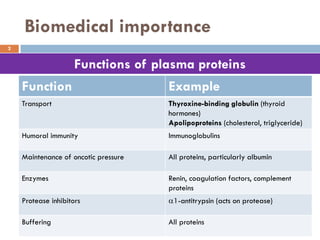
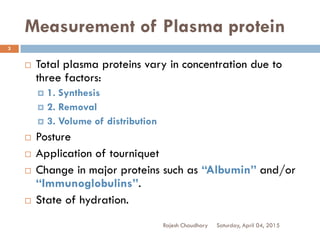
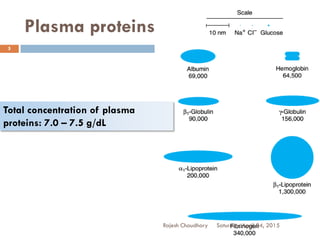
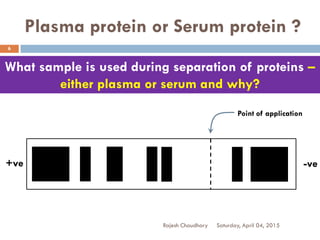
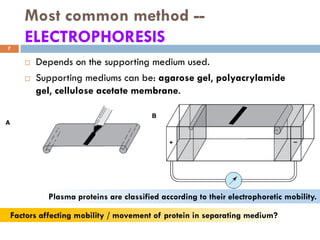
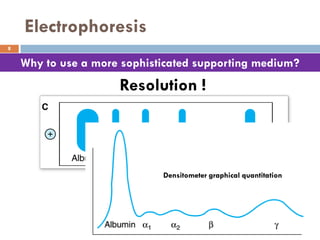
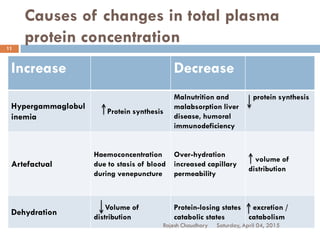
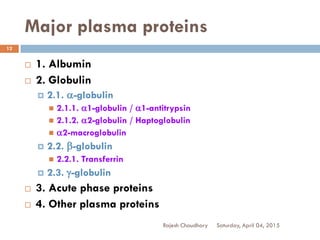
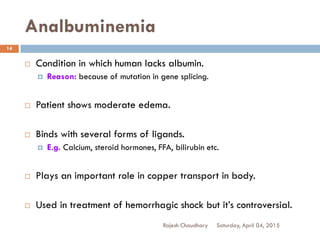
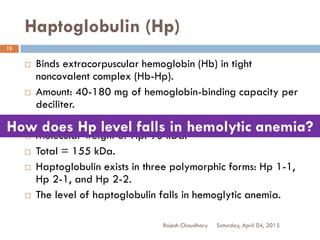
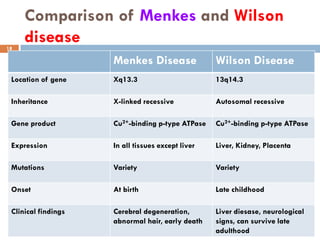
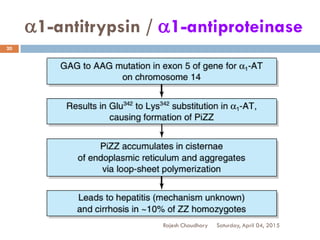
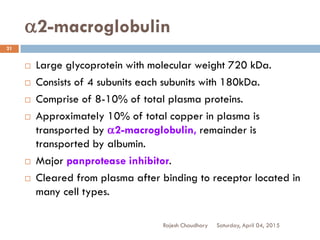
This document discusses plasma proteins, including their functions, measurement, classification, and major types. It notes that plasma contains thousands of proteins like albumin, globulins, antibodies, enzymes, and transport proteins. Total plasma protein concentration is normally 7-7.5 g/dL. Major classes of globulins include alpha, beta, and gamma globulins. Key plasma proteins discussed in more detail include albumin, immunoglobulins, haptoglobin, transferrin, ceruloplasmin, alpha-1 antitrypsin, and alpha-2 macroglobulin.