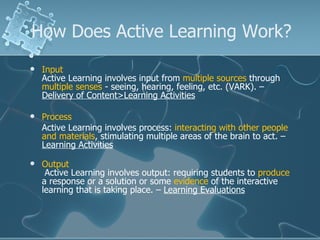
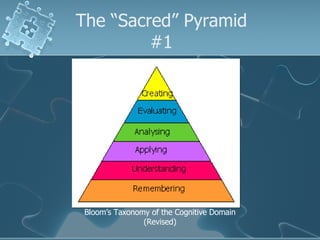
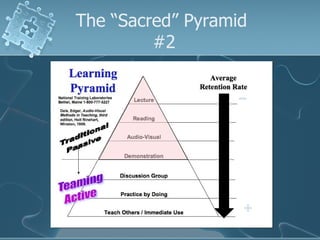
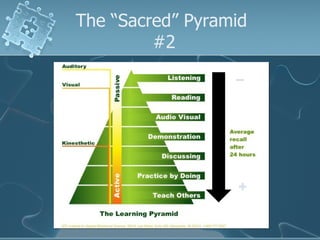
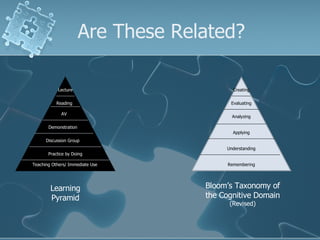
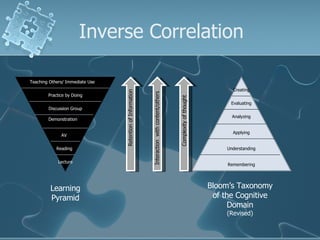
The document discusses active learning techniques to maximize student retention and comprehension. It defines active learning as learner-centered, involving input from multiple sources and senses. Active learning also involves students interacting with content and each other, such as through collaborative work. Using active learning strategies that require higher-order thinking and greater interaction is linked to higher retention of course material. The document provides examples of active learning techniques and how instructors can incorporate student learning preferences, including visual, auditory, reading/writing and kinesthetic styles.