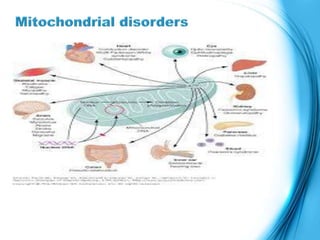
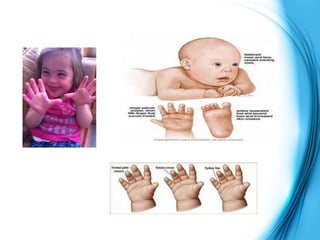
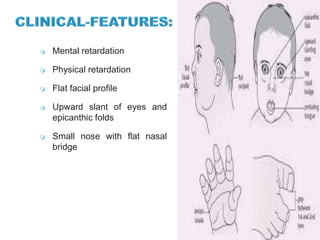
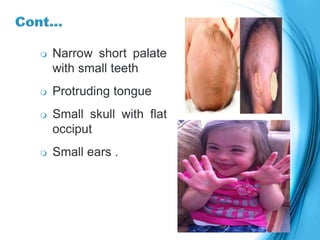
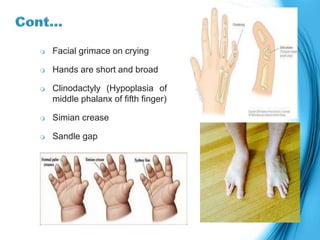
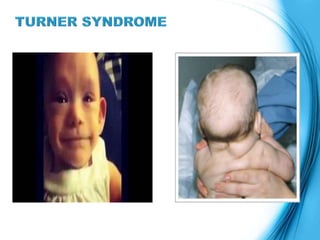
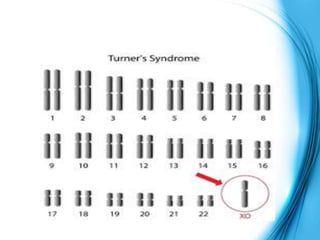
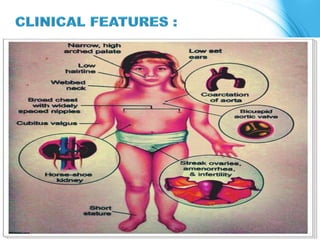
This document discusses the inheritance of common pediatric genetic disorders. It describes five types of genetic disorders: chromosomal disorders, single gene disorders, polygenic disorders, mitochondrial disorders, and somatic cell disorders. Two specific chromosomal disorders are discussed in detail: Down syndrome and Turner syndrome. Down syndrome is caused by trisomy 21 and is characterized by physical and mental retardation. Turner syndrome is caused by a missing or structurally abnormal X chromosome in females and can cause short stature and infertility. Both require lifelong medical care and treatment of associated health issues.