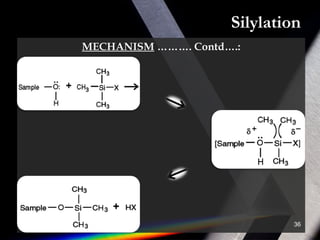
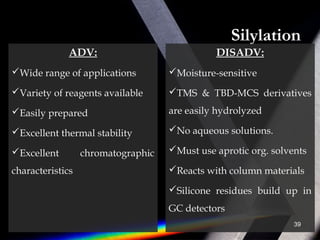
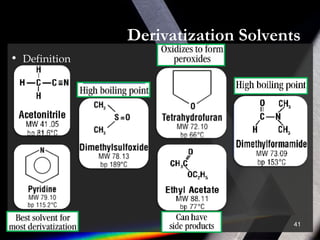
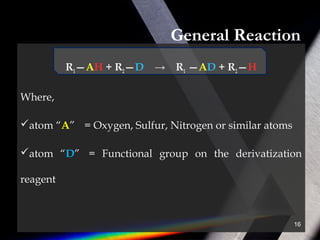
Derivatization is a process that chemically modifies compounds to produce derivatives suitable for GC analysis. It is commonly used to impart volatility and thermal stability. The most widely used derivatization techniques are alkylation, acylation, and silylation which substitute active hydrogens with functional groups. Choosing the appropriate technique depends on the analyte's properties and available reagents. Derivatives must be volatile, thermally stable, and efficiently separated by GC. For example, carboxylic acids are often derivatized via esterification while silylation is effective for alcohols, phenols, carboxylic acids and amines. Chiral derivatization can also allow separation of enantiomers using GC.






























![Silylation
INTRODUCTION:
•Introduction of a “silyl group” into a molecule, usually in
substitution for active hydrogen such as dimethylsilyl
[SiH(CH3)2], t-butyldimethylsilyl [Si(CH3)2C(CH3)3] and
chloro-methyl-dimethylsilyl [SiCH2Cl(CH3)2].
•Replacement of “active hydrogen” by a silyl group
reduces the polarity of the compound and reduces
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcfinalall-140701040650-phpapp02/85/Derivatization-in-GC-33-320.jpg)