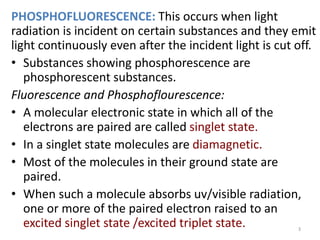
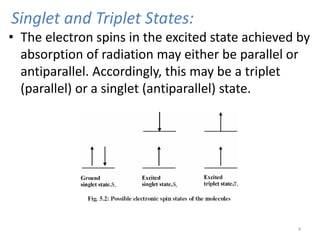
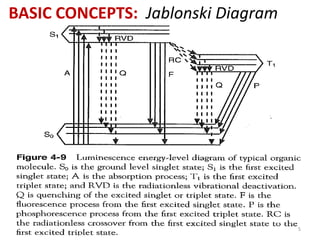
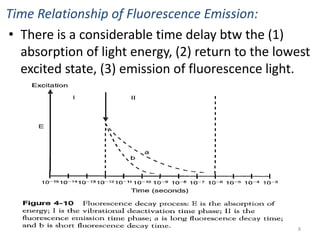
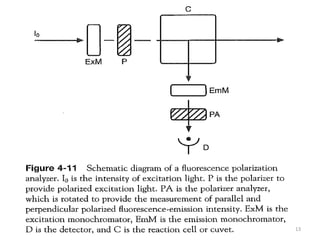
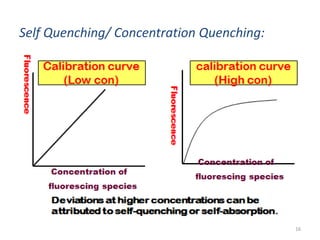
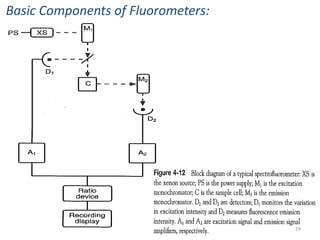
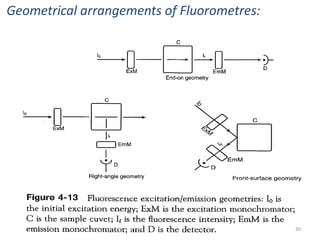
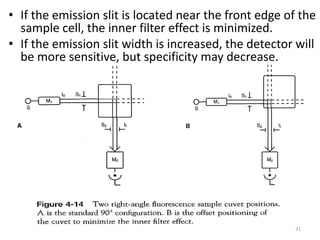
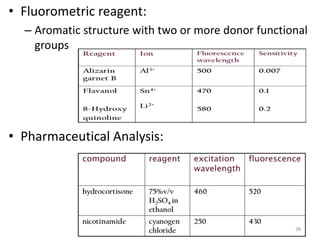
This document provides an overview of fluorometry, including basic concepts, instrumentation, and applications. It discusses how fluorescence occurs when a molecule absorbs light at one wavelength and reemits light at a longer wavelength. Factors that affect fluorescence such as temperature, pH, and dissolved oxygen are also covered. The relationship between fluorescence intensity and concentration is explained. Additionally, the document defines fluorescence polarization and describes various types of quenching including self-quenching, chemical quenching, and collisional quenching.