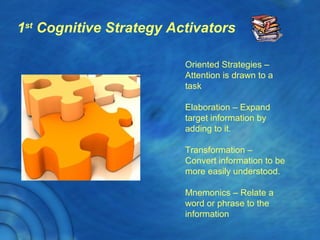
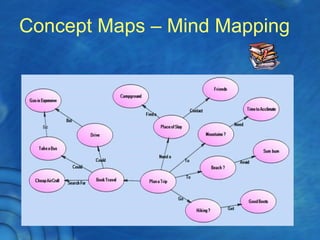
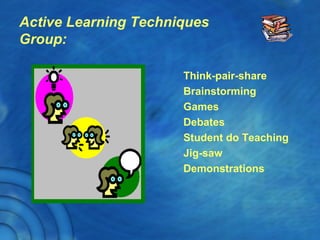
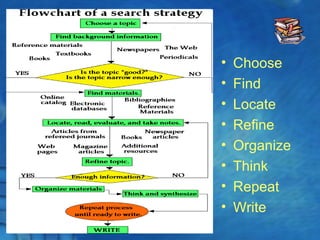
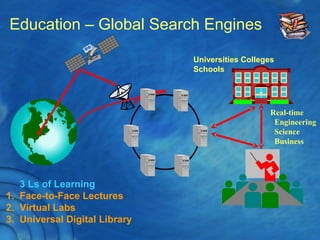
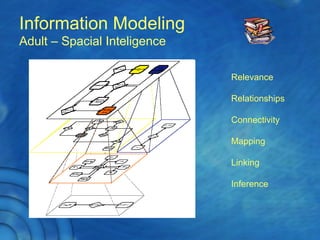
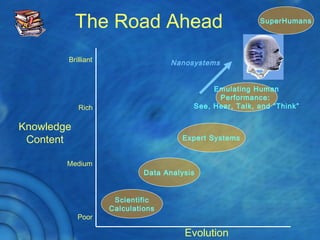
This document discusses the history and theory of active learning pedagogy and its implementation in Thai classrooms. It defines active learning as involving students in higher-order thinking tasks like processing, applying, and connecting information to motivate learning. Active learning techniques discussed include individual activities like concept maps and group work like think-pair-share. The document advocates designing cognitive routines and selecting active learning techniques to build lessons that develop students' thinking. It envisions future education relying more on virtual labs, universal libraries, and search engines for personalized learning paths.