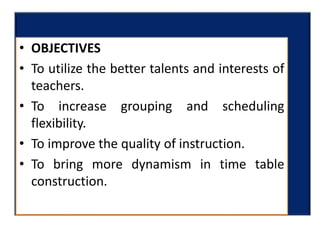
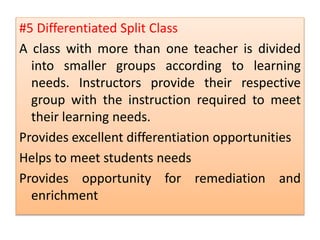
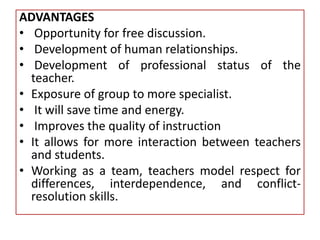
Team teaching is an instructional approach where two or more teachers collaboratively plan, conduct, and assess learning activities for a shared group of students. This method promotes professional collaboration, creates dynamic learning environments, and enhances instructional quality through various models like traditional team teaching, collaborative teaching, and parallel instruction. The process involves clear roles, effective communication, and adaptability to meet diverse learning needs.