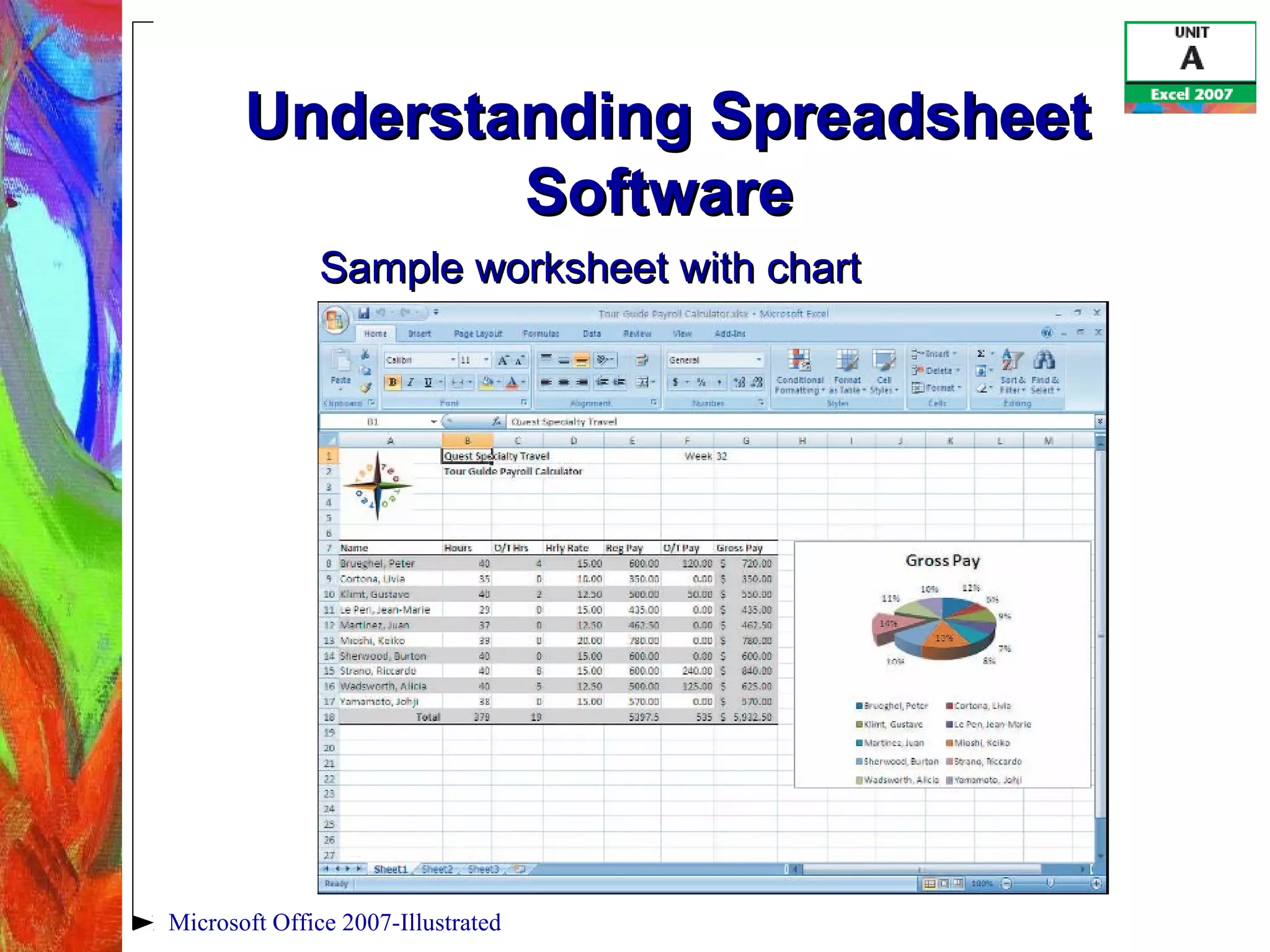
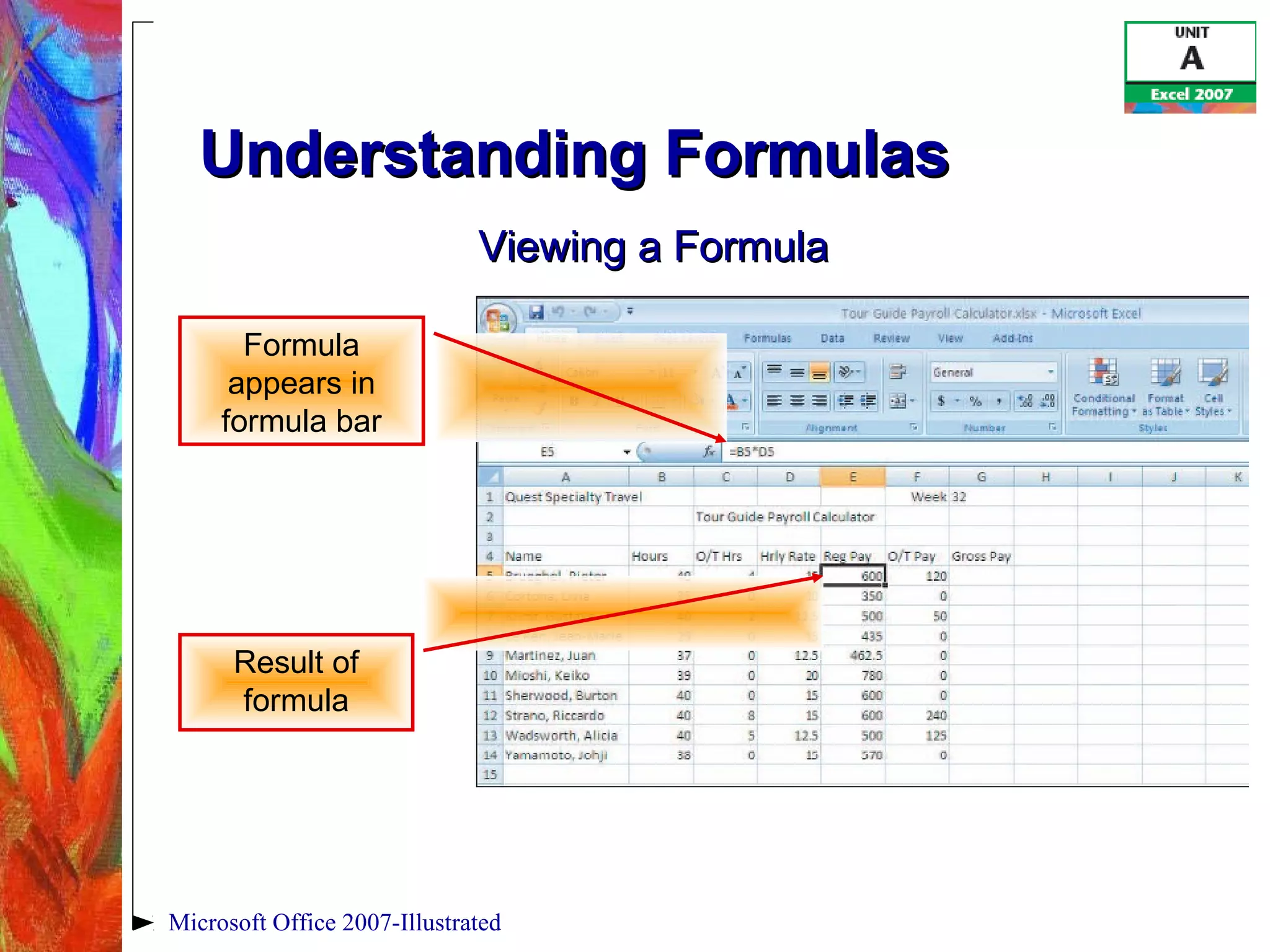
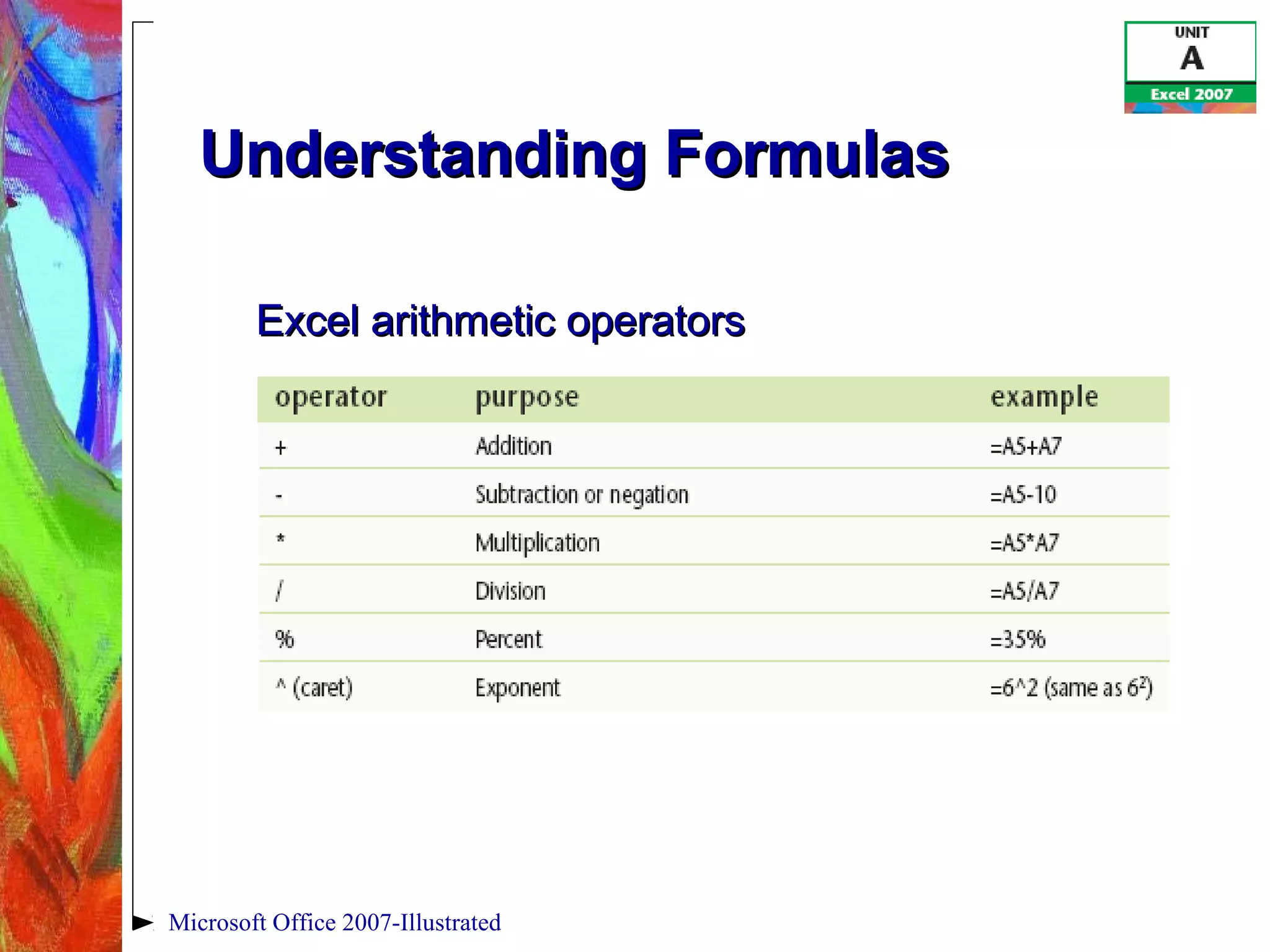
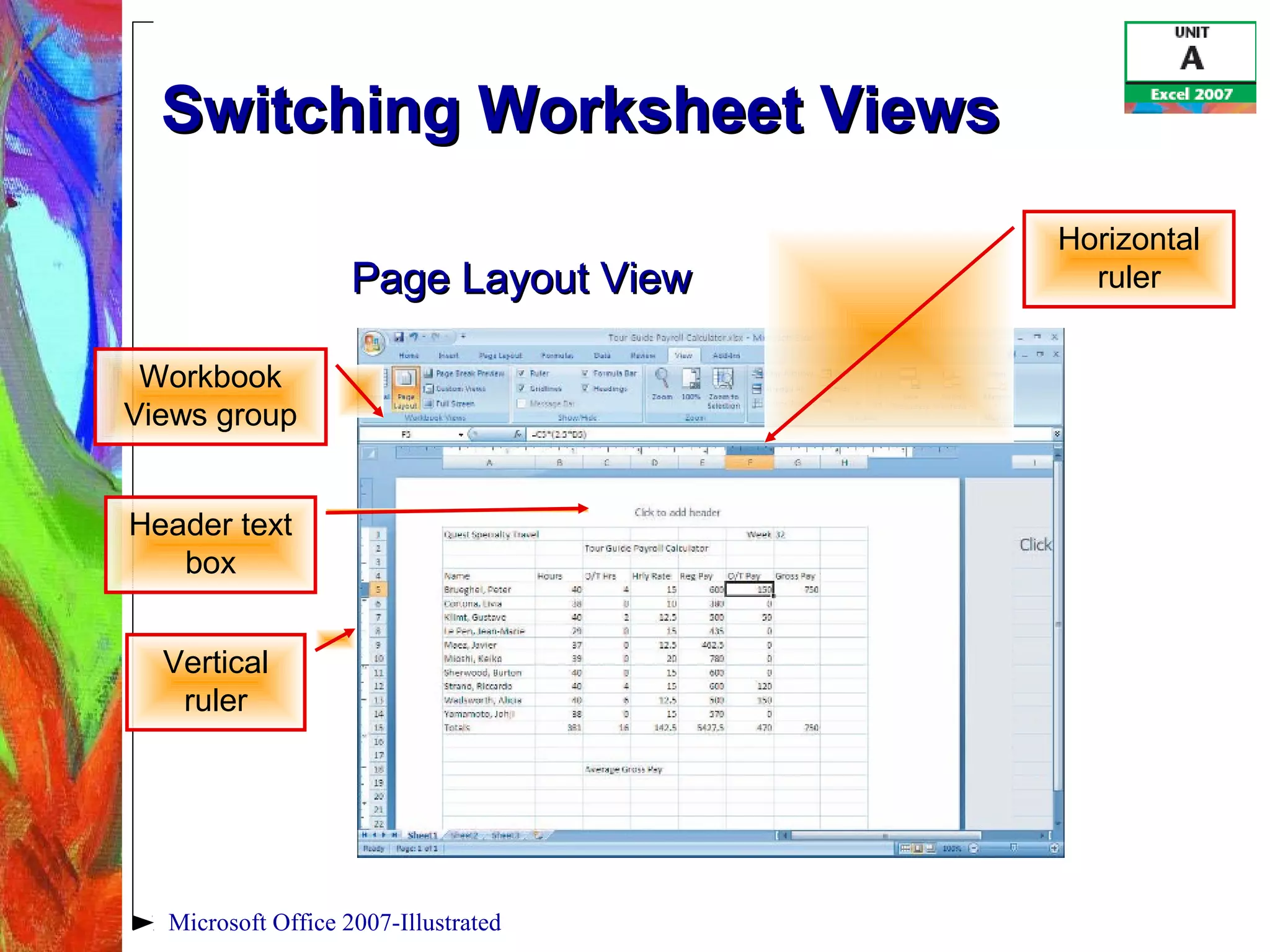
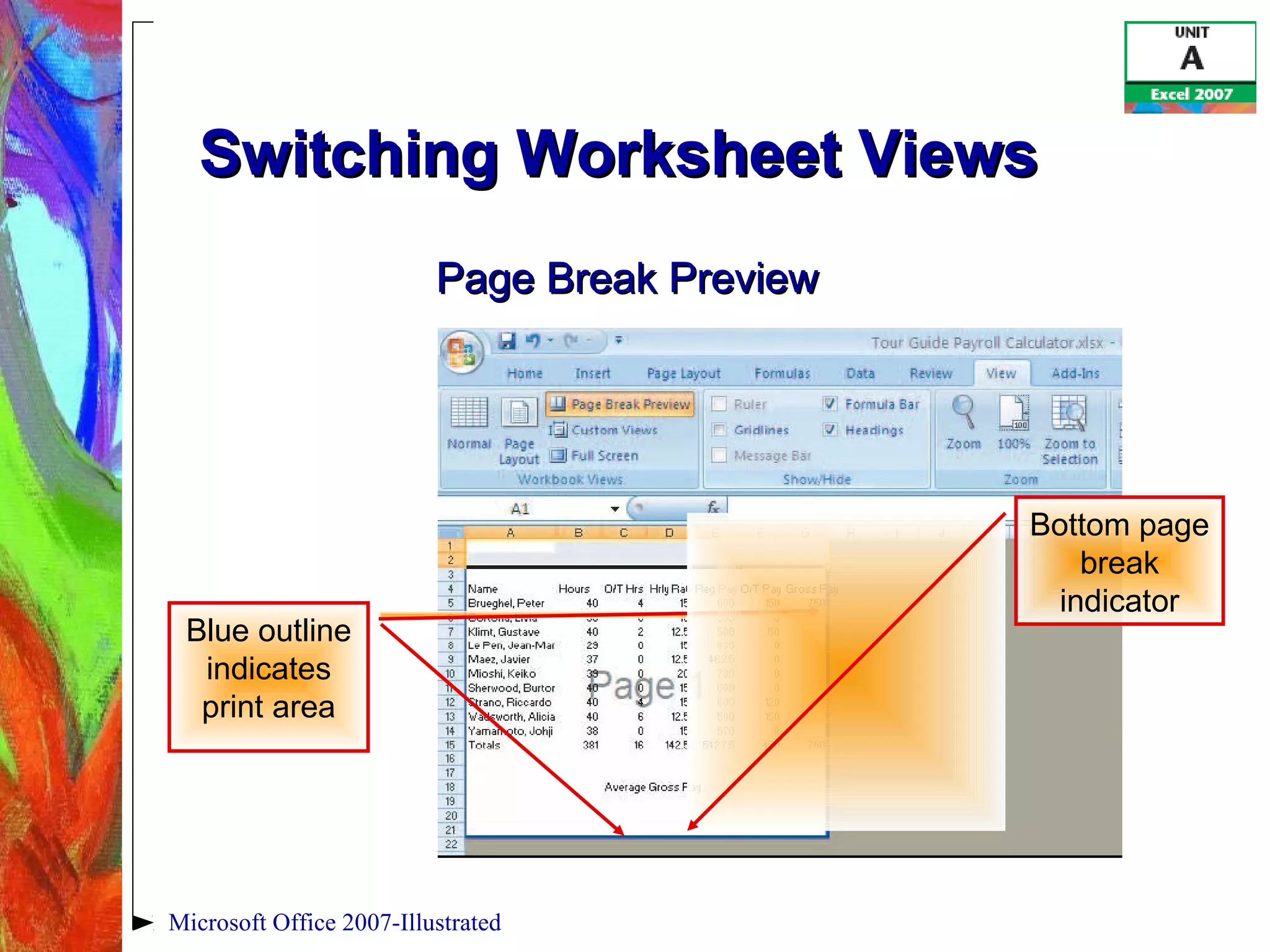
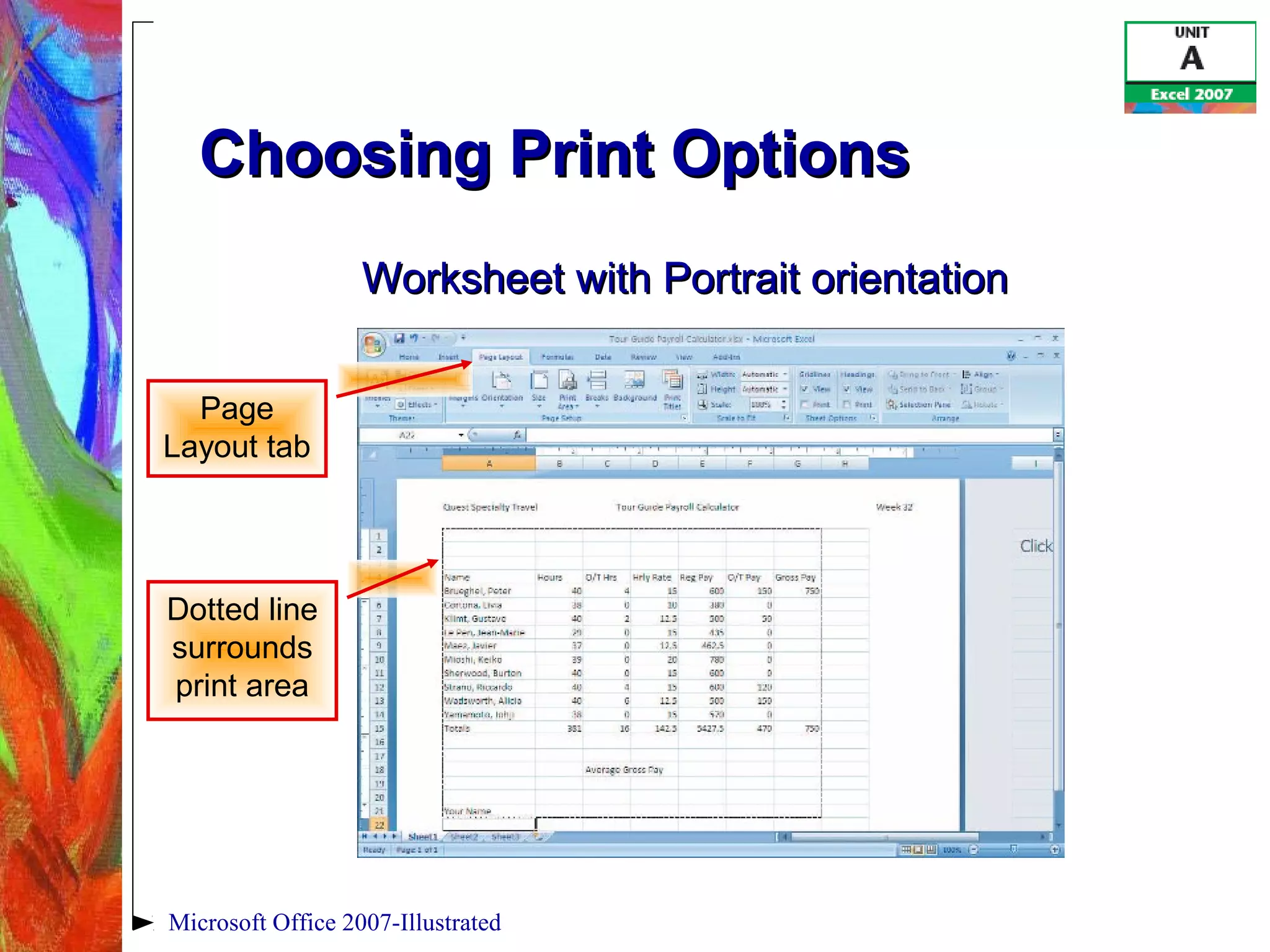
This document provides an overview of getting started with Excel 2007. It discusses understanding spreadsheet software and formulas, touring the Excel window, entering labels and values using AutoSum, editing cell entries, creating simple formulas, and switching between worksheet views. The objectives are to understand key Excel concepts like worksheets, cells, formulas and functions, and learn basic tasks like navigating the interface, entering data, and changing views.