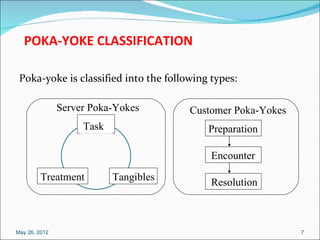
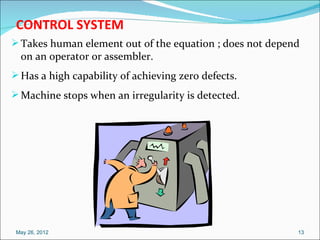
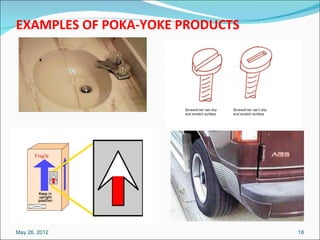
The document defines poka-yoke as a Japanese term meaning "mistake-proofing" and discusses its use in manufacturing to eliminate defects. Poka-yoke aims to prevent human errors by making processes foolproof through simple mechanisms that detect and correct mistakes. The document outlines principles of mistake-proofing, types of poka-yoke devices, and how poka-yoke can be implemented at different stages of production to catch errors early.