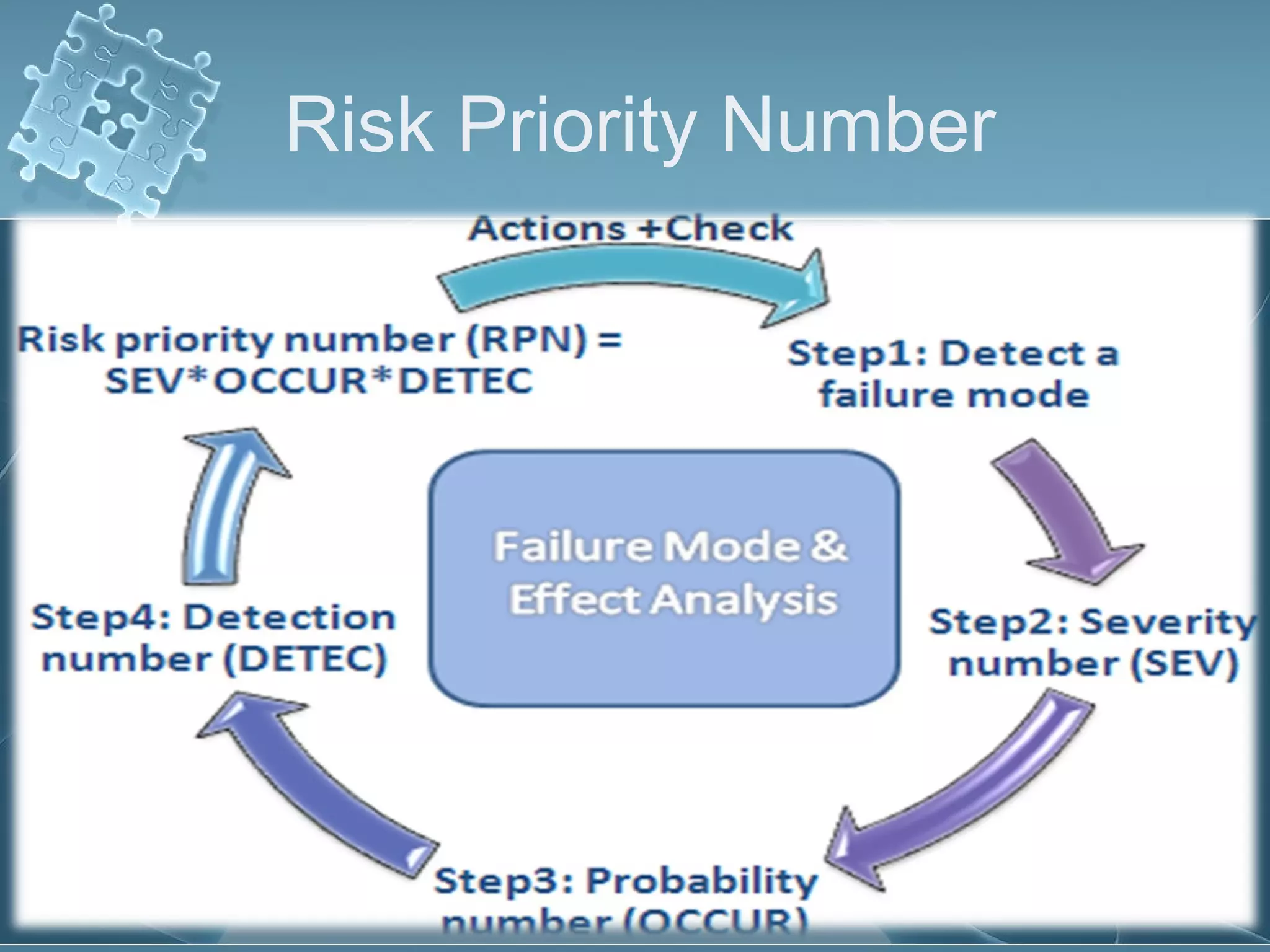
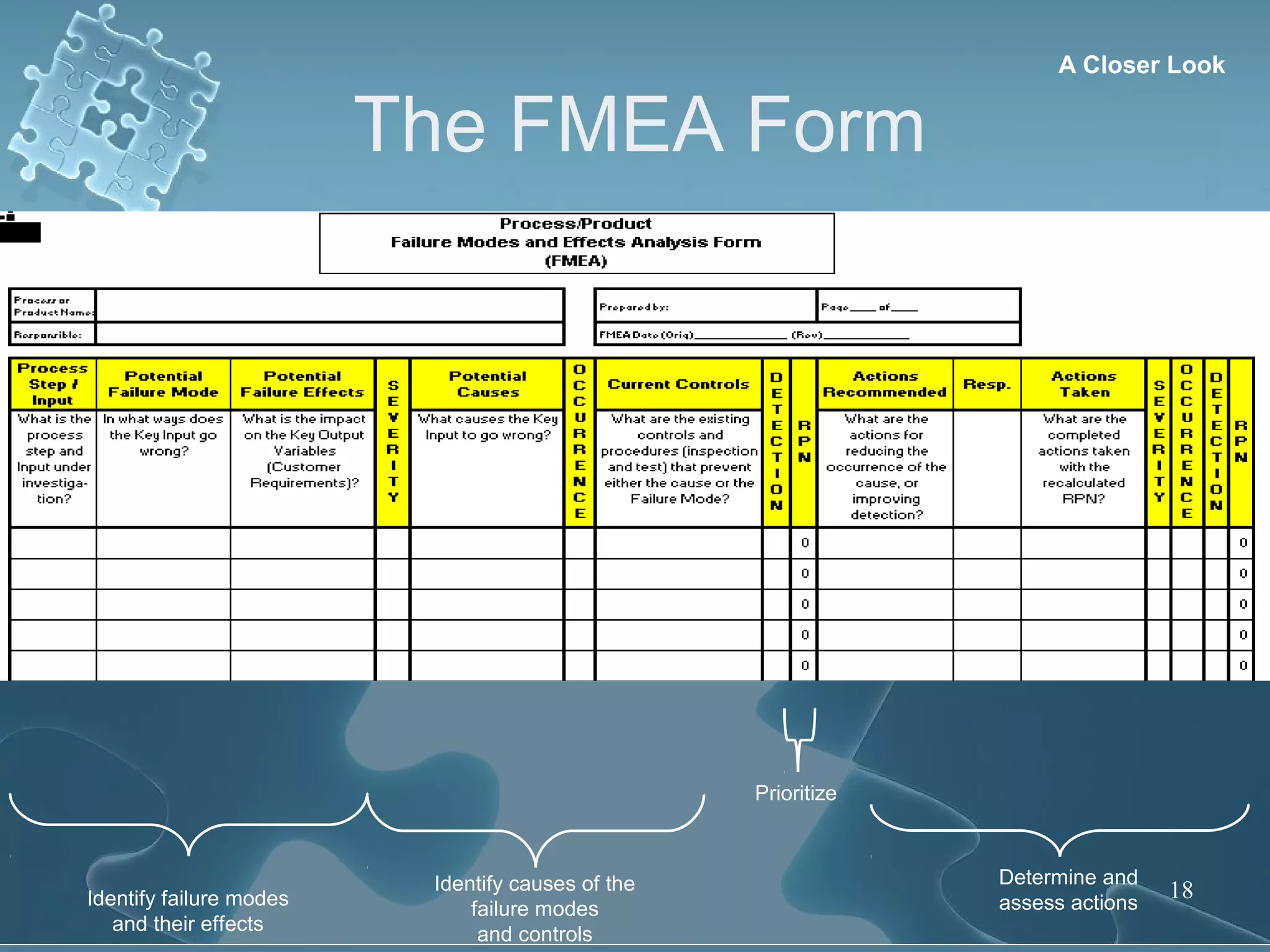
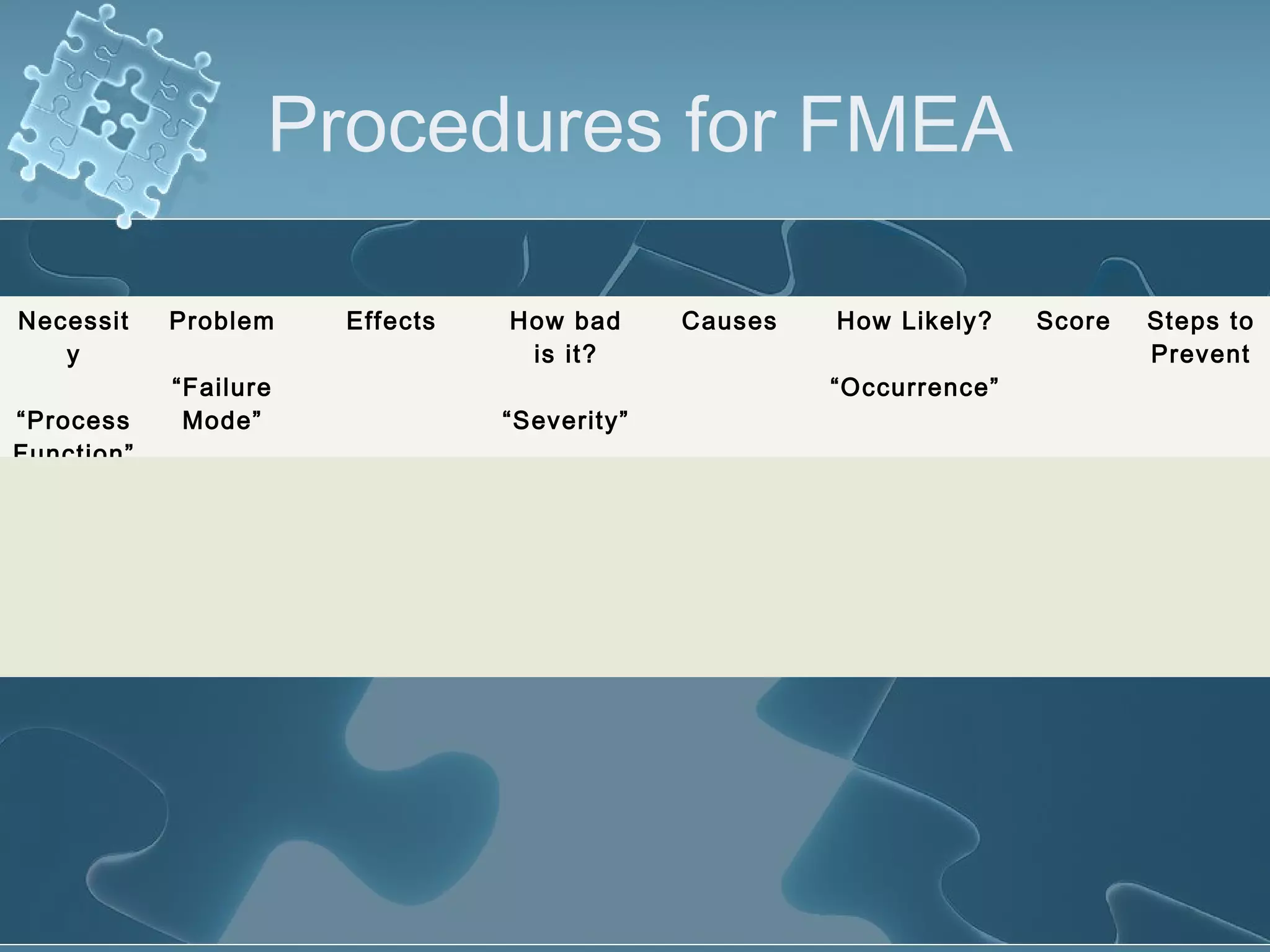
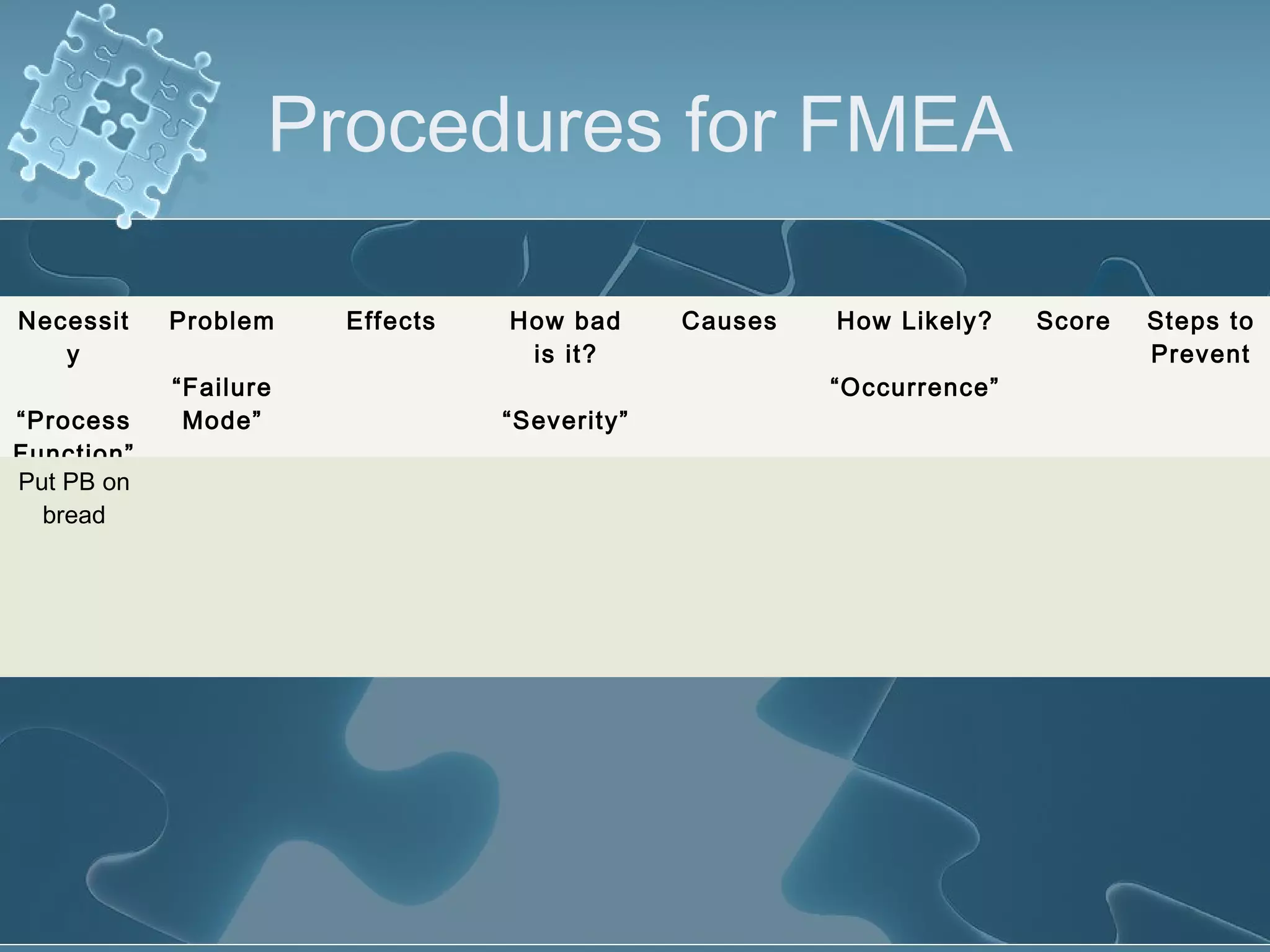
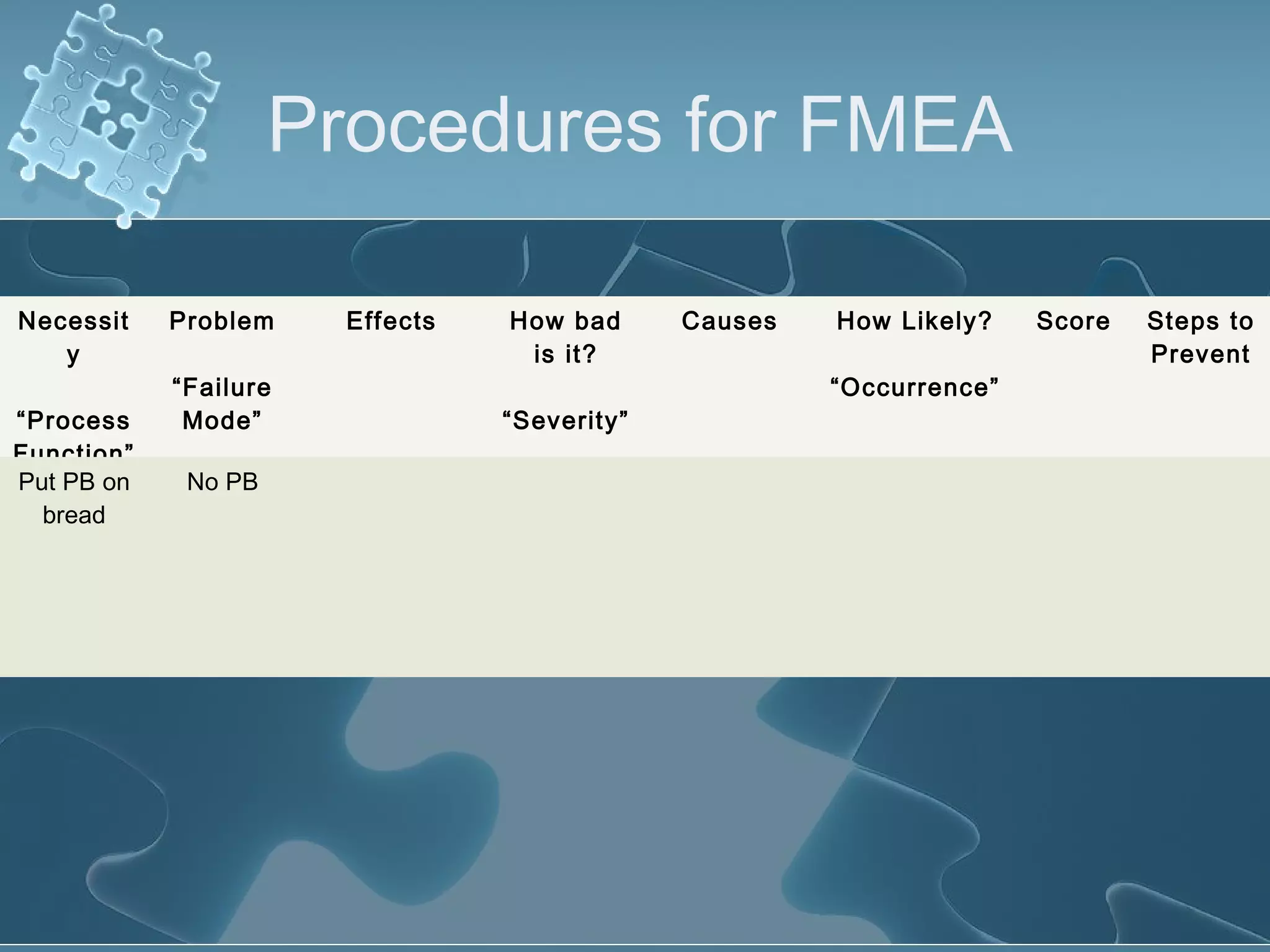
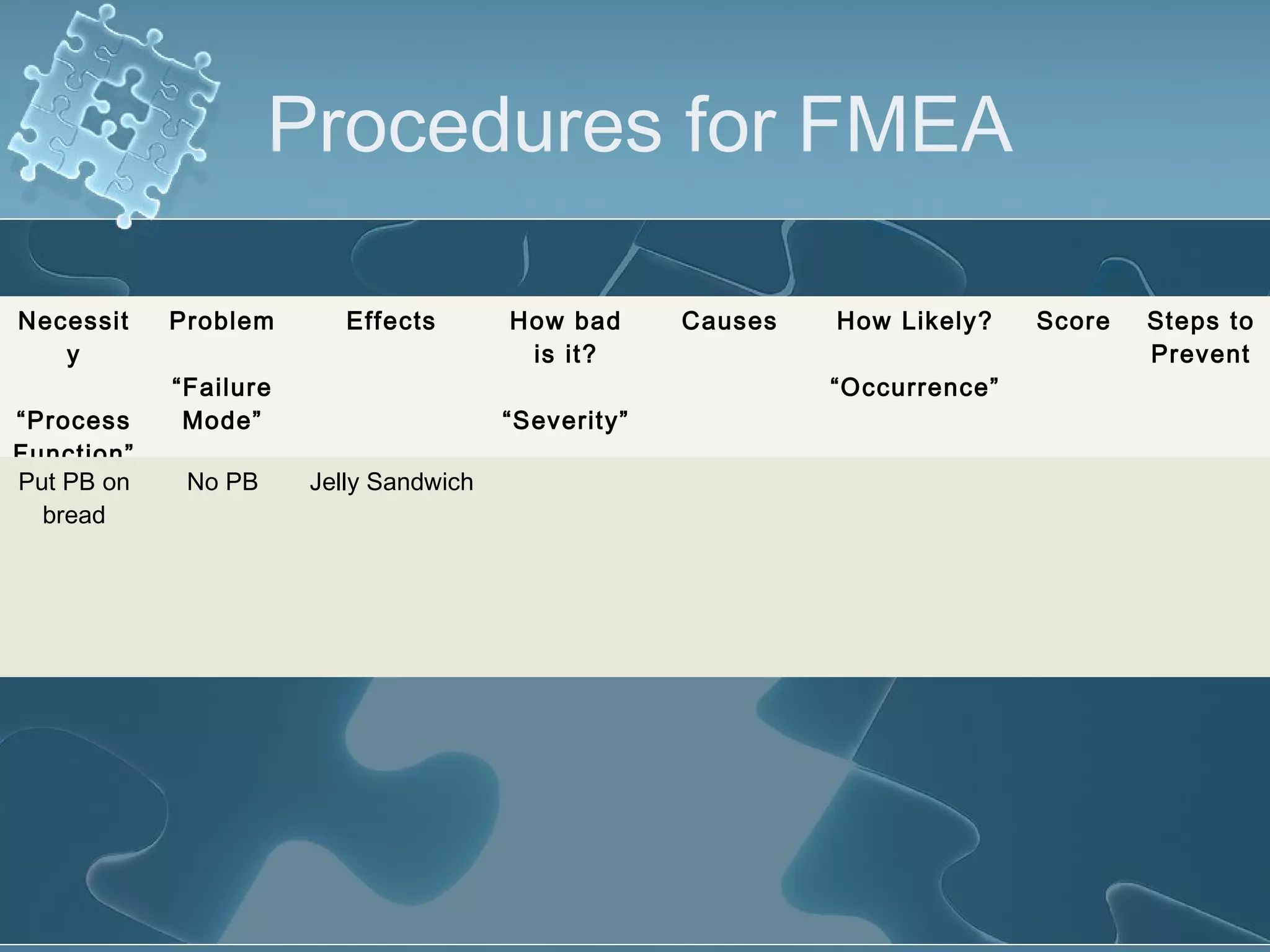
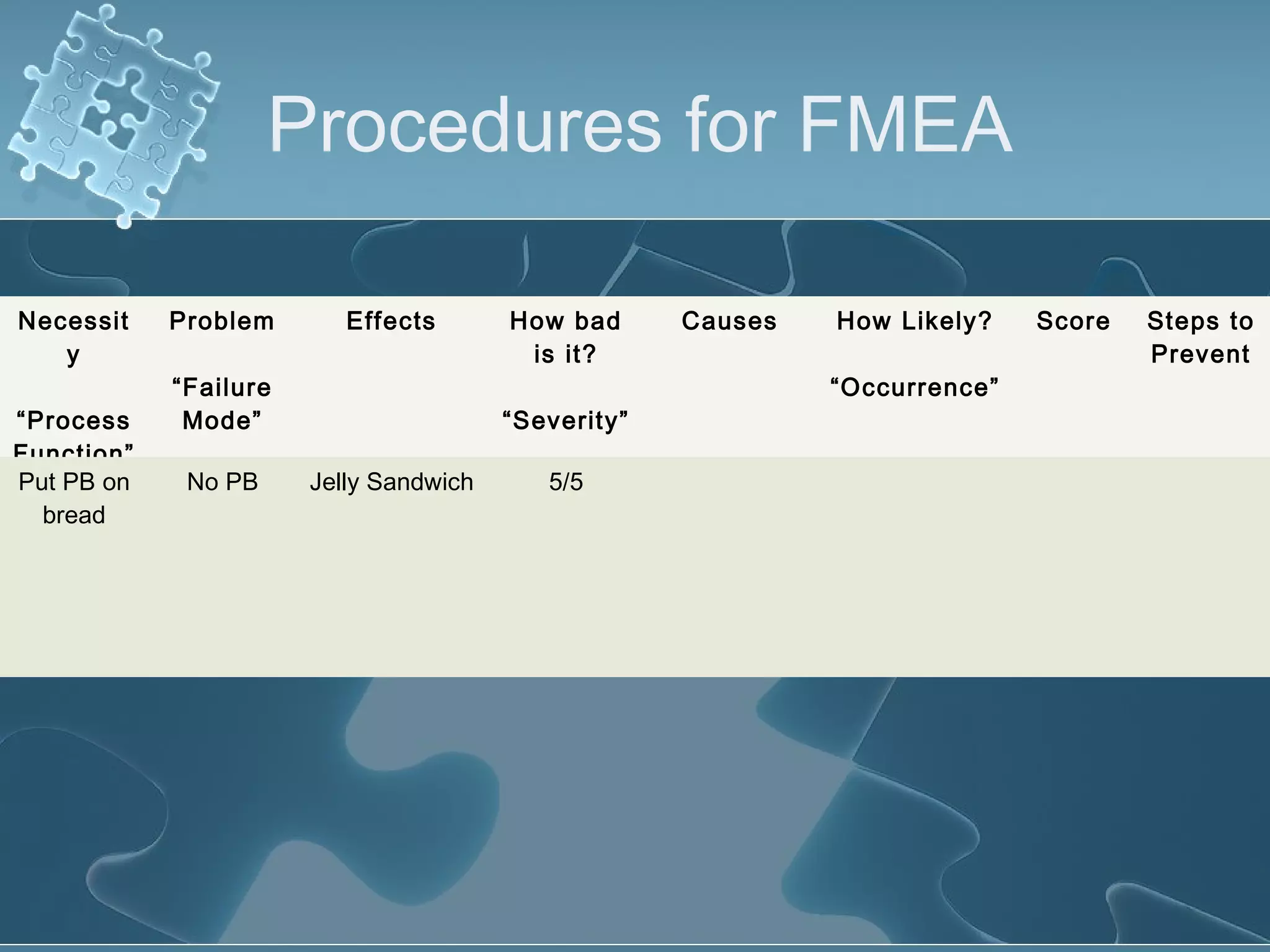
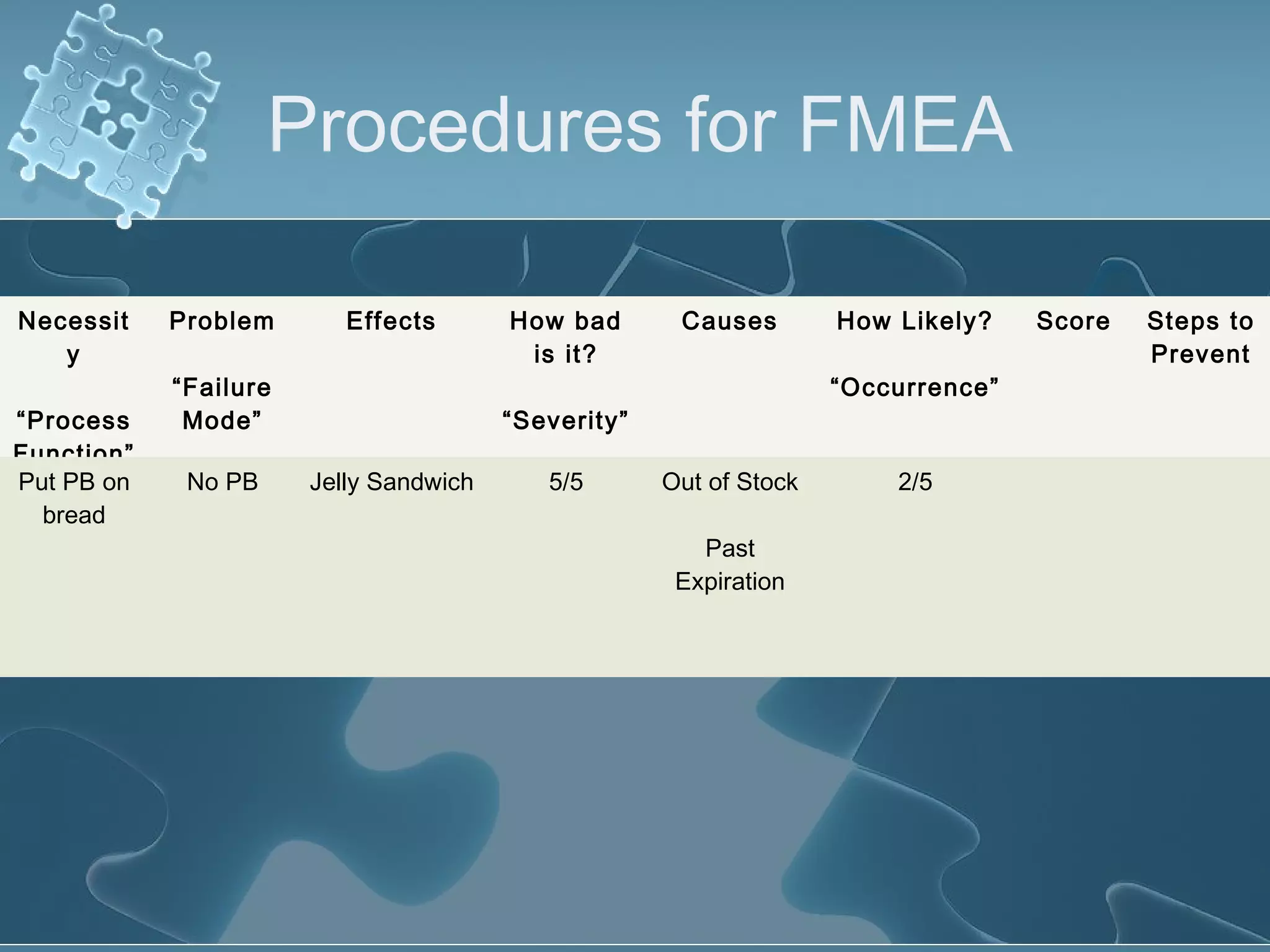
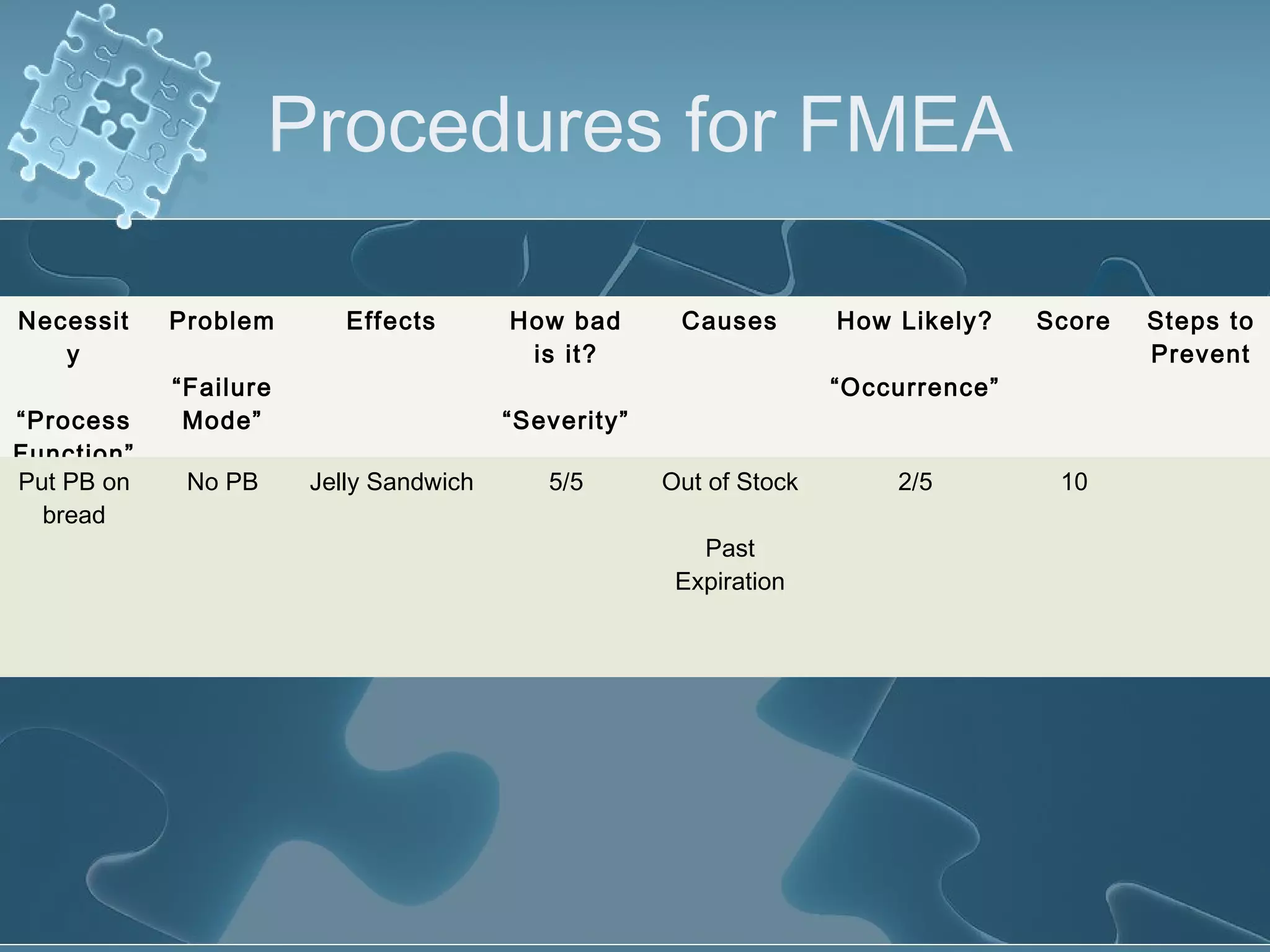
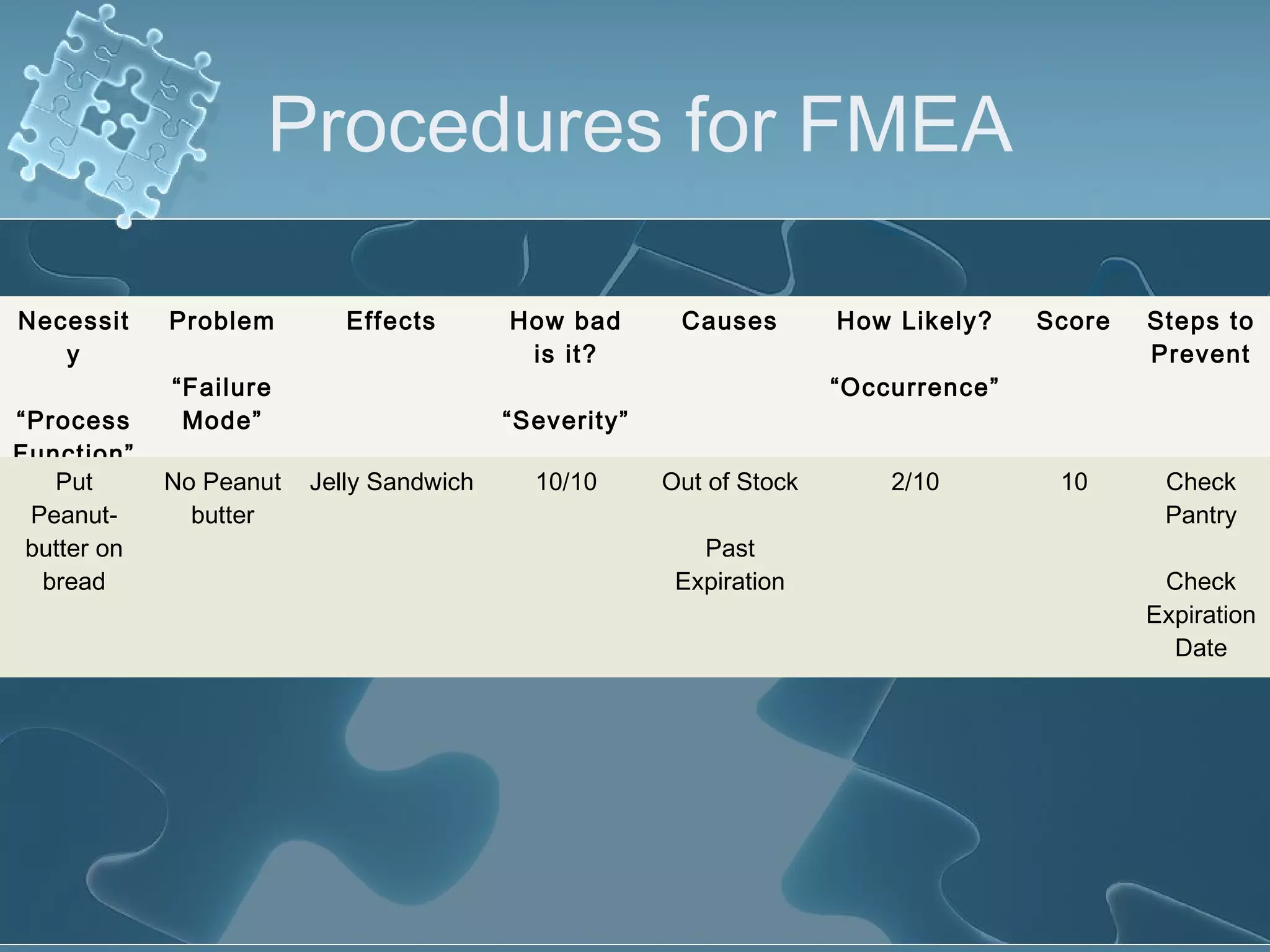
The document discusses Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA), including its objectives, history, benefits, limitations, and how to conduct one. An FMEA is a process that identifies all possible failures in a service or process, assesses their effects and risks, and prioritizes actions to reduce risks. It was first used in the aerospace industry in the 1960s and has since been adopted by other industries like automotive. Conducting an FMEA involves a team identifying failure modes, effects, causes, controls, and risk levels to develop corrective actions.