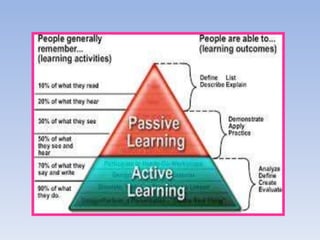
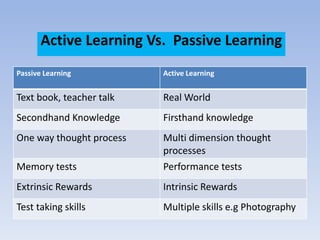
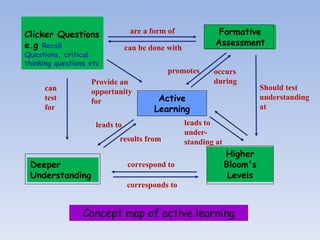
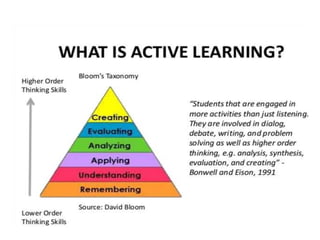
The document discusses active learning, its principles, and methods such as the jigsaw strategy that promotes student engagement and higher-order thinking. It contrasts active learning with passive learning, highlighting the benefits of active engagement in skill development and collaboration. Additionally, it offers insights into effective questioning techniques and various tools to facilitate active learning in both traditional and online settings.













































![ACTIVE LEARNING TOOLS
A massive open online course (MOOC /muːk/) is
an online course aimed at unlimited participation and
open access via the web.[1]
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NfP92tlC
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-qGx2DOaRZ8
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aTlkUMEkA-8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activelearningjigsawmethod1-merged-191009152003/85/Active-learning-jigsaw-method-1-merged-51-320.jpg)

