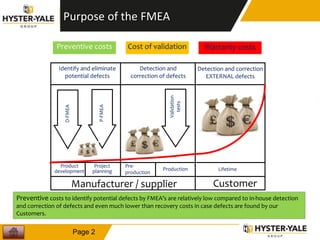
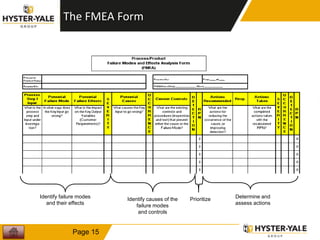
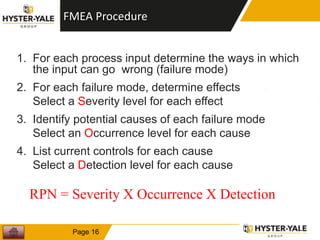
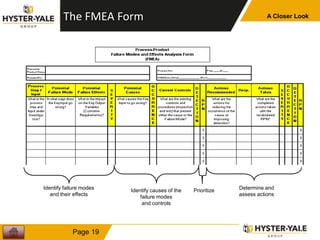
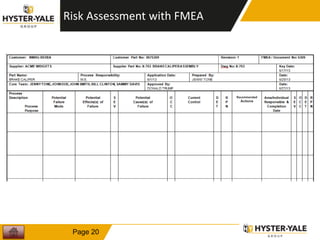
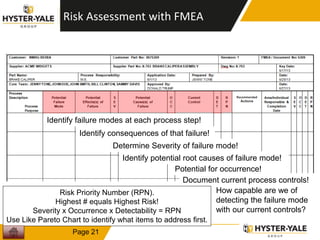
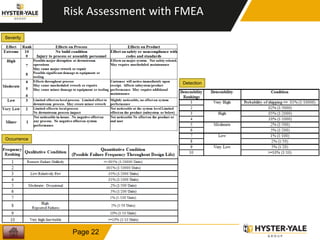
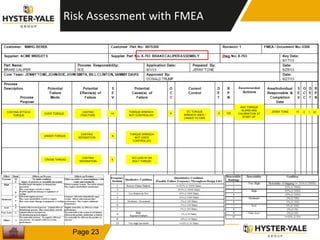
The document provides information on conducting a Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA). It discusses that the purpose of an FMEA is to identify potential defects early and that preventive costs of an FMEA are lower than detection and recovery costs. It outlines the key steps of an FMEA including identifying failure modes and their causes and effects, prioritizing risks via a Risk Priority Number, and determining actions. The document also discusses FMEA training objectives, types of FMEAs, how to conduct an FMEA, and a 10 step FMEA process checklist.