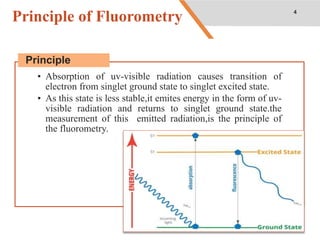
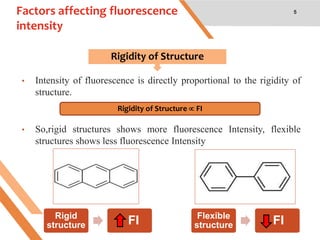
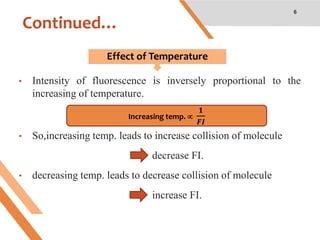
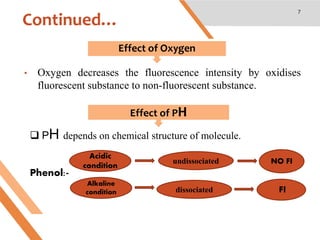
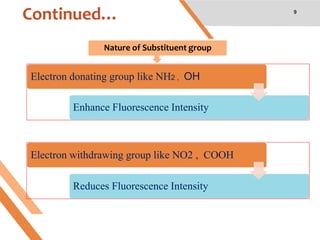
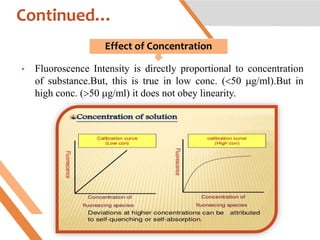
This document discusses factors that affect fluorescence intensity. It explains that fluorescence intensity is directly proportional to the rigidity of a structure and inversely proportional to temperature. Other factors that can decrease fluorescence intensity include oxygen, which can oxidize fluorescent substances, as well as electron withdrawing substituent groups. Fluorescence intensity is directly proportional to concentration at low concentrations but does not obey linearity at high concentrations. The presence of other non-fluorescent solutes can also impact intensity through inner filter effects. In conclusion, several physicochemical factors influence fluorescence intensity measurements.