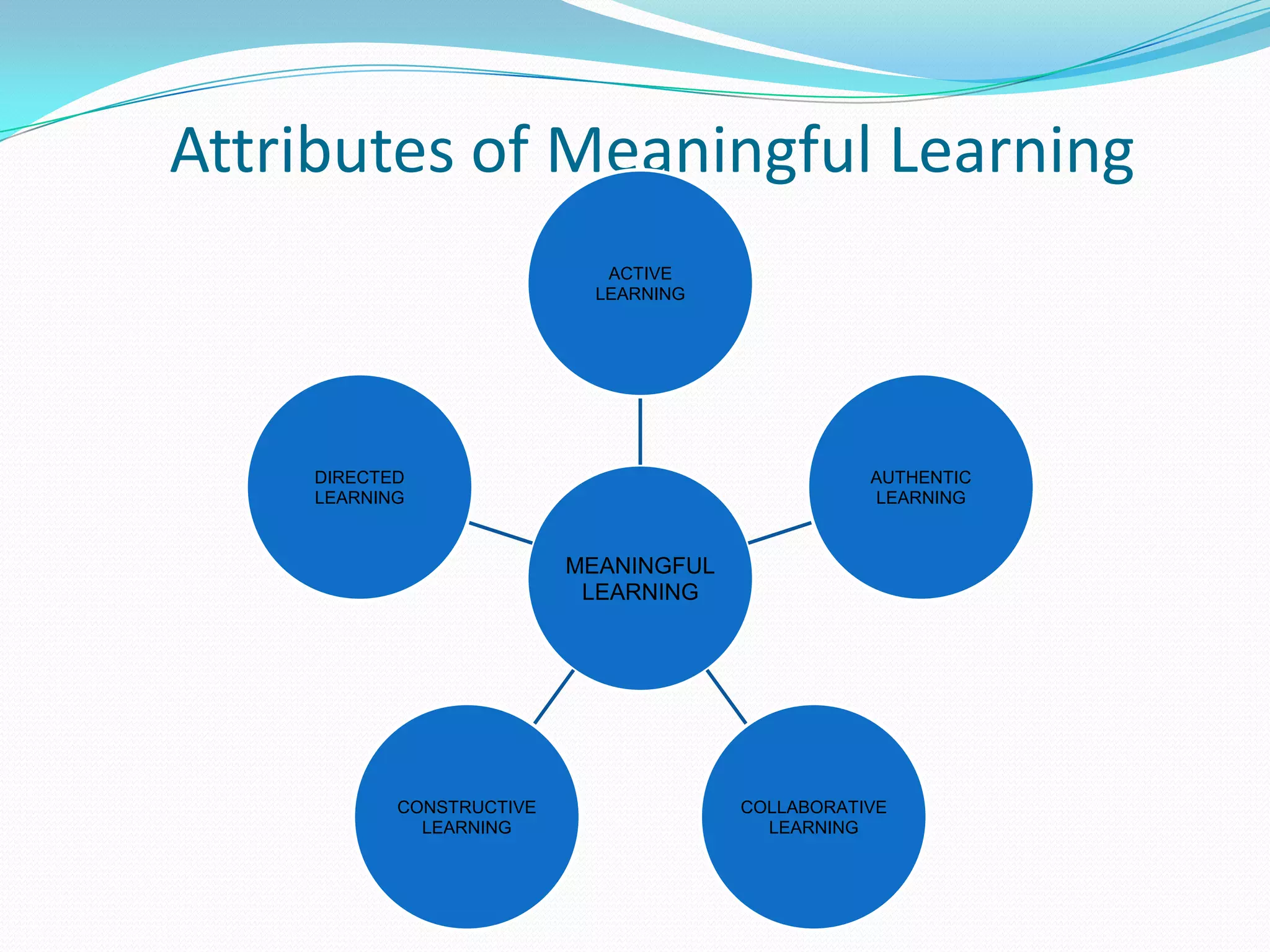
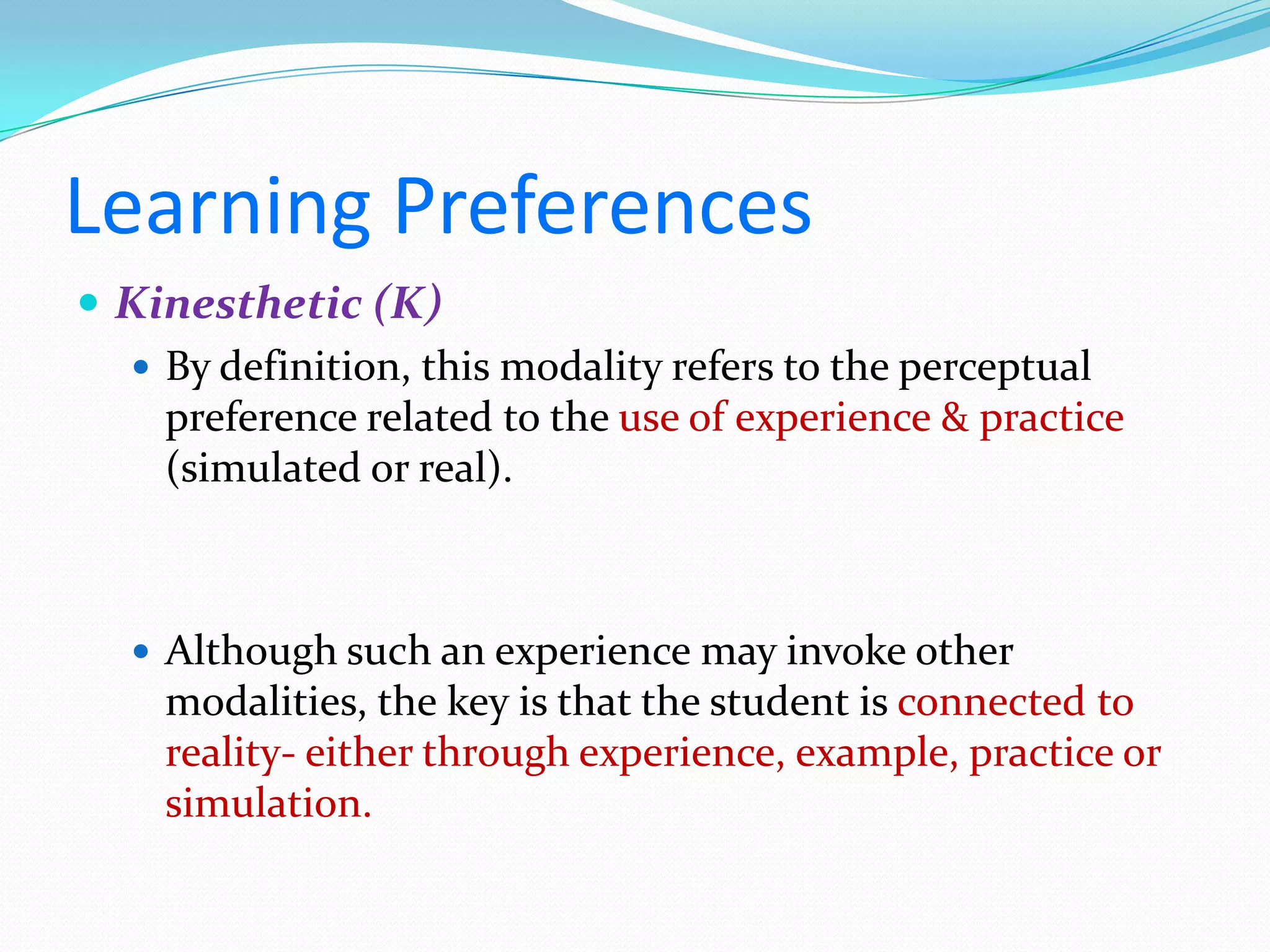
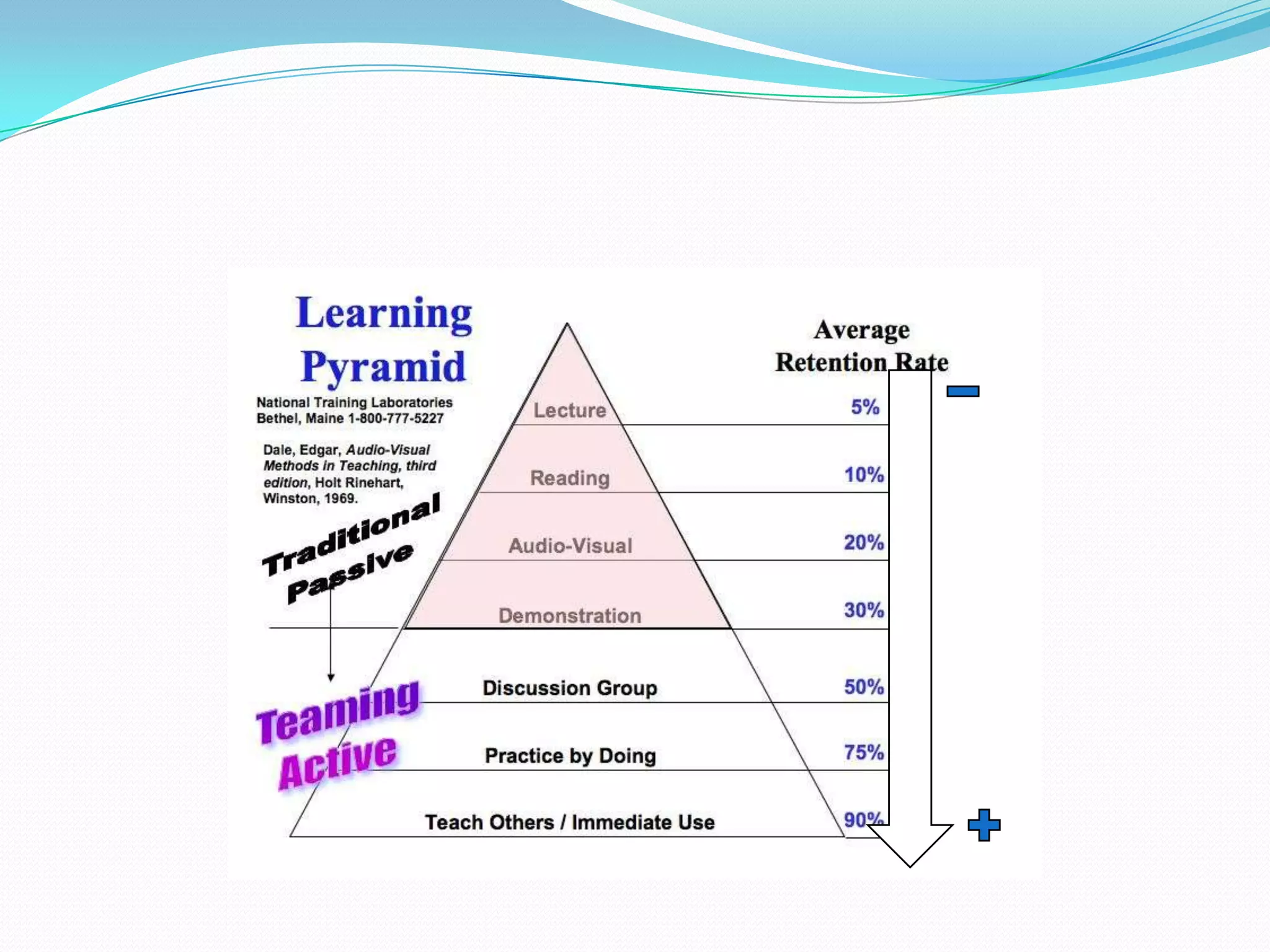
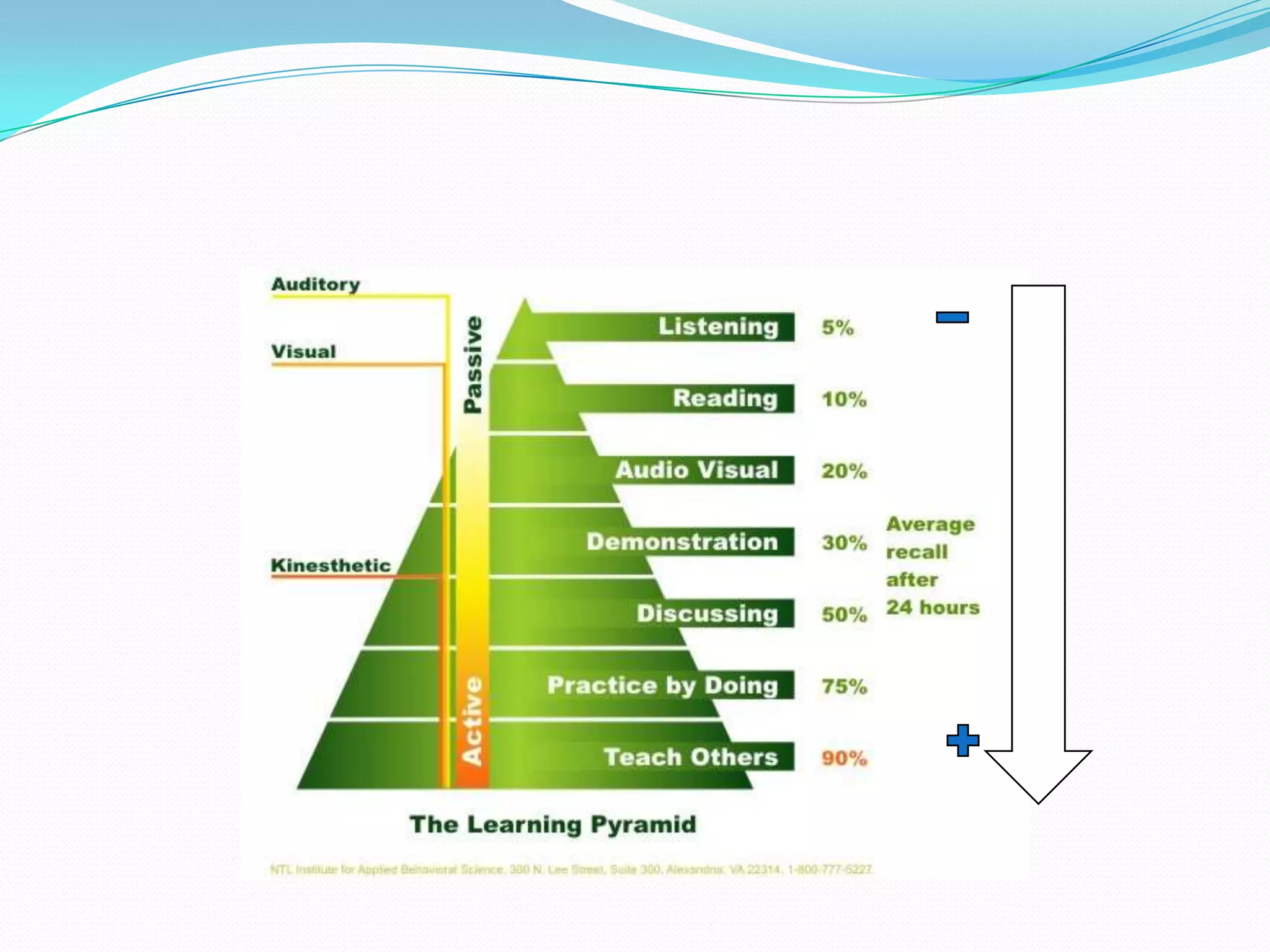
Here are some web tools that can be used to promote active learning:
- Discussion forums/boards - Allow students to discuss and debate topics, ask questions of each other.
- Wikis - Students can collaboratively create and edit content on a topic. Encourages participation and knowledge building.
- Blogs - Students can reflect on their learning by writing blog posts. Others can comment and continue the discussion.
- Google Docs/Slides - Real-time collaboration on documents and presentations fosters interaction and group work.
- Padlet - A virtual bulletin board where students can post responses, resources, ask questions in a low-stakes format.
- Kahoot! - Eng