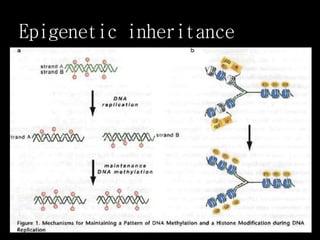
Epigenetics is the study of mechanisms that control which genes are switched on or off. It involves epigenetic mechanisms like methylation and histone modification that manipulate the genome without changing the DNA sequence. Experiments show that exposures like chemicals, smoking, diet, and stress during pregnancy can cause epigenetic changes that affect gene expression and traits in subsequent generations. A study in Sweden found that poor harvests and malnutrition during pregnancy were associated with higher risk of cardiovascular disease in offspring, and periods of feast after famine extended this risk to grandchildren through epigenetic inheritance. Understanding epigenetics is important for studying evolution and treating diseases like cancer, genetic disorders, immunity and neuropsychiatric conditions.