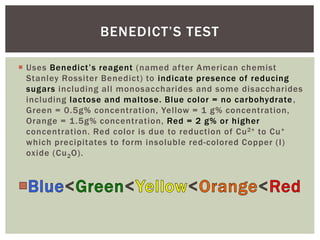
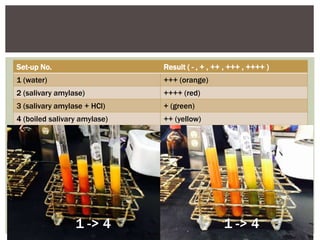
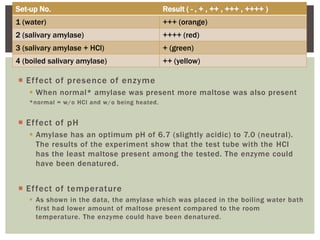
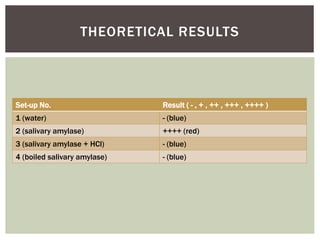
This lab document summarizes an experiment using Benedict's test to analyze the effects of enzymes, pH, and temperature on carbohydrate digestion. Benedict's test uses a color indicator to detect the presence of reducing sugars. The experiment used salivary amylase and starch solutions with variations in pH, temperature, and enzyme presence. The results showed that normal amylase produced the most reducing sugars, acid pH and boiling reduced amylase activity, indicating enzyme function is dependent on environmental conditions.