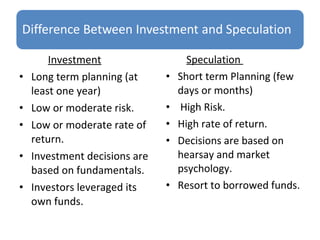
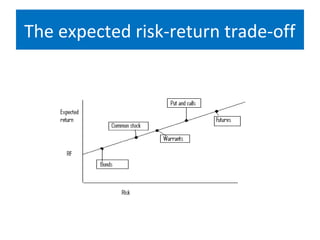
This document discusses the key differences between investment and speculation. Investment involves committing money for long-term gains with low to moderate risk and returns based on fundamentals. Speculation involves short-term, high risk bets with potential for high returns based on market psychology. The document also outlines the traditional two-step investment decision process of security analysis and portfolio management to evaluate individual assets and construct a balanced portfolio.