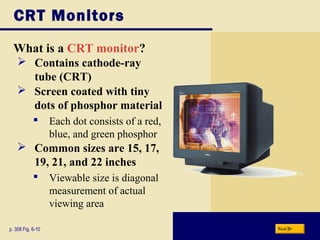
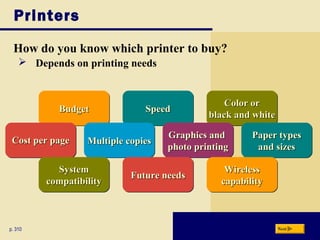
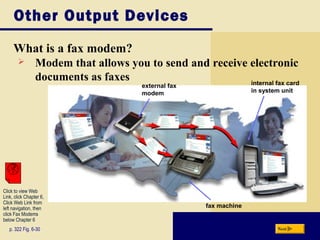
This document provides an overview of the key topics and objectives covered in Chapter 6 on output devices. It describes the four main categories of output as display devices, printers, speakers and audio output, and other devices. For display devices, it summarizes the characteristics of LCD monitors, LCD screens, plasma monitors, and CRT monitors. It also explains how graphics cards work with monitors. For printers, it differentiates between non-impact and impact printers and summarizes the characteristics and uses of various printer types including inkjet, photo, laser, thermal, and mobile printers. It also describes speakers, headphones, and voice output, as well as other devices like fax machines.