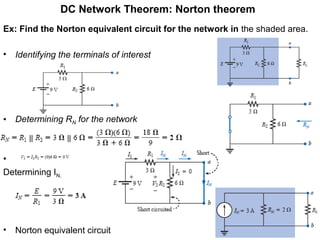
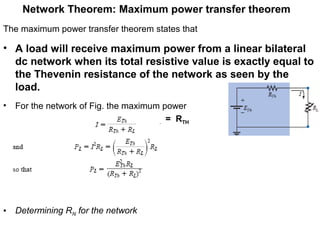
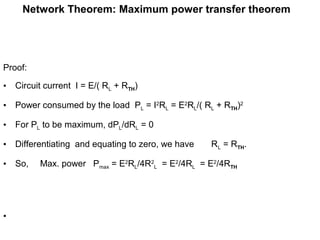
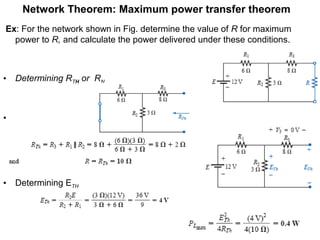
The document discusses several theorems for analyzing DC networks:
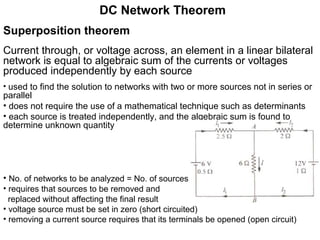
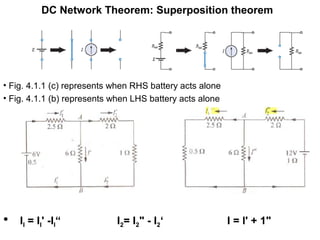
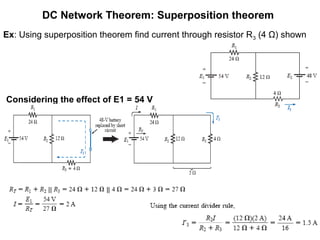
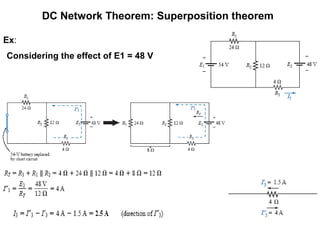
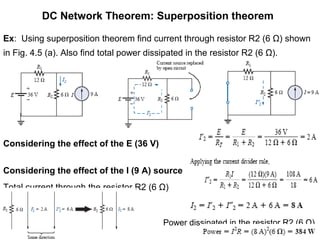
1. Superposition theorem states that the current or voltage across an element is equal to the algebraic sum of currents/voltages from each independent source.
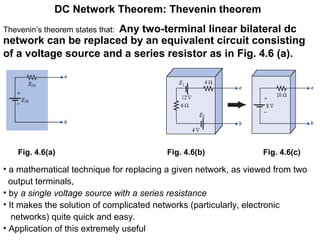
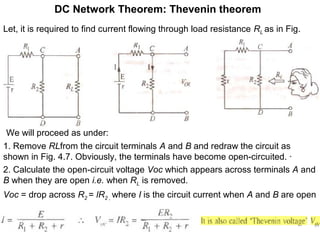
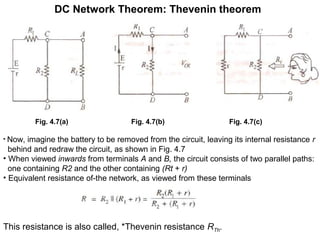
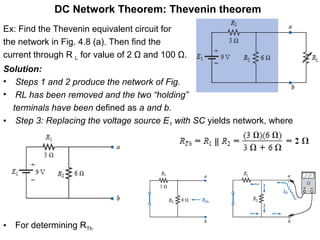
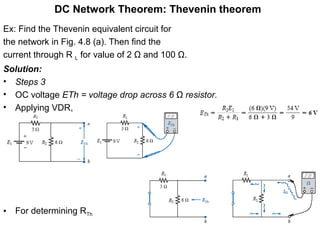
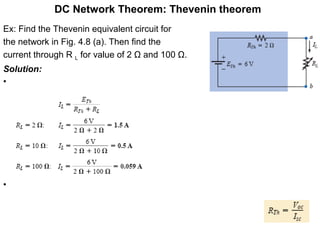
2. Thevenin's theorem states that any linear bilateral network can be reduced to a single voltage source in series with an equivalent resistance.
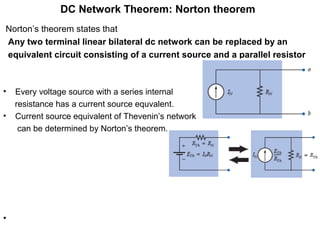
3. Norton's theorem states that any linear bilateral network can be reduced to a current source in parallel with an equivalent resistance.
4. Maximum power transfer theorem states that maximum power is delivered to a load when its resistance equals the Thevenin resistance of the network.