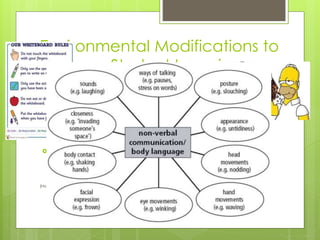
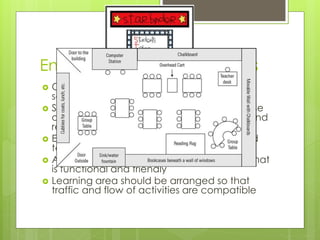
The document discusses impactful management strategies for modern classrooms, emphasizing student-centered approaches that build trust and consistent engagement among students and teachers. It outlines strategies for classroom structure, communication, behavior management, and the importance of environmental modifications to foster a positive learning environment, especially for students with special needs. Additionally, it highlights the collaborative nature of positive behavior support and the necessity of involving all educational stakeholders in supporting student growth.