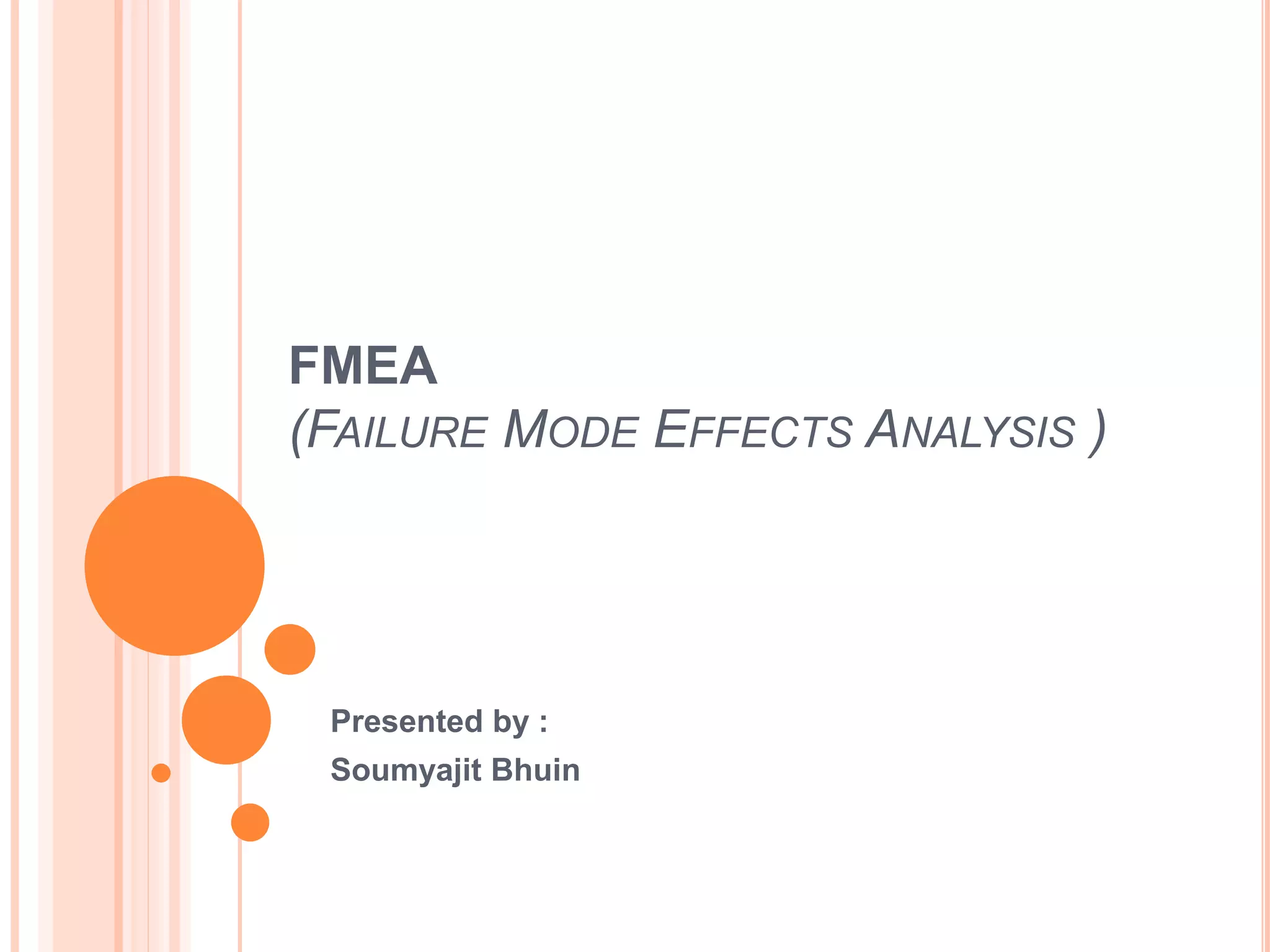
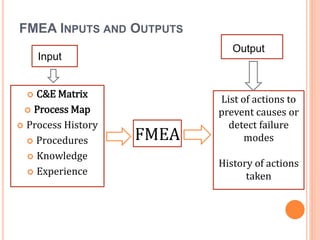
FMEA (Failure Mode Effects Analysis) is a systematic method aimed at identifying and preventing potential problems in product design or process development to enhance safety and customer satisfaction. Originating in the 1960s, it evaluates risks by assessing the severity, probability of occurrence, and probability of detection of failure modes, leading to a Risk Priority Number (RPN) that categorizes the level of risk. Despite its advantages, FMEA also involves limitations such as employee training, initial impacts on schedules, and financial costs for upgrades.