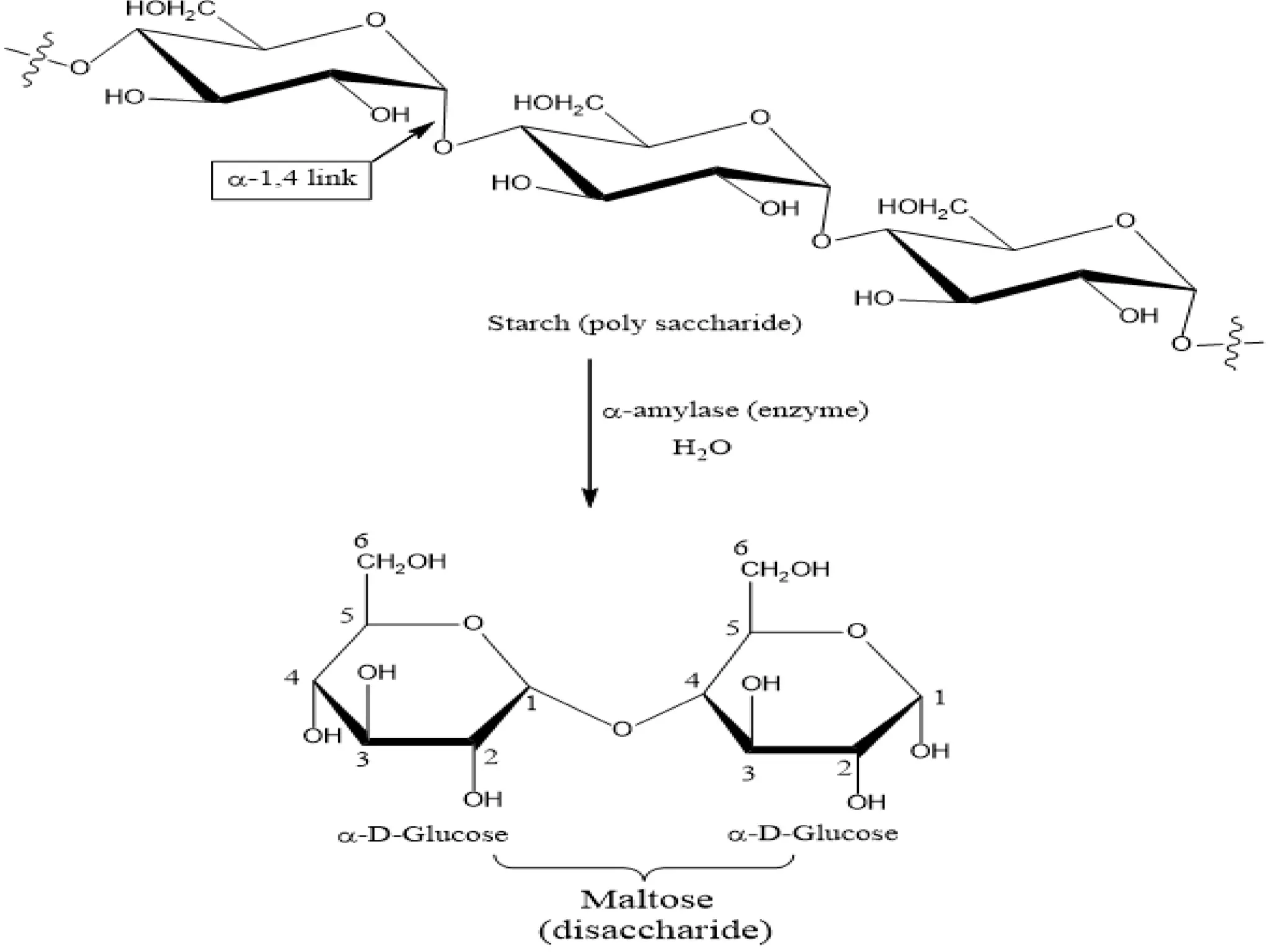
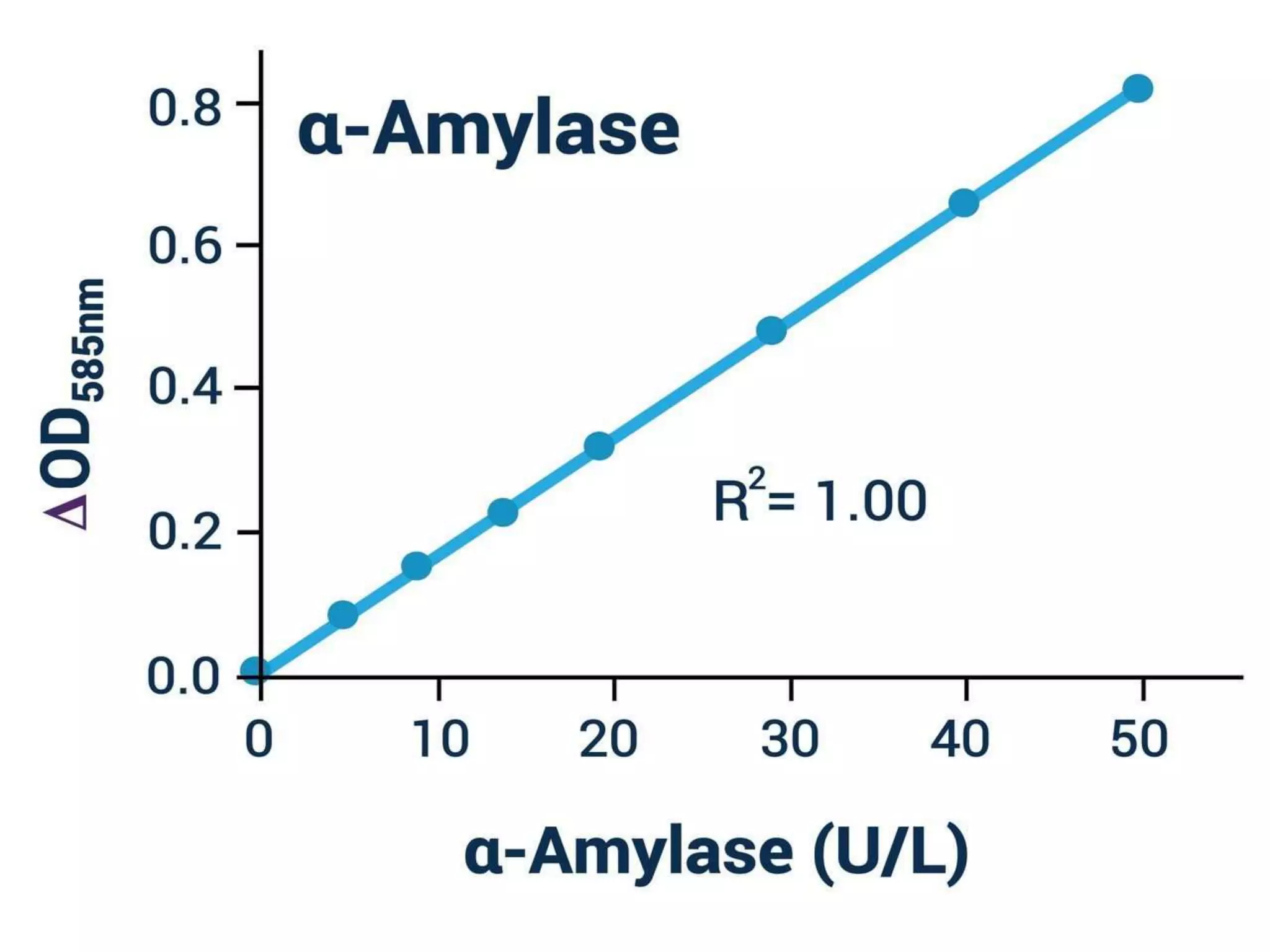
The document describes a procedure to estimate the activity of amylases in food by measuring the hydrolysis of starch into maltose sugars. It outlines the materials required, including various reagents and solutions, and details the extraction and estimation process involving enzyme extracts from germinated seeds. Additionally, it includes definitions and concepts related to enzymes and amylases, as well as the factors affecting enzyme activity.