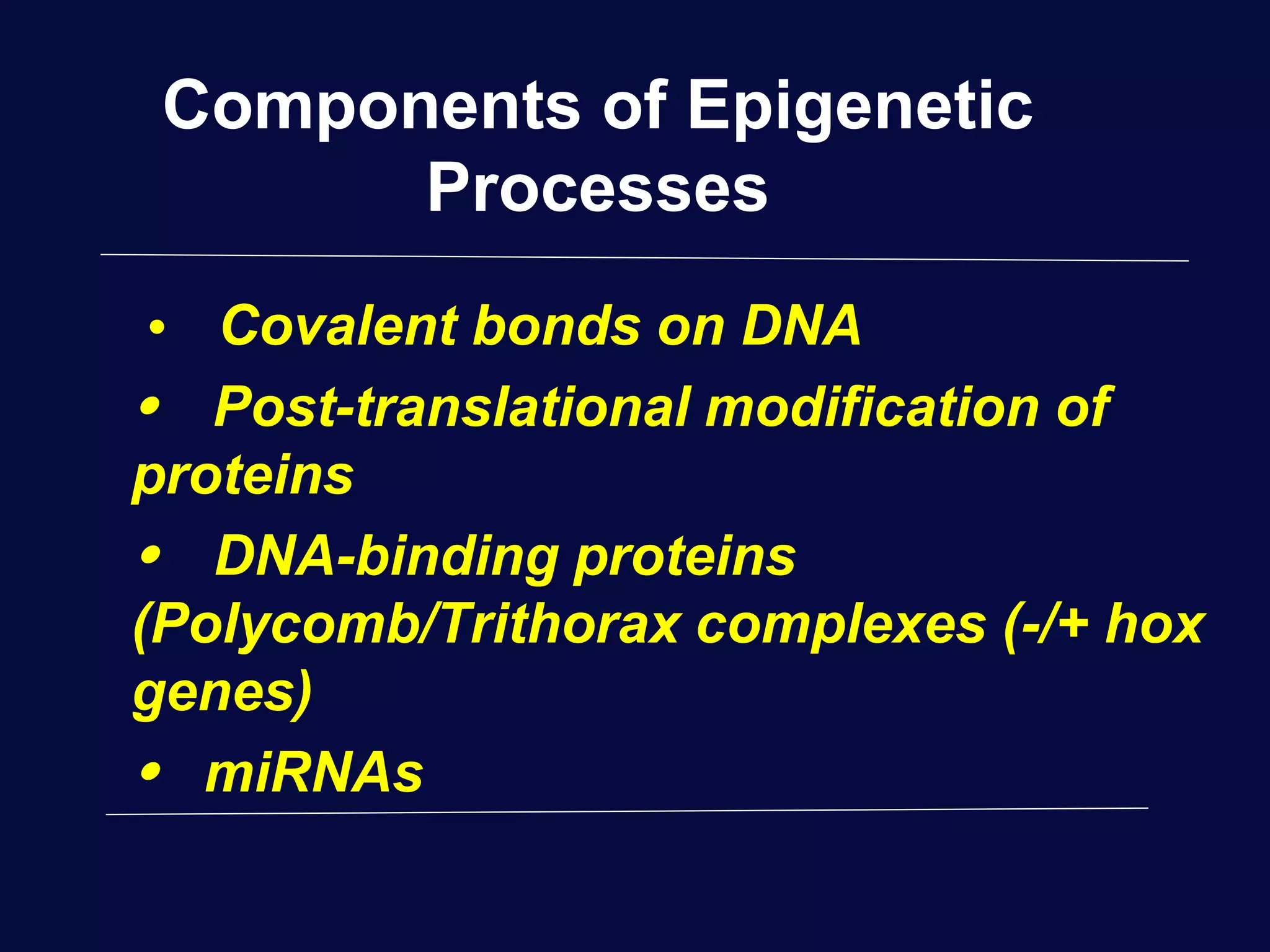
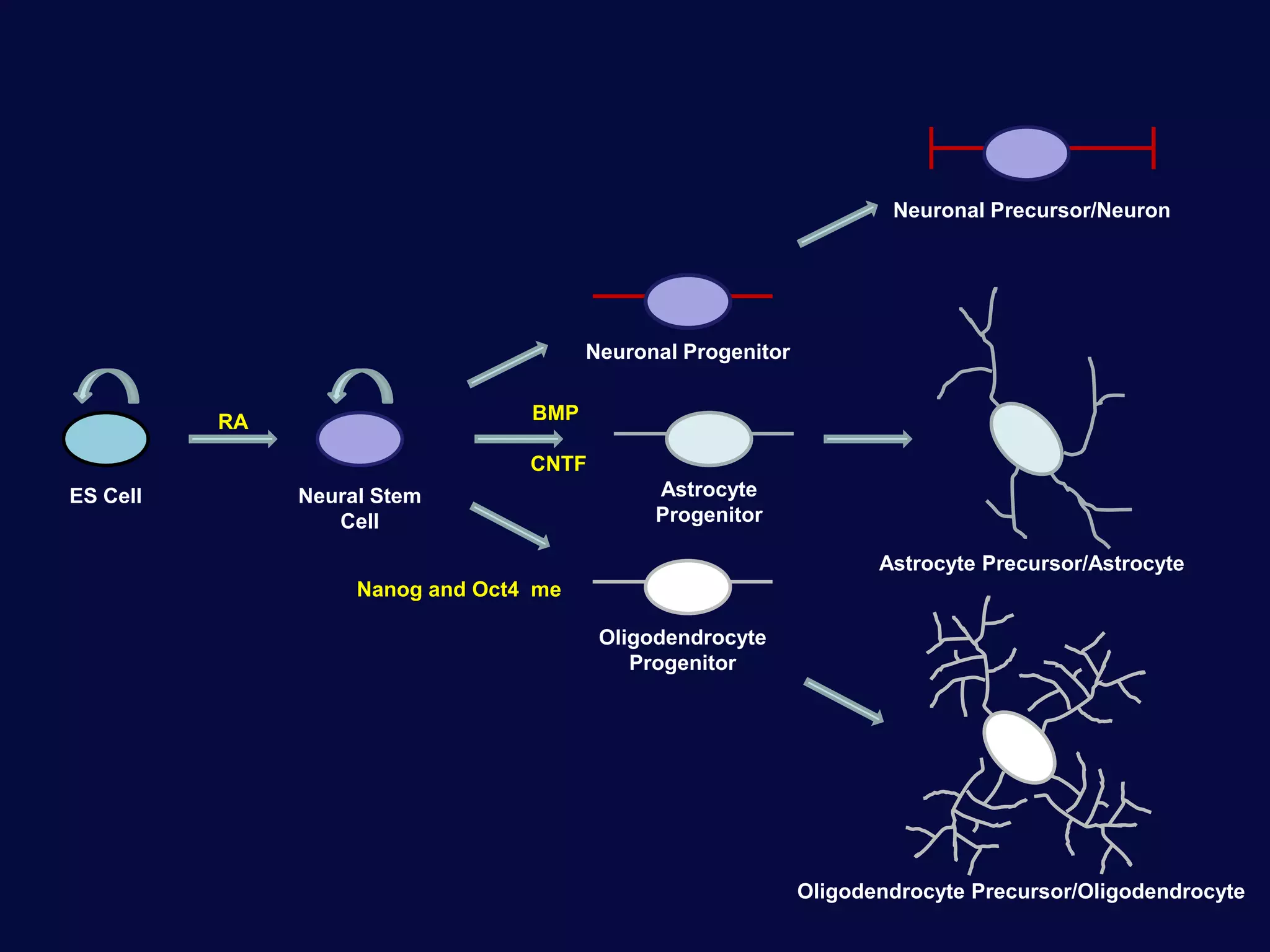
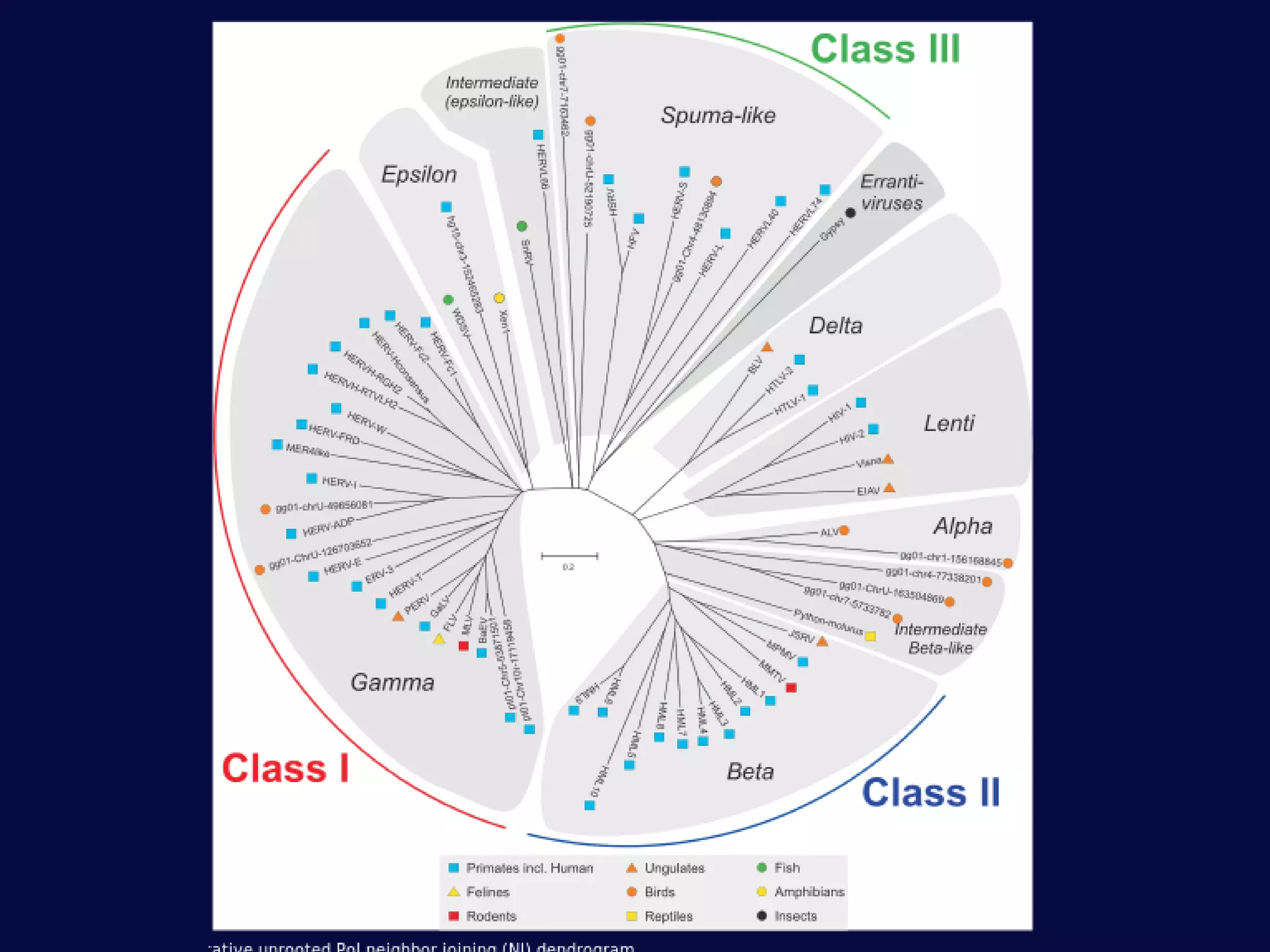
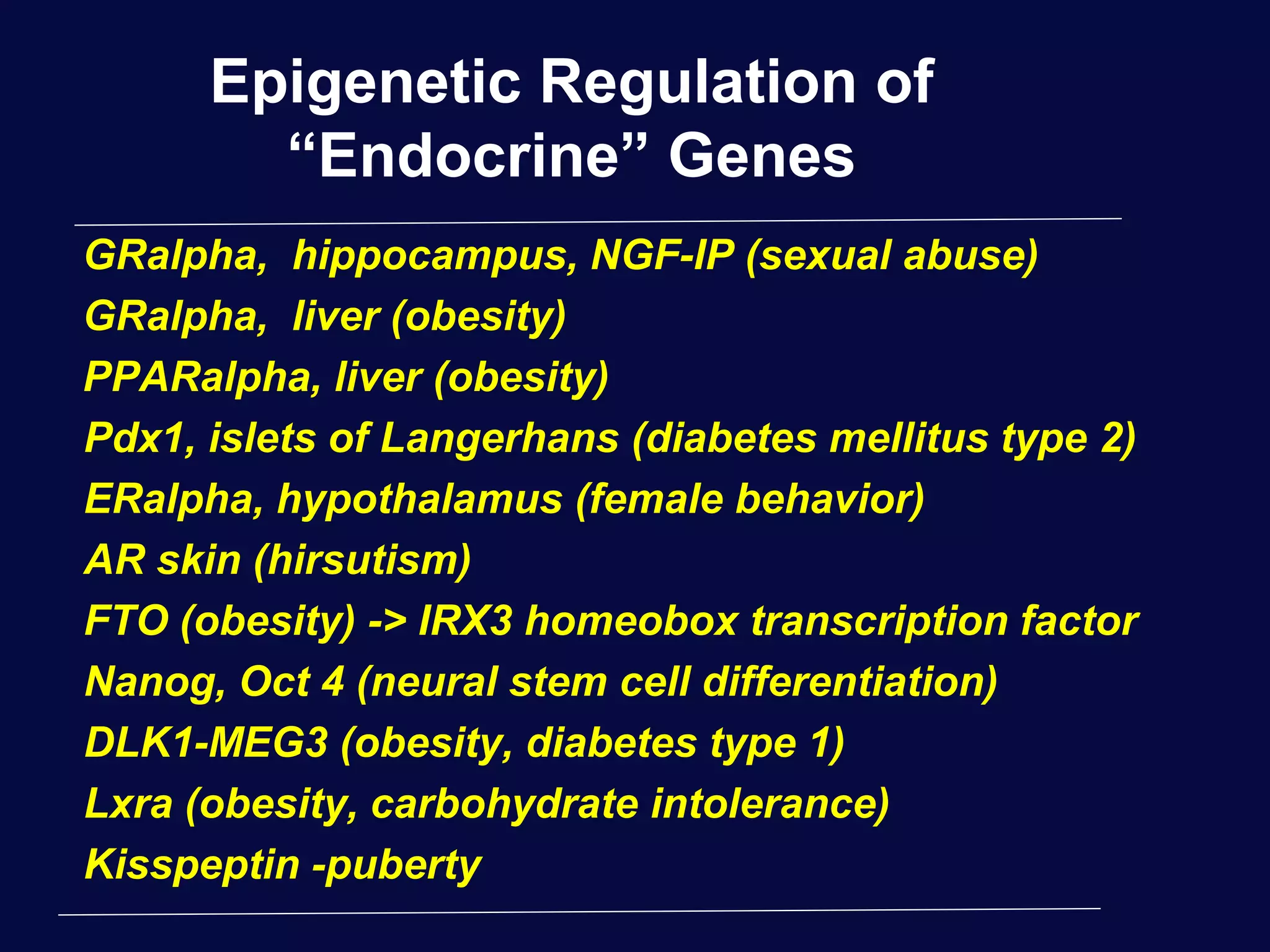
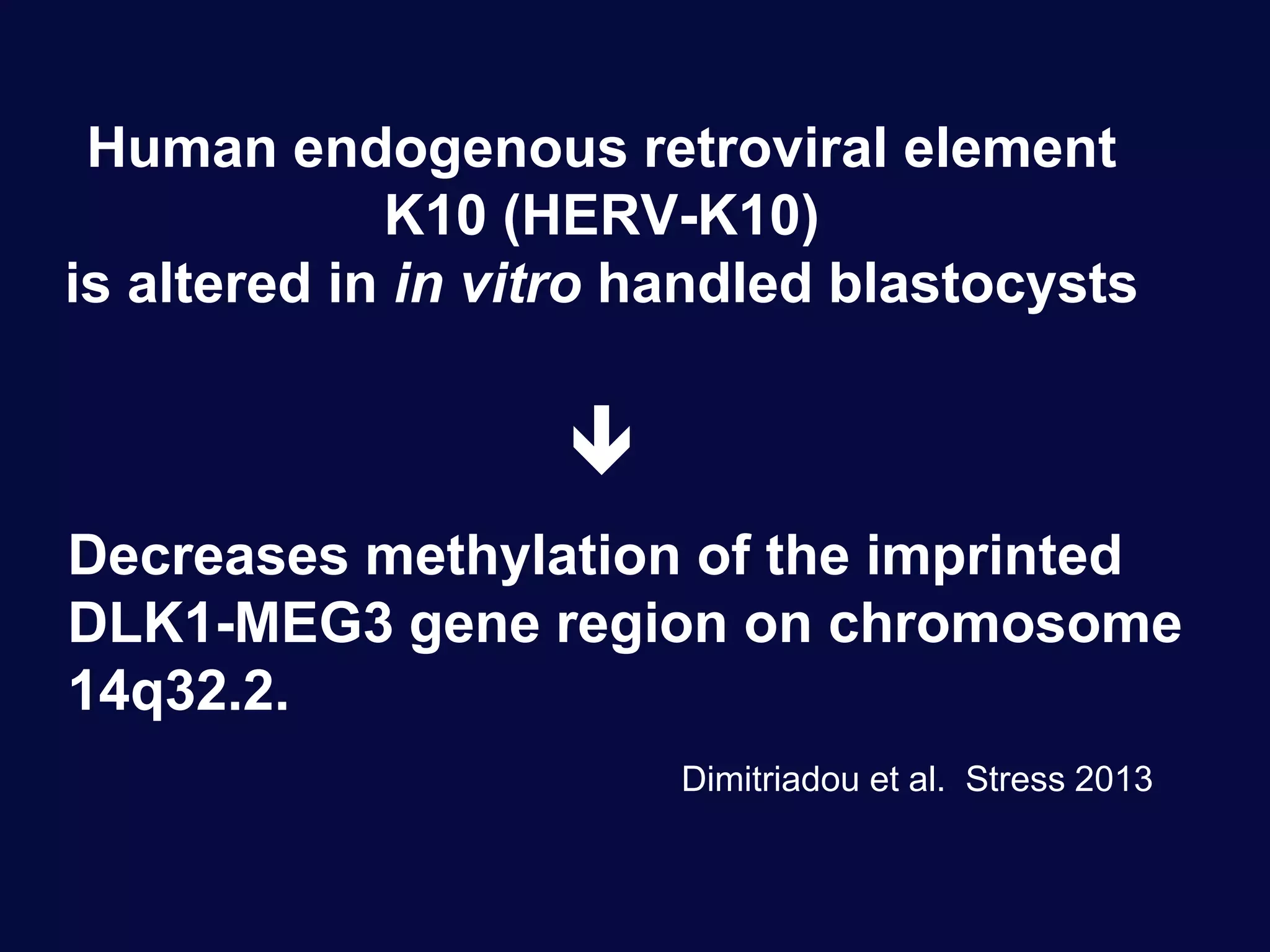
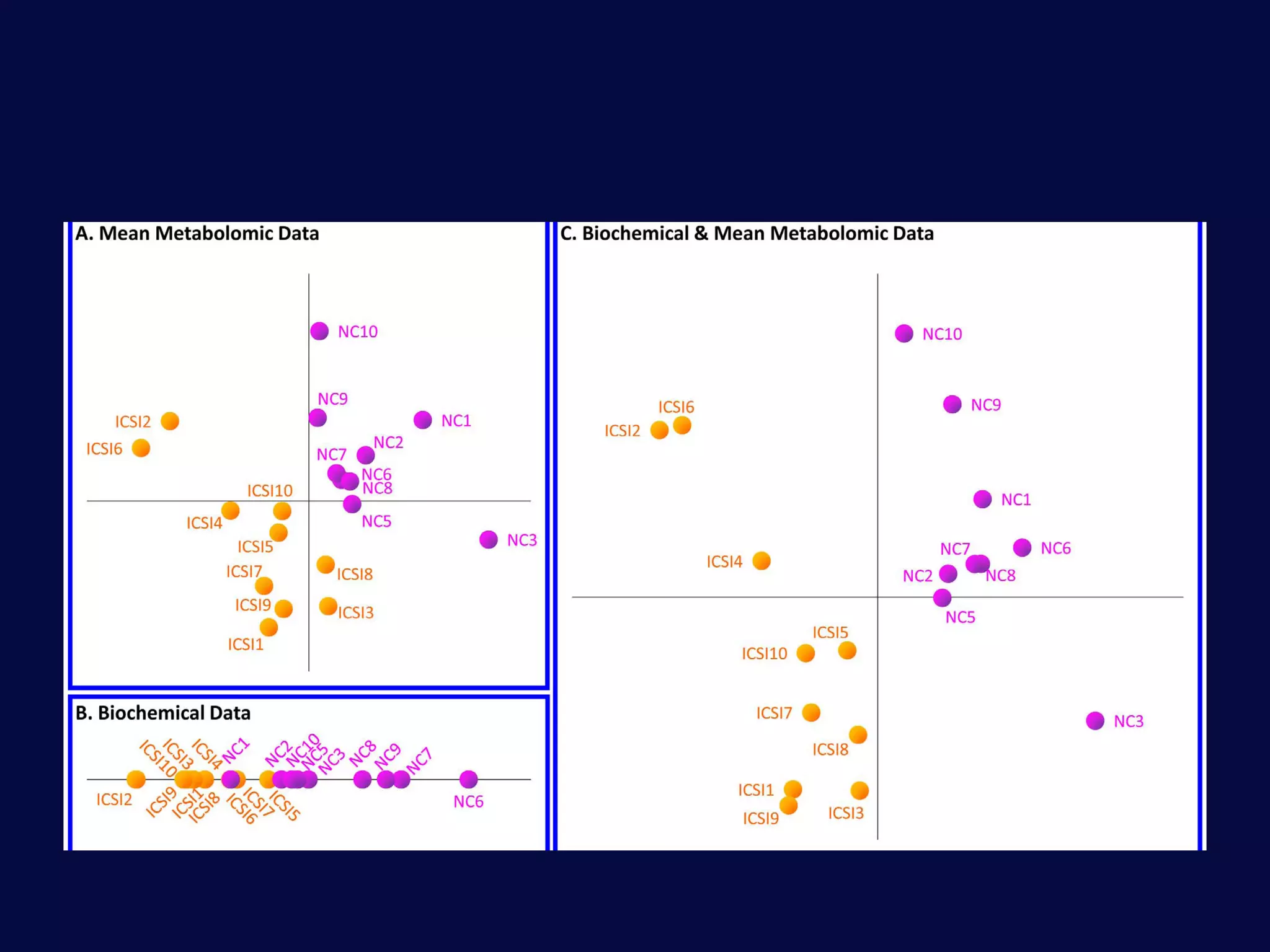
This document discusses epigenetics and its role in early childhood development. It explores how genetics and epigenetics interact, with genetics providing the blueprint and epigenetics influencing how genes are expressed. Environmental stressors during development can trigger epigenetic changes that affect phenotypic outcomes. The role of epigenetics in processes like cell differentiation, genomic imprinting, and retrotransposon repression is also reviewed.