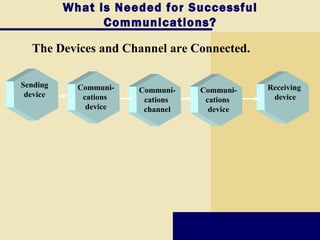
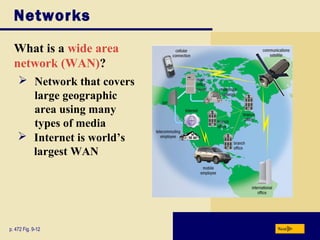
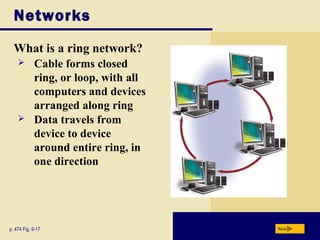
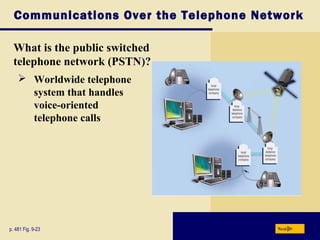
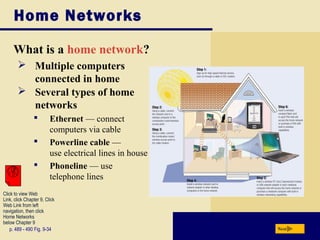
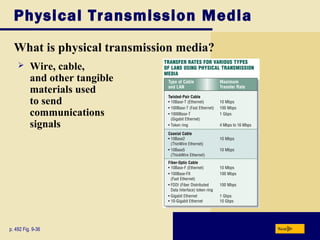
This document provides an overview of key topics covered in Chapter 9 of the textbook "Discovering Computers 2008". It discusses computer communications and networks, including components required for successful communications, uses of computer communications, types of networks, network communication standards, communications devices, setting up home networks, transmission media, and more. The objectives are to understand concepts like client/server networks, wireless technologies, and the infrastructure that enables computer and data transmission.