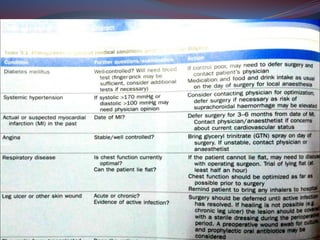
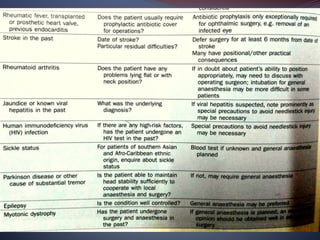
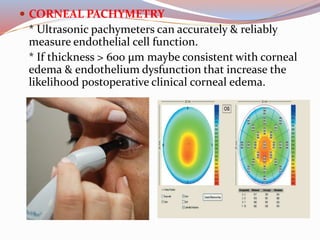
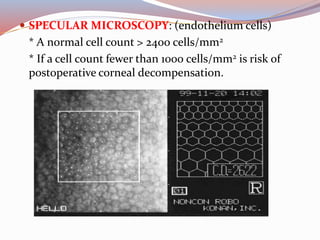
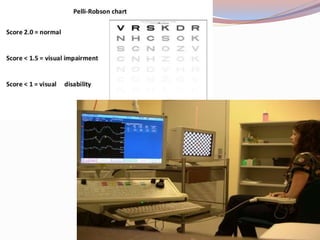
This document provides a thorough pre-operative assessment for cataract surgery. It summarizes the patient's ocular and systemic history, examines the eye, performs investigations including visual acuity tests and biometry to determine IOL power. Key areas assessed include lens density, corneal thickness, endothelial cell count, intraocular pressure, and checking for other ocular pathology. Informed consent discusses potential complications. Relevant lab tests and pre-op measures are also outlined. The goal is to fully evaluate the patient and eye pre-operatively to plan the surgery, guide IOL selection, and maximize the visual outcome.