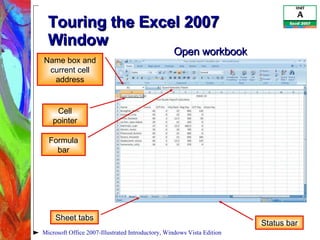
This document provides an overview of getting started with Excel 2007, including how to understand spreadsheets and the Excel window interface. It describes how to enter labels and values, use formulas with cell references and functions, edit cells, switch between worksheet views, and choose print options. The objectives are to tour the Excel window, enter and edit formulas, work with different views, and set up print layouts.