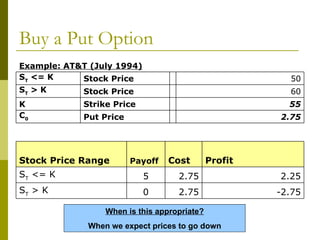
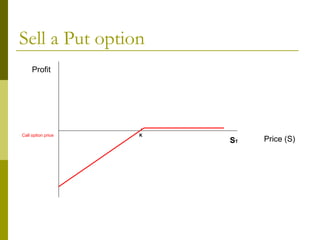
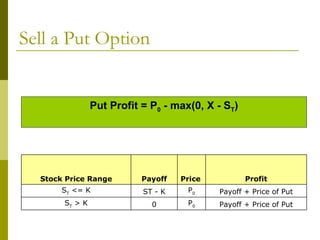
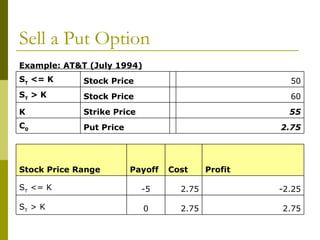
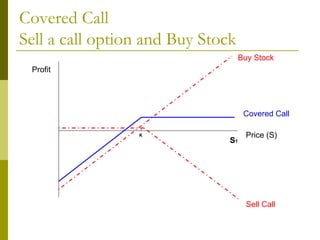
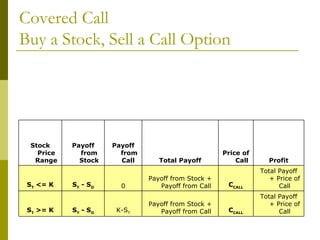
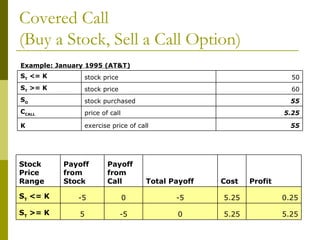
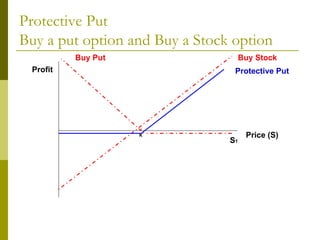
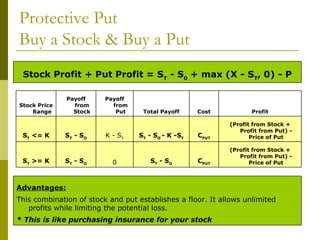
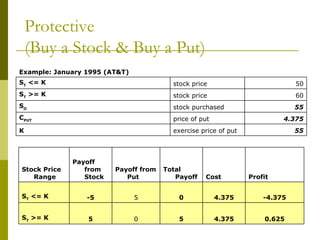
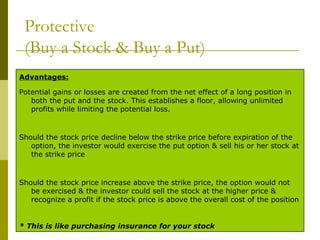
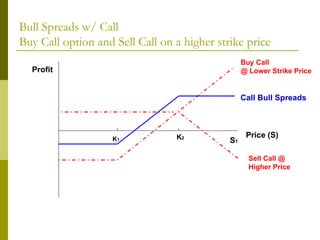
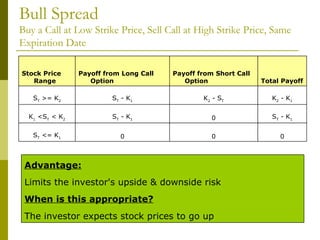
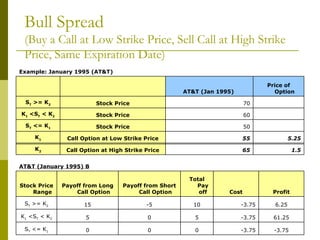
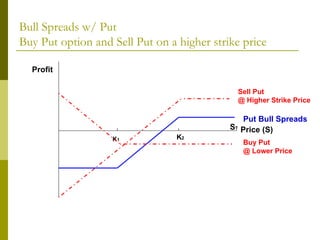
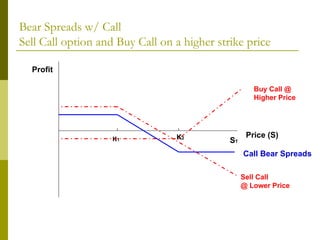
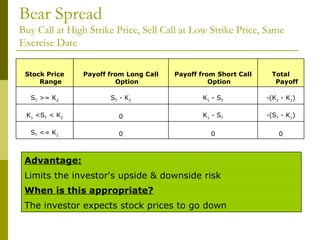
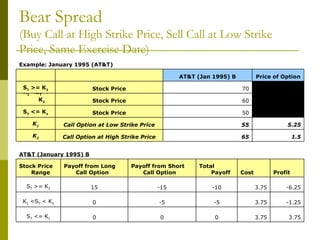
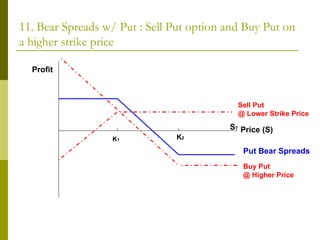
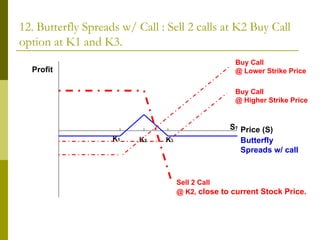
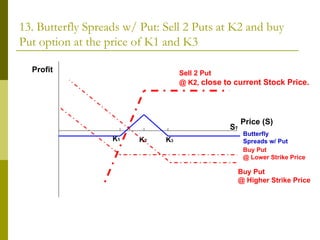
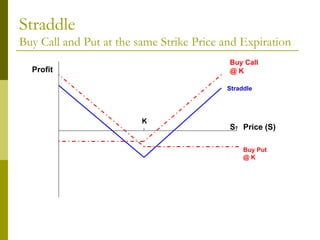
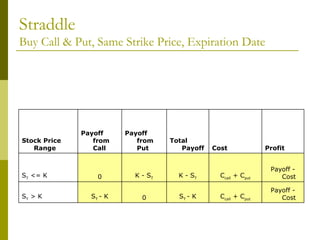
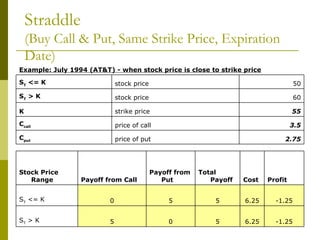
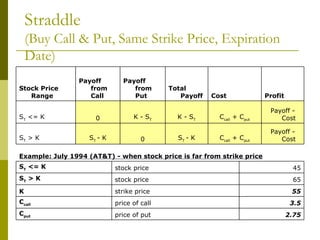
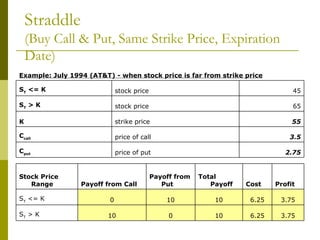
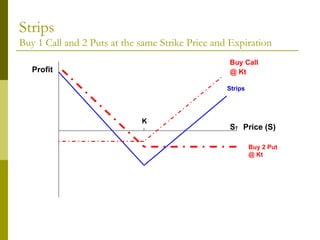
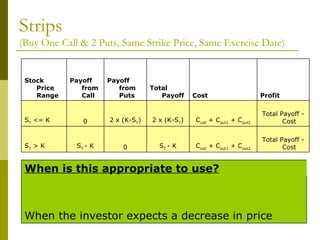
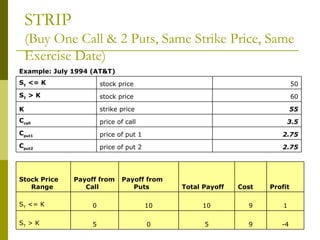
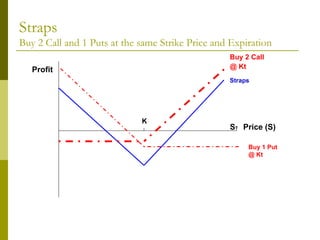
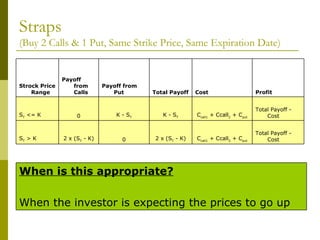
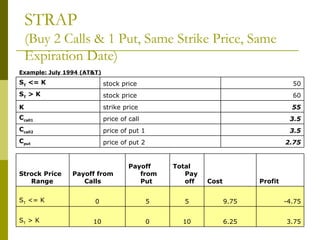
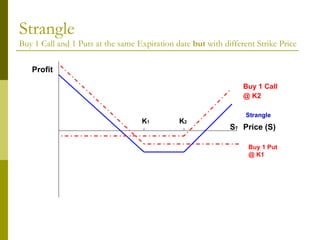
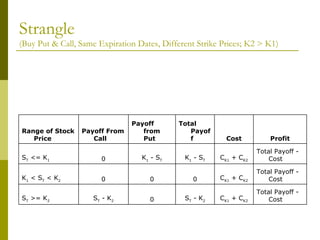
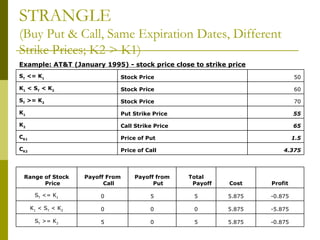
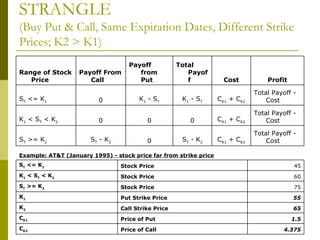
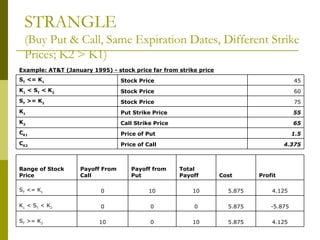
The document covers various options investment strategies, detailing the fundamental concepts of call and put options, as well as various trading strategies, including spreads, straddles, and protective puts. It explains how these strategies can be used based on the investor's expectations of stock price movements, outlining potential profits and risks associated with each. Additionally, it provides practical examples to illustrate the application of these strategies in real-world scenarios.