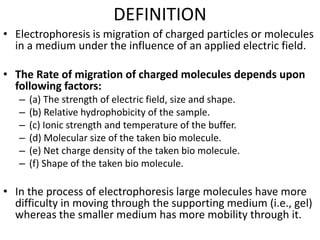
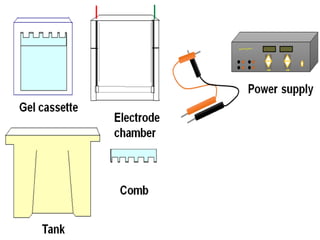
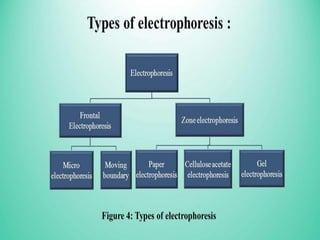
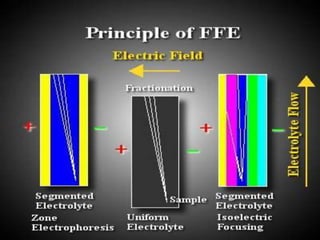
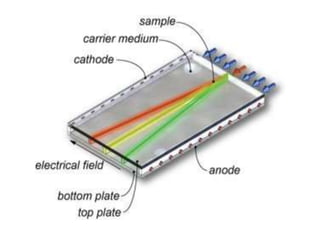
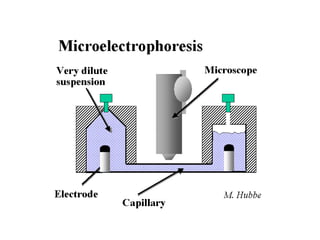
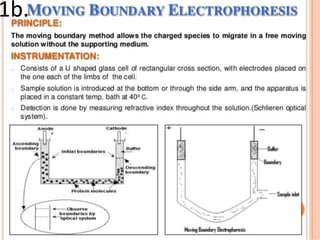
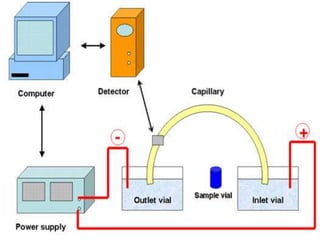
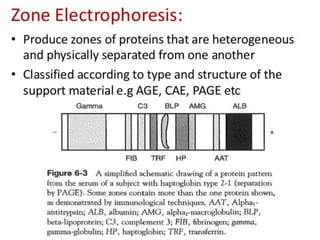
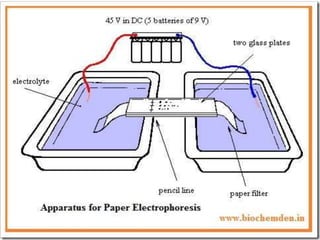
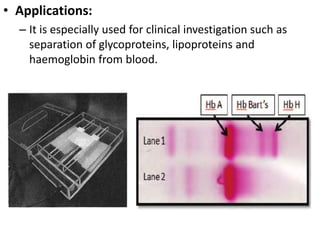
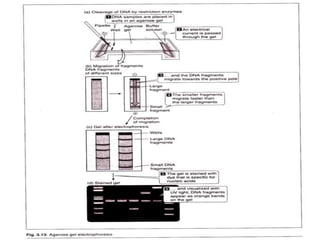
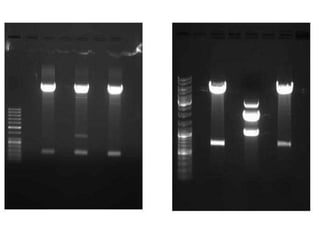
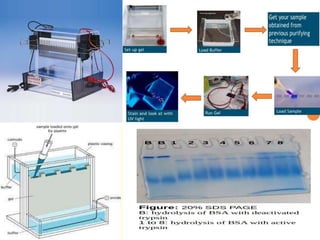
Electrophoresis is a technique that facilitates the migration of charged particles in an electric field, primarily used for the separation of biological molecules like proteins and nucleic acids based on their charge and size. It can be classified into free and zone electrophoresis, with zone electrophoresis being the more prevalent method today, employing various media such as paper, cellulose acetate, and gels. The applications of electrophoresis span multiple fields, including biomolecular analysis, diagnostics, and environmental monitoring.