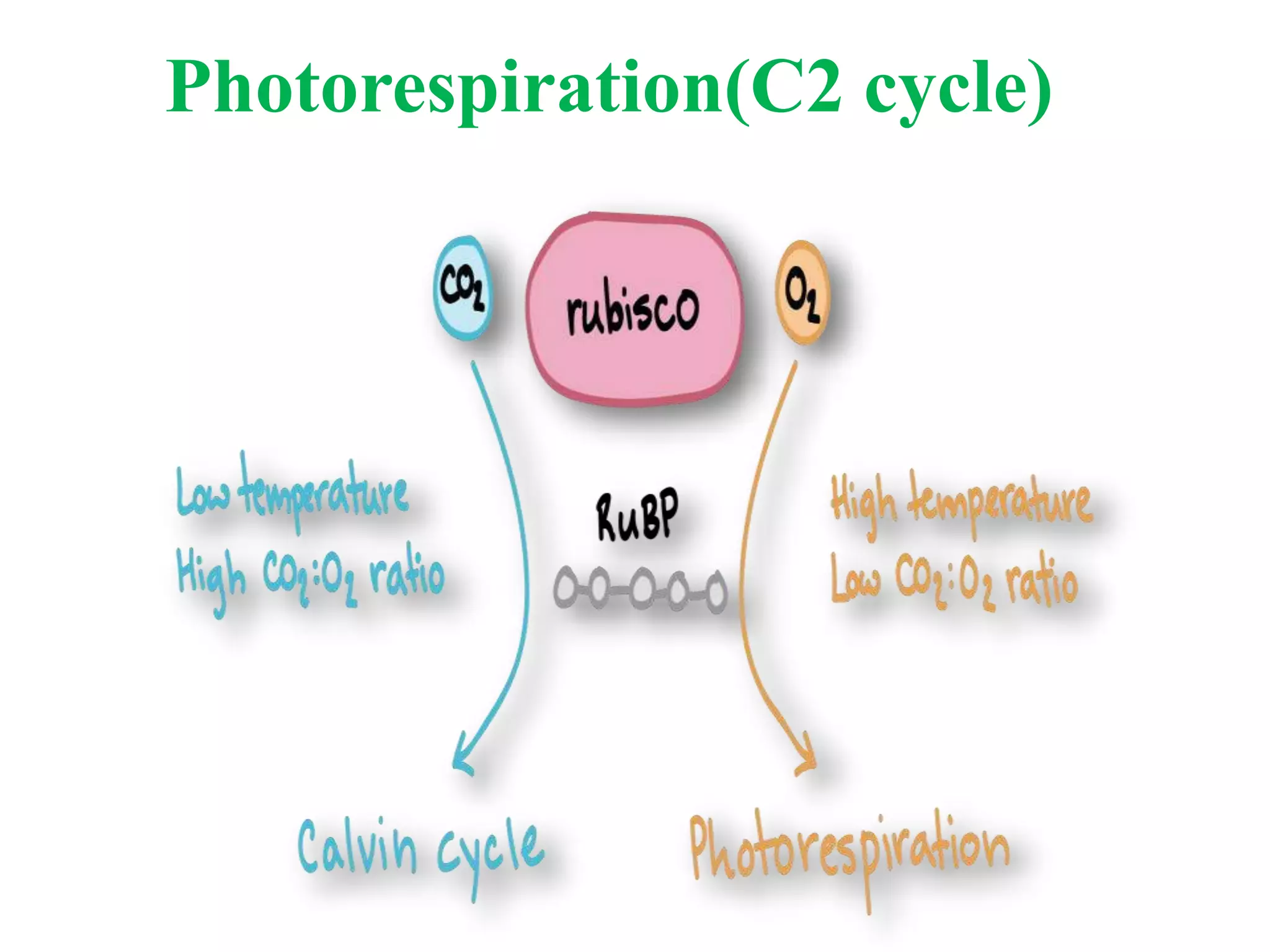
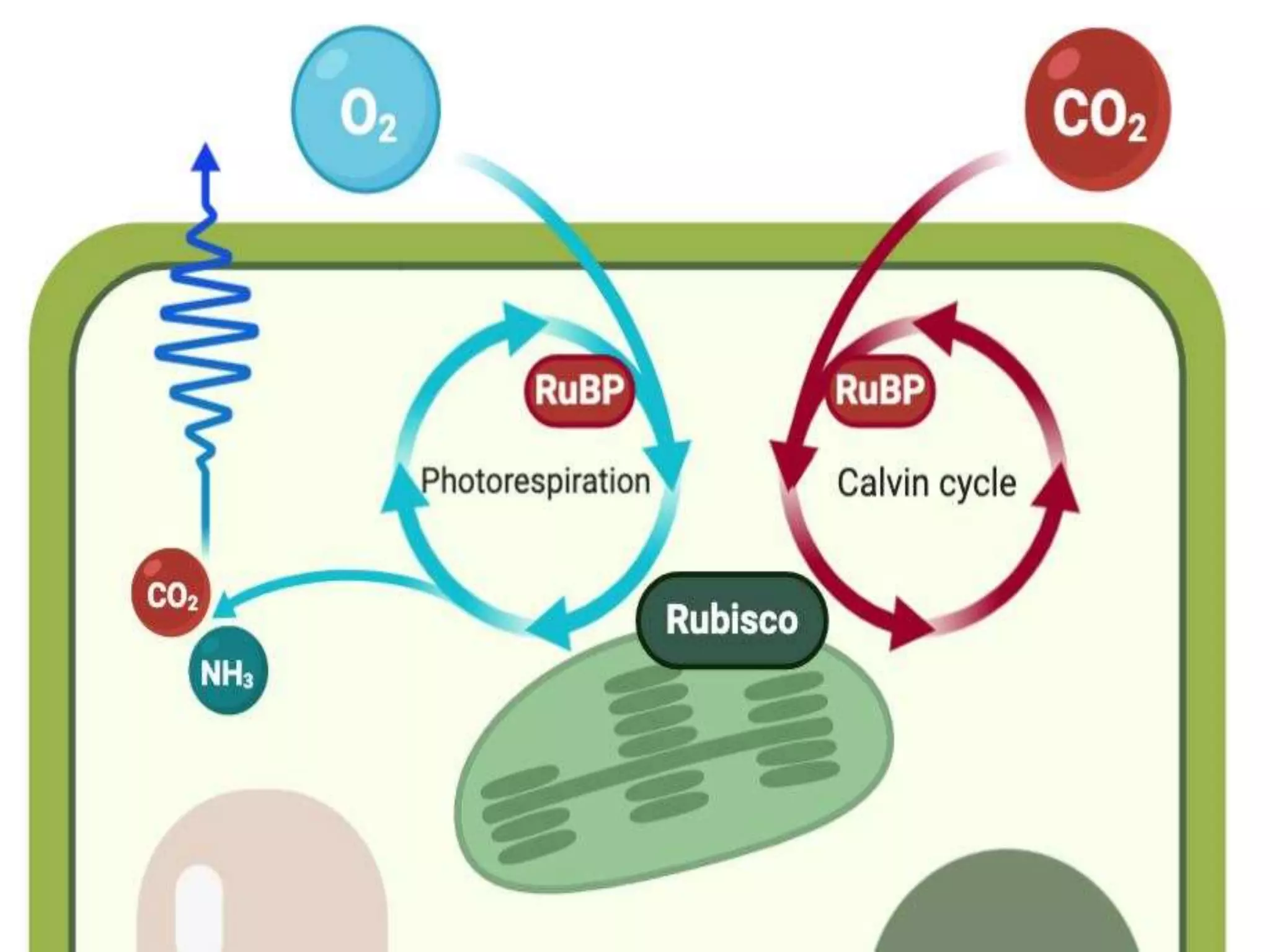
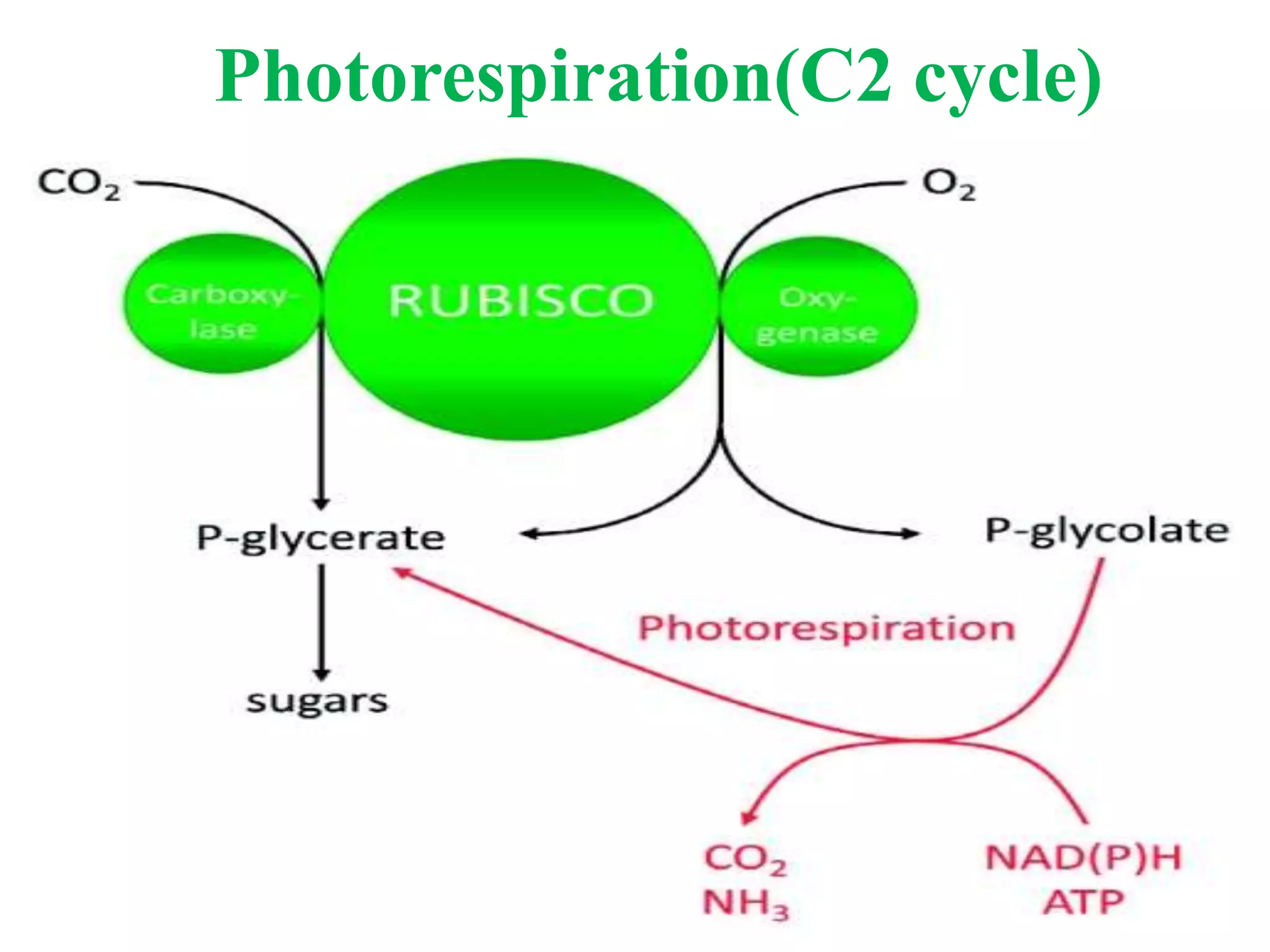
Photorespiration is a metabolic pathway in photosynthetic organisms that consumes oxygen and releases carbon dioxide without generating energy or food, limiting plant growth. The process occurs primarily on hot, dry days when oxygen levels are high, disrupting normal photosynthesis involving the enzyme rubisco. Despite its drawbacks, photorespiration can provide some benefits, such as photoprotection and maintenance of cellular redox balance.