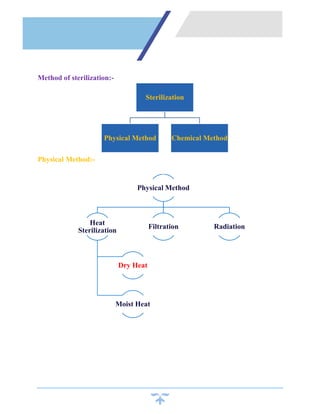
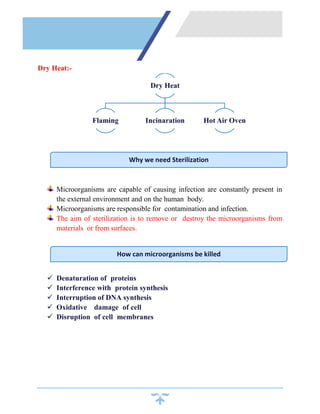
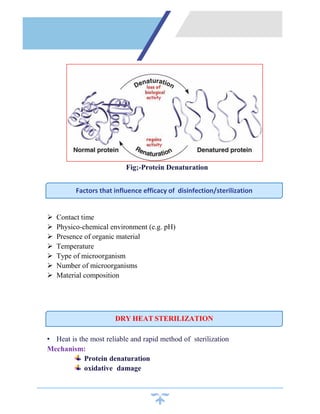
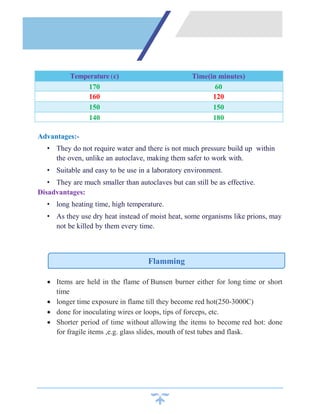
Sterilization is a process that kills all microorganisms through various means like heat, chemicals, irradiation, etc. Dry heat sterilization uses high temperatures without moisture to destroy microbes. Common dry heat methods include hot air ovens, flaming, and incineration. Hot air ovens circulate hot air above 170°C for at least 60 minutes to ensure sterilization through protein denaturation and cell membrane disruption. Flaming uses the flame of a Bunsen burner to heat items red hot above 250°C, while incineration reaches temperatures over 870°C to sterilize through complete burning. Dry heat requires higher temperatures and longer times than wet heat sterilization methods.