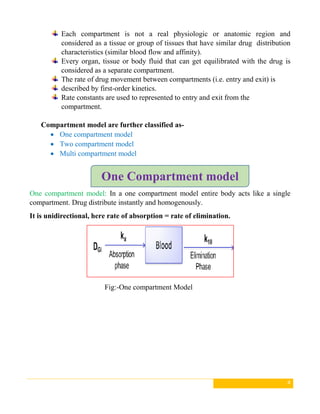
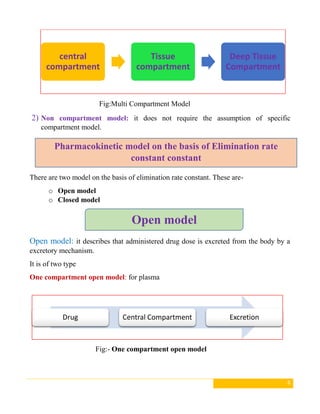
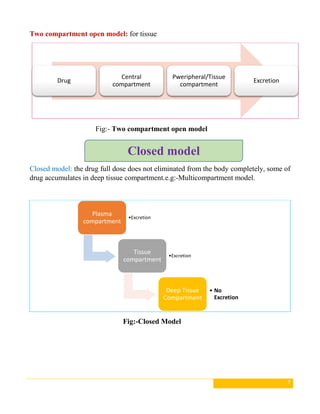
This document discusses pharmacokinetic models, which are mathematical models used to predict how drugs move through the body over time. It describes several types of pharmacokinetic models including compartment models that divide the body into hypothetical compartments and non-compartment models. Compartment models include one, two, and multi-compartment models. Pharmacokinetic models can also be classified based on elimination rate constants, compartment arrangement, and physiology. The document provides examples and diagrams of different pharmacokinetic models and discusses their applications in drug development and clinical practice.