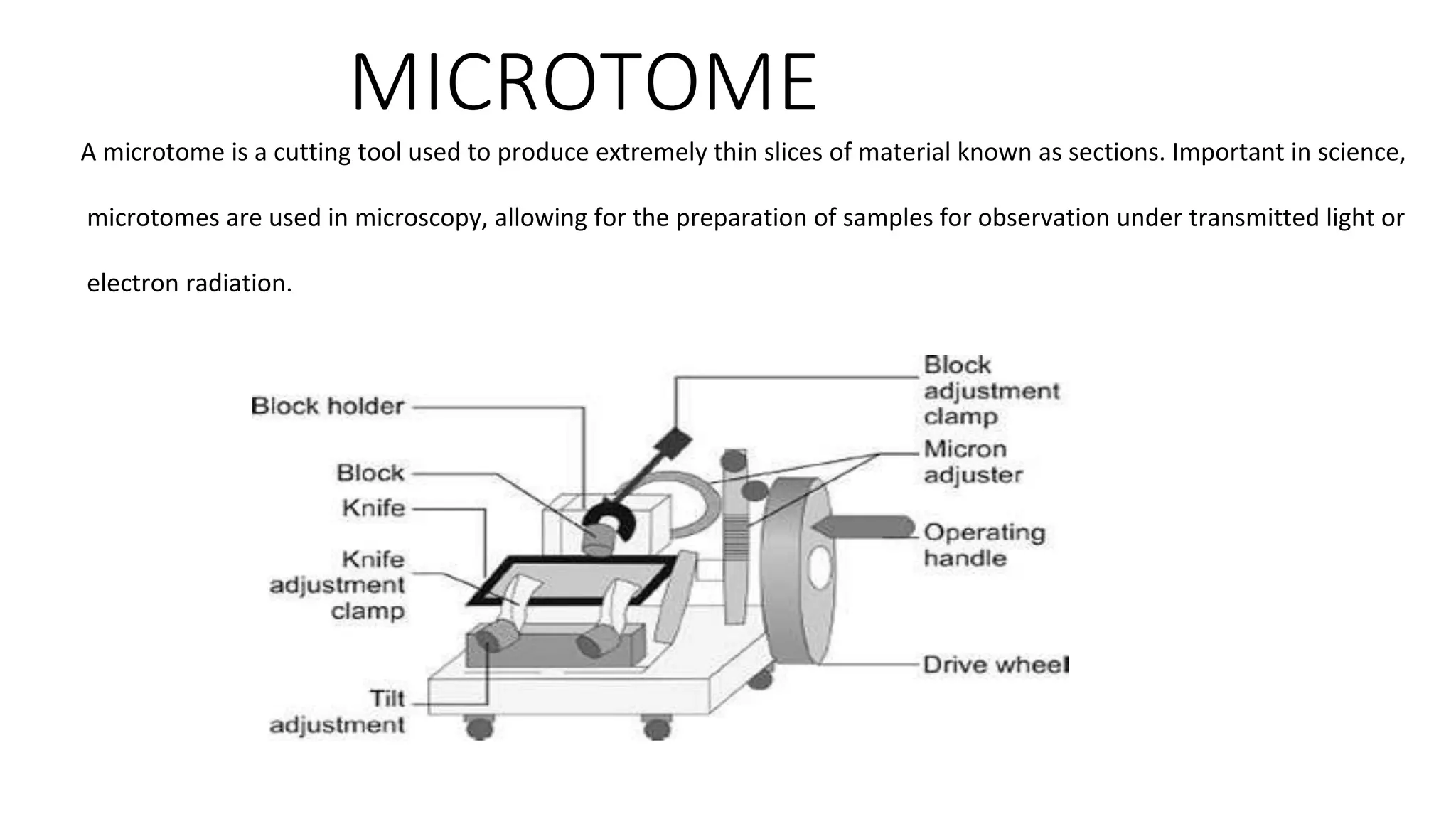
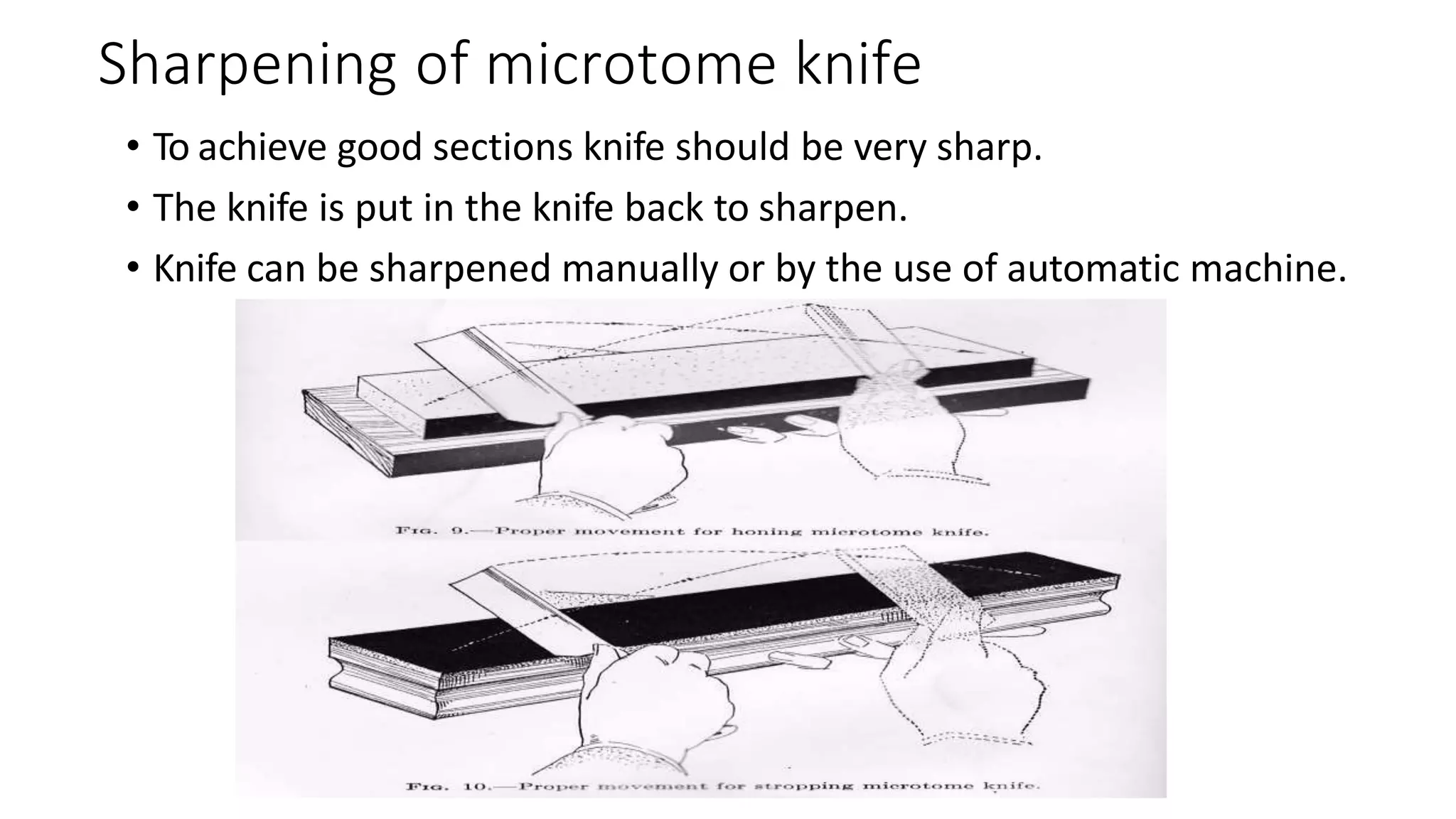
A microtome is a tool used to cut extremely thin slices of materials for examination under microscopes. It consists of a base, knife attachment, and tissue holder. Various types exist for different applications, such as rotary microtomes for histology and ultramicrotomes for electron microscopy. Proper sharpening and maintenance of the microtome knife is important for obtaining high quality slices.