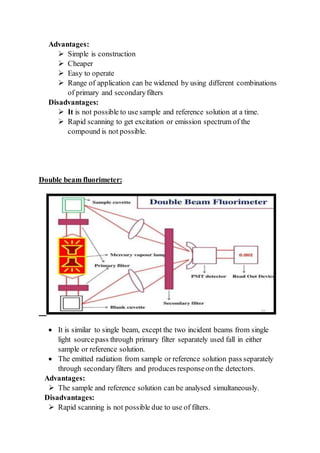
Fluorimetry involves measuring the fluorescence light emitted by a substance. A fluorimeter is used, which contains a light source, filters or monochromators to select excitation and emission wavelengths, sample cells, and a detector. Fluorescence occurs when molecules absorb light and emit light of a longer wavelength as they transition from an excited singlet state to the ground state. Factors like concentration, pH, and temperature can affect fluorescence. Fluorimetry is used in applications like determining ions and vitamins, and in organic analysis.