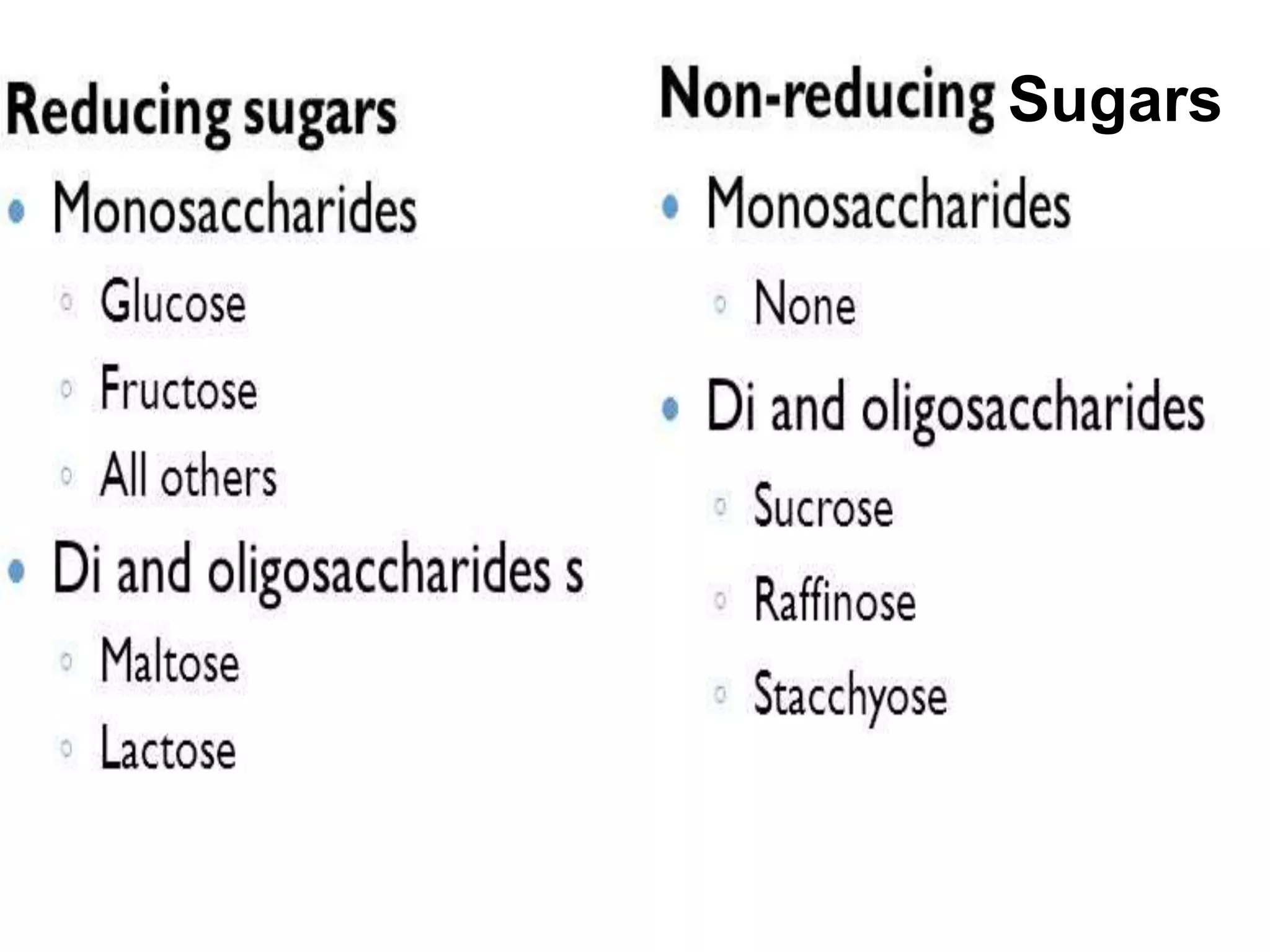
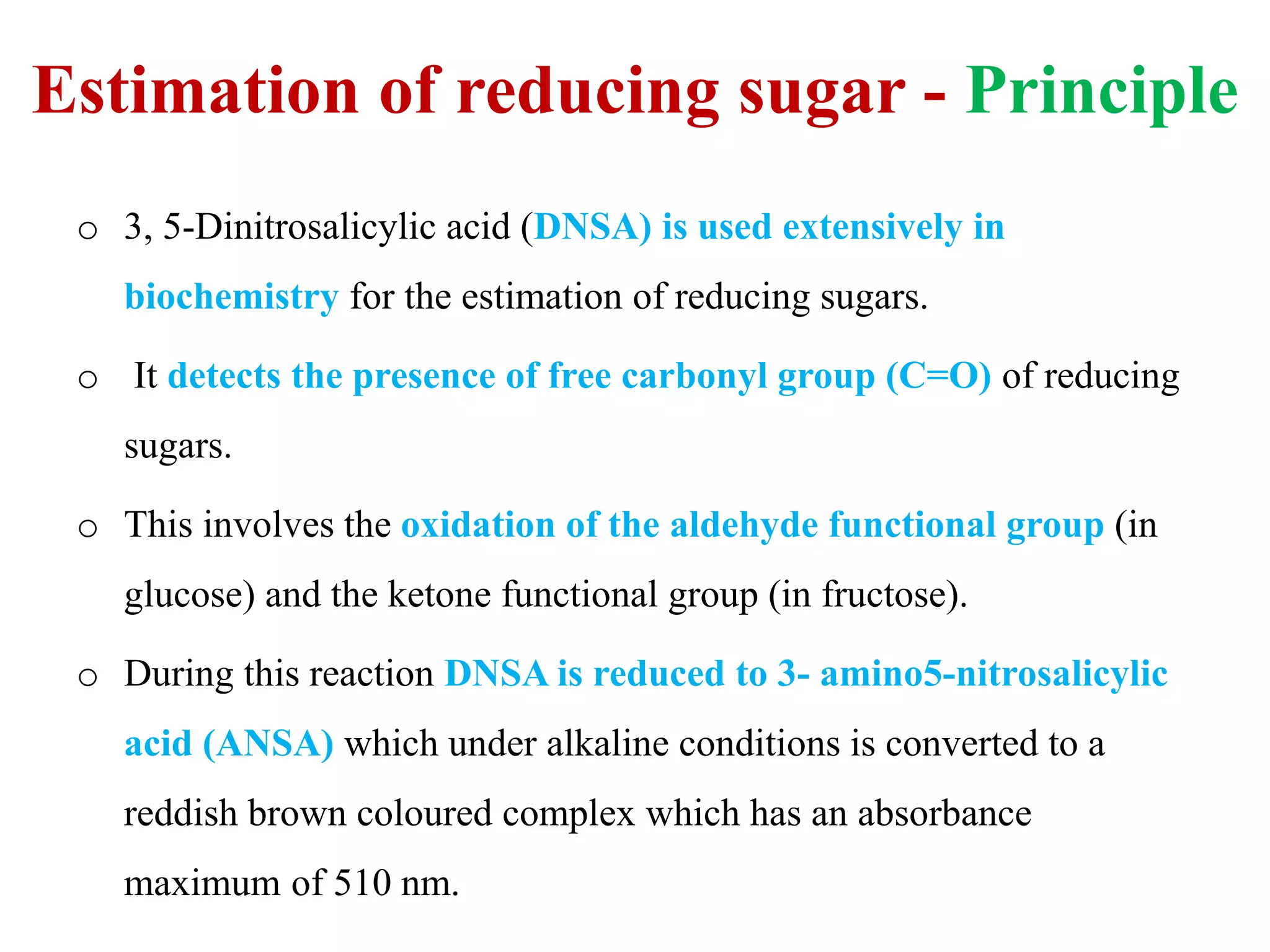
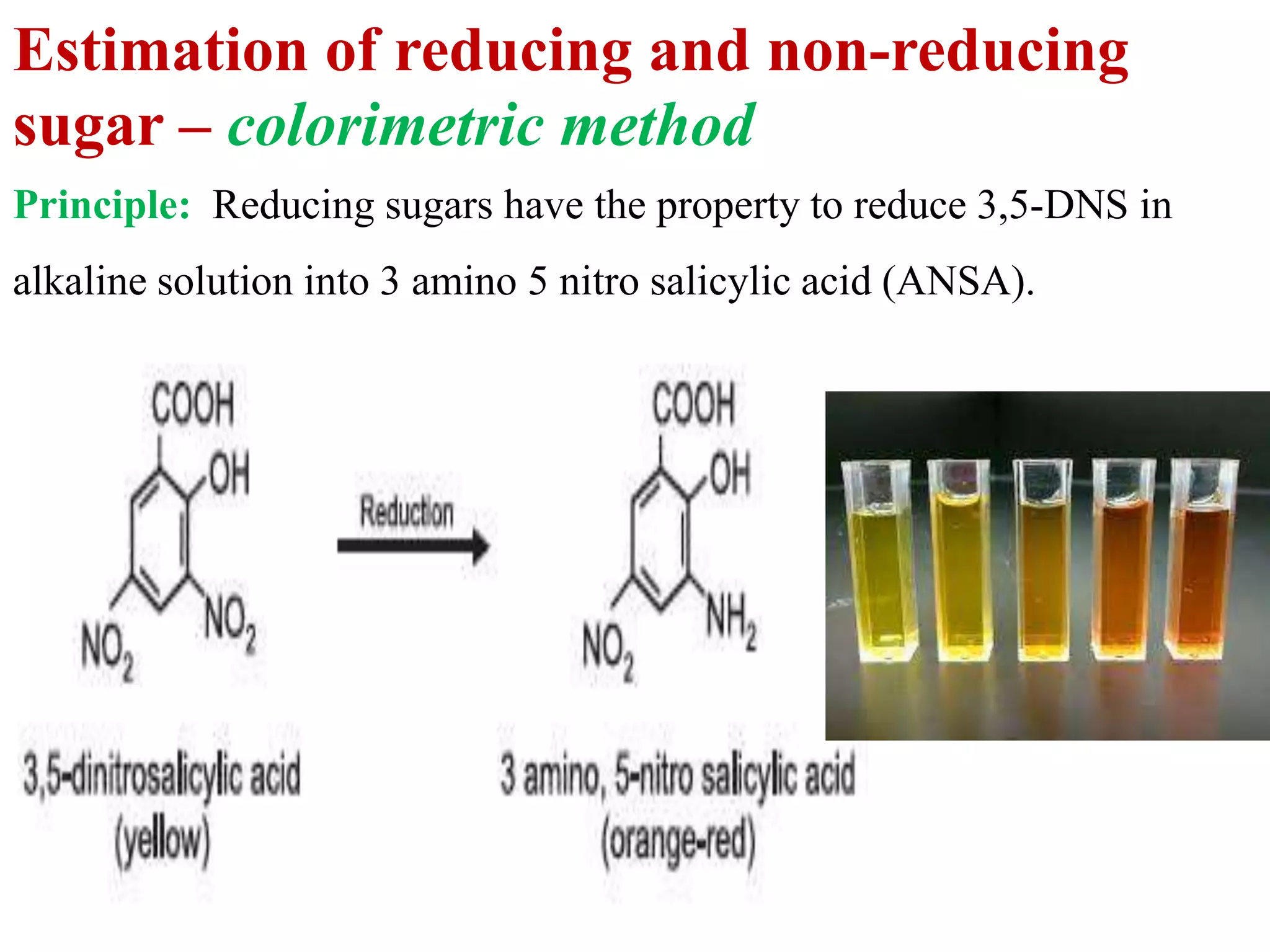
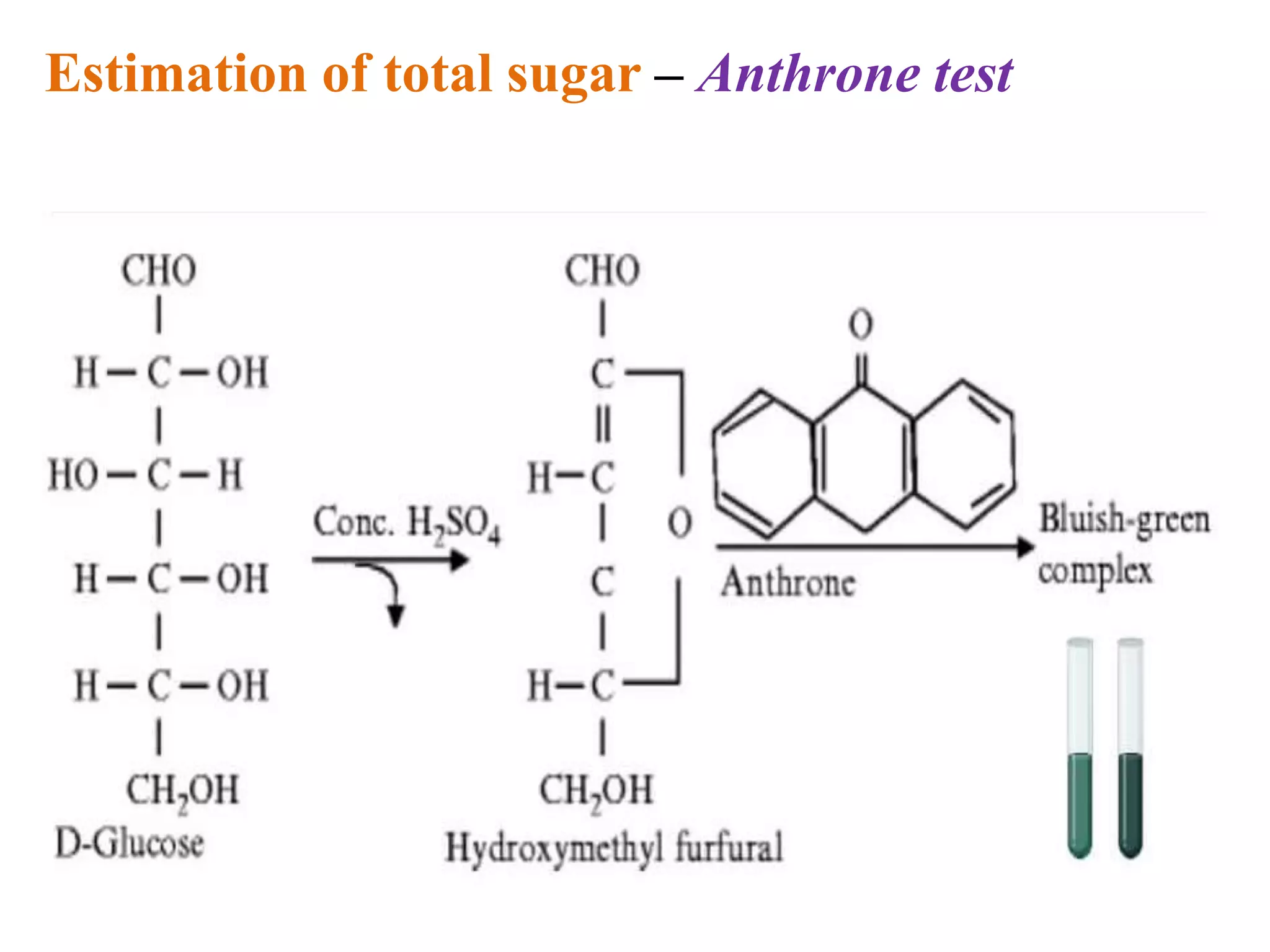
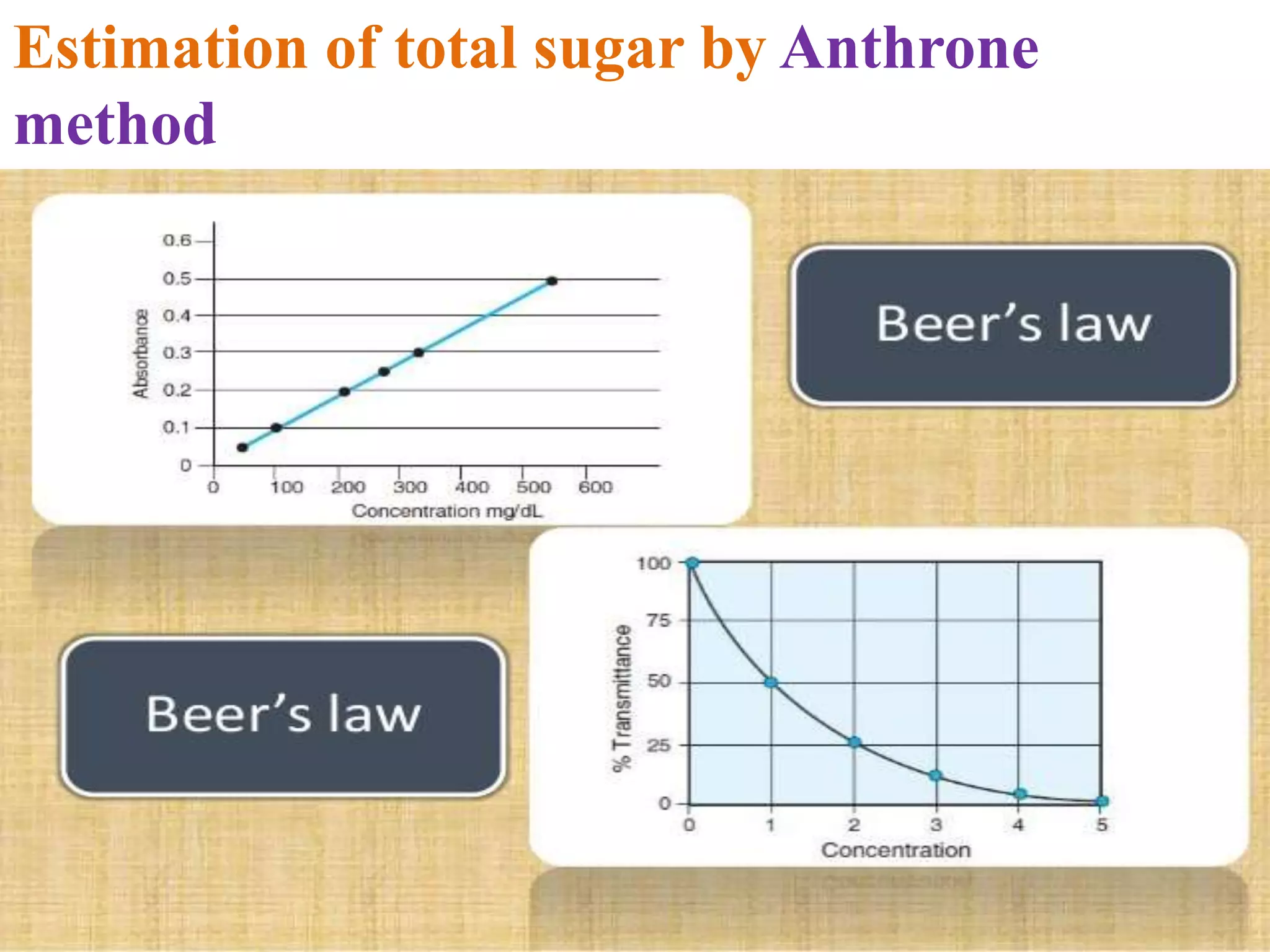
The document describes methods for estimating reducing and non-reducing sugars, including the colorimetric method using dinitrosalicylic acid (DNSA) and the anthrone method for total sugars. It details the principles, reagents, procedures, and calculations for both methods. Non-reducing sugars are determined by subtracting estimated reducing sugars from total sugars.