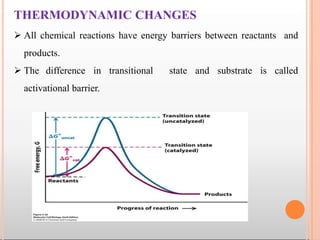
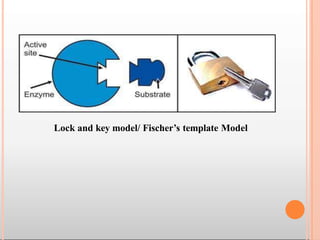
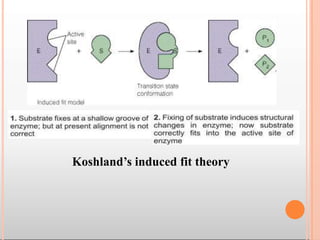
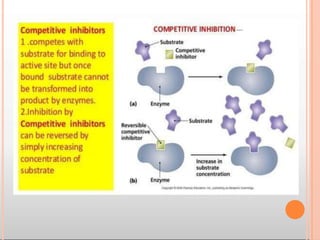
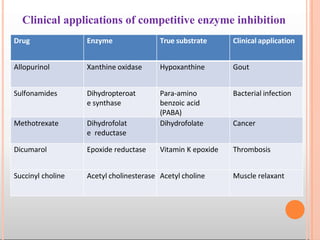
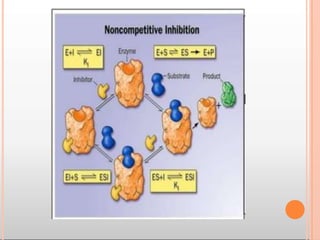
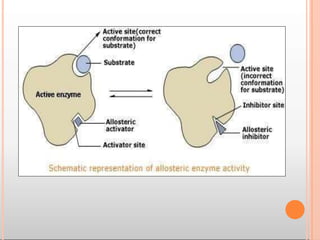
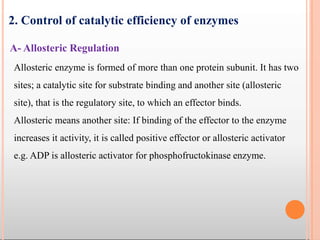
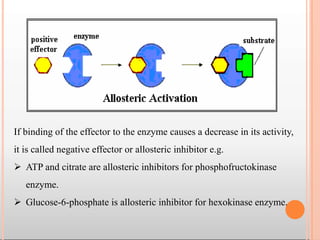
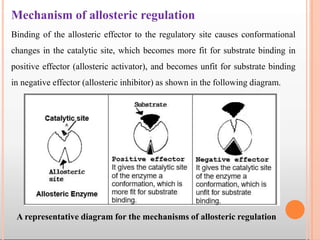
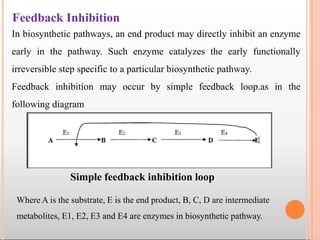
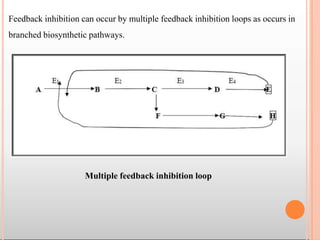
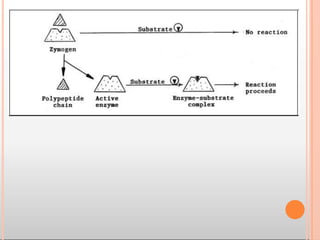
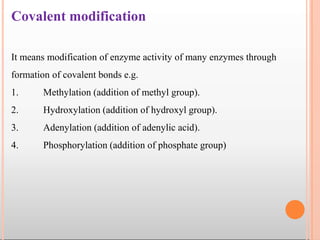
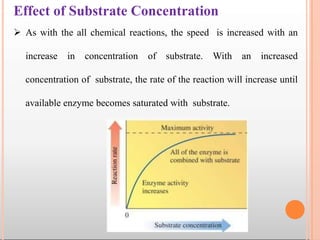
Enzymes are biological catalysts that are usually proteins and speed up biochemical reactions. They work by lowering the activation energy of reactions. Enzymes are very specific and only catalyze one type of reaction. The active site of an enzyme binds to specific substrates. Enzyme activity is affected by factors like pH, temperature, and substrate/product concentration. There are two main models for enzyme activity - the lock and key model suggests a rigid enzyme structure that substrates fit into, while the induced fit model suggests substrates cause enzyme structures to change shape for binding. Enzymes can be inhibited competitively by substrates that resemble their real substrates or non-competitively by other molecules.






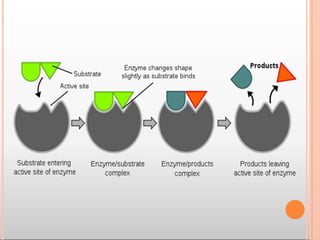











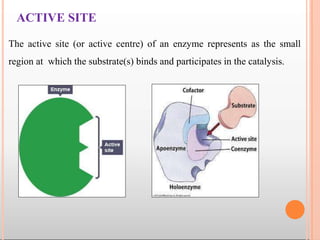

![ The coenzymes or cofactors on which some enzymes depend are
present as a part of the catalytic site.
The substrate(s) binds at the active site by weak noncovalent bonds.
Enzymes are specific in their function due to the existence of active
sites.
The commonly found amino acids at the active sites are serine,
histidine etc. Among these amino acids, serine is the most frequently
found.
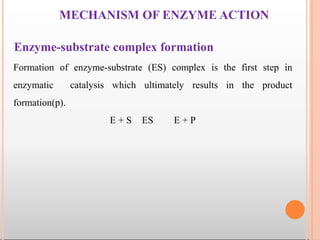
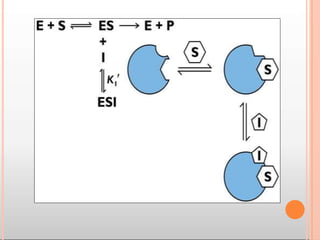
The substrate [S] binds with the enzyme (E) at the active site to form
enzyme- substrate complex(ES). The product (P) is released after the
catalysis and the enzyme is available for reuse.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mainppt-enzymes-230209044452-e33f7306/85/MAIN-PPT-ENZYMES-pptx-30-320.jpg)